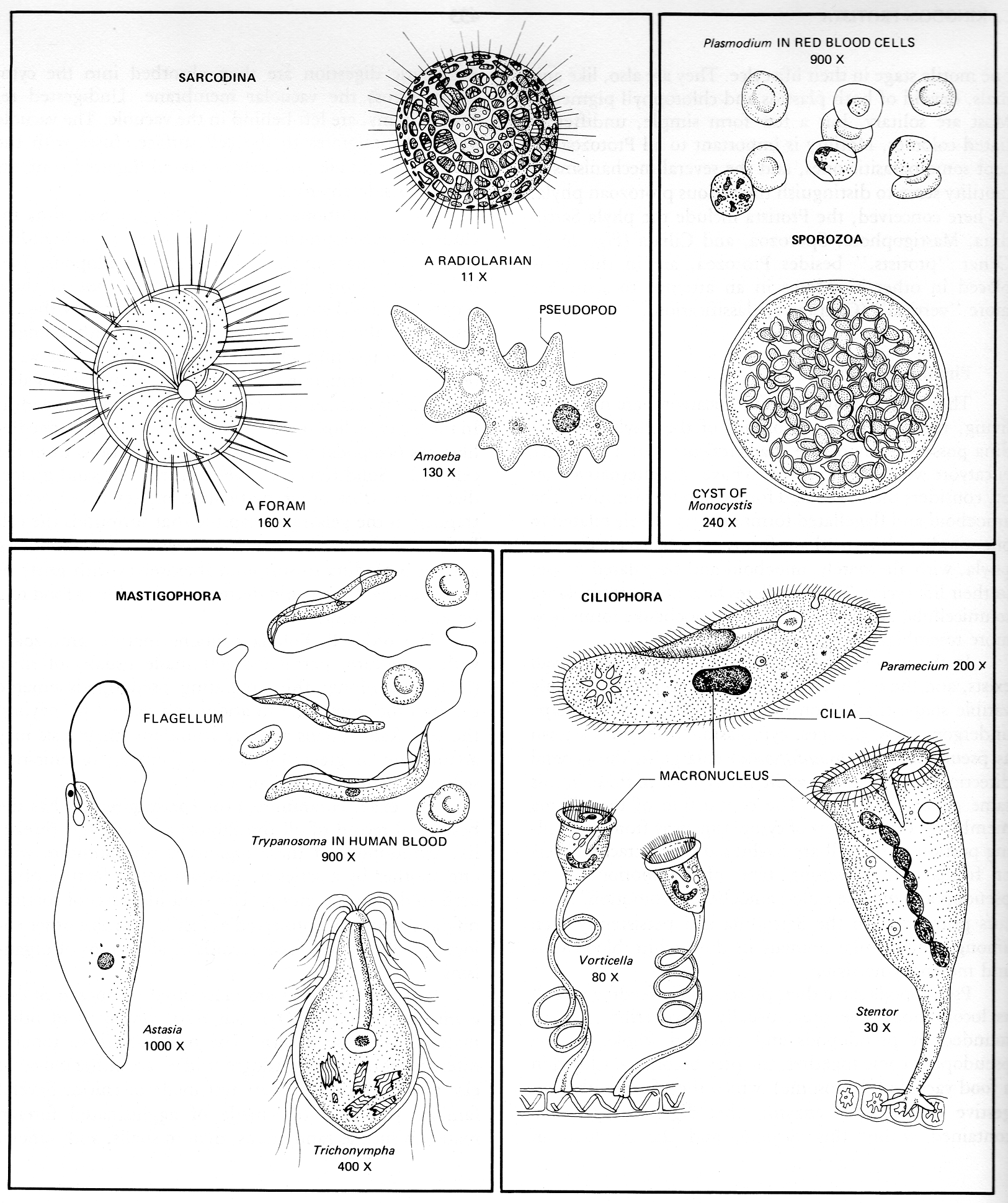
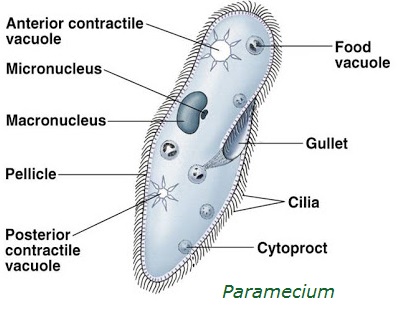
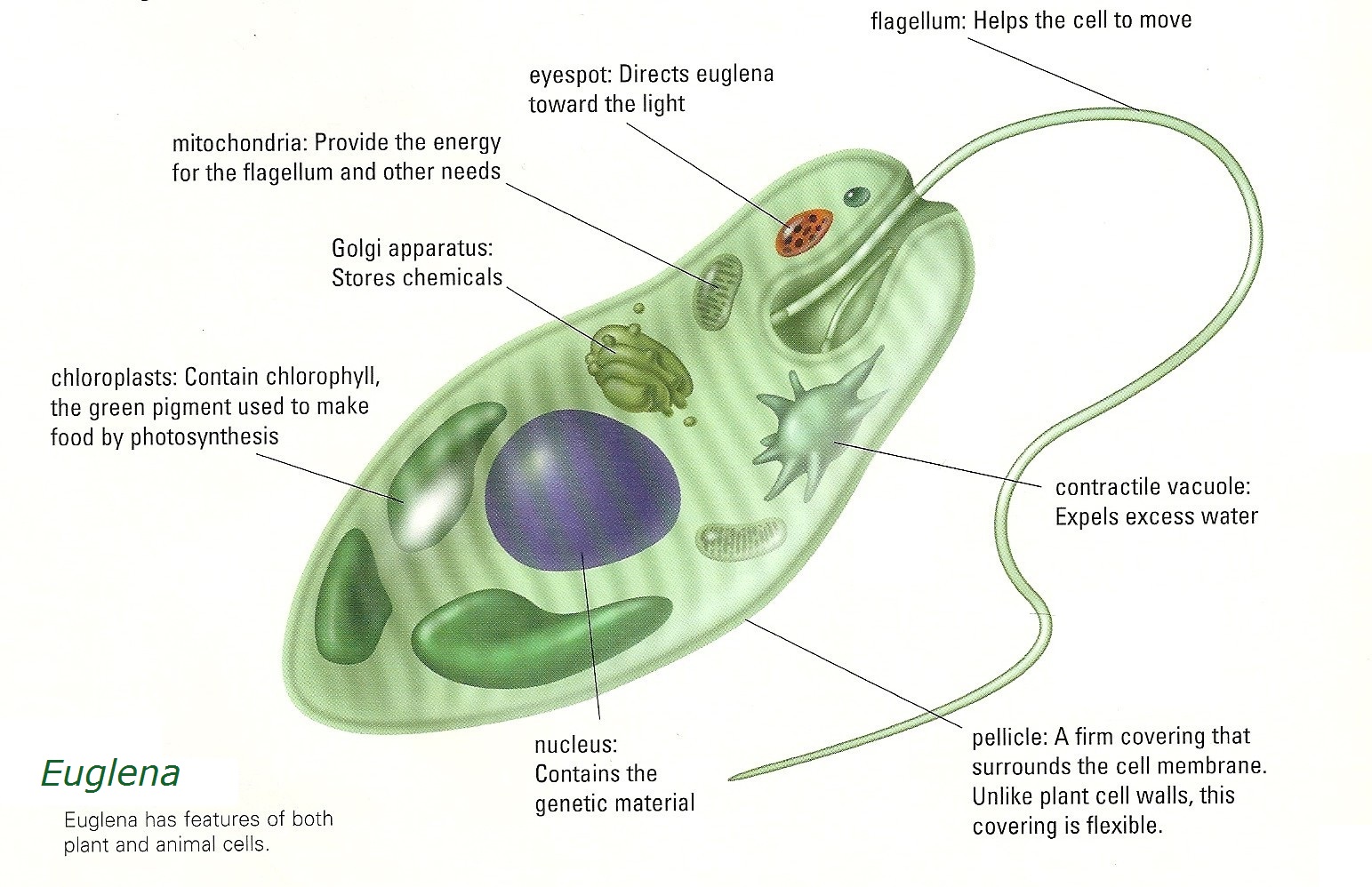
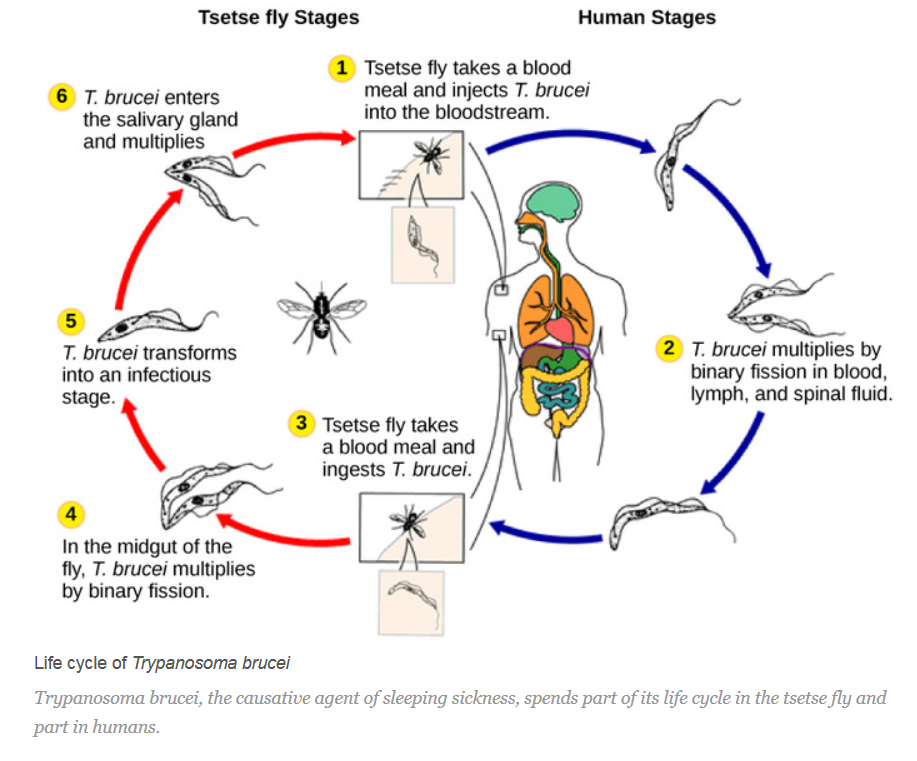
CHARACTERISTICS OF GROUPS in the preceding family trees:
- Excavata: Energy-dependent parasites with degenerate or vestigial mitochondria; feeding groove "excavated" from one side.
- Chromalveolata: A possibly heterogeneous group, possessing cellulose cell walls, and thought by some
experts to have originated by a "secondary endosymbiosis" in which a red algal cell became a secondary chloroplast.
(Many experts have questioned the validity of this group.)
- Rhizaria: Mostly planktonic predators using needle-like pseudopods to capture prey; usually with hardened shells.
- Archaeplastida: Photosynthetic organisms with plastids (but excluding those with chlorophyll c).
- Unikonta: Organisms with a single flagellum (or none) and/or lobe-like pseudopods.
- Amoebozoans: move principally by lobe-like pseudopods.
- Opisthokonts: move principally by a posterior flagellum (lost in many advanced species)
|