PLANT KINGDOM
Plants are organisms sharing the following derived characteristics:
- Autotrophic, using CO2 as the source of carbon for organic compounds
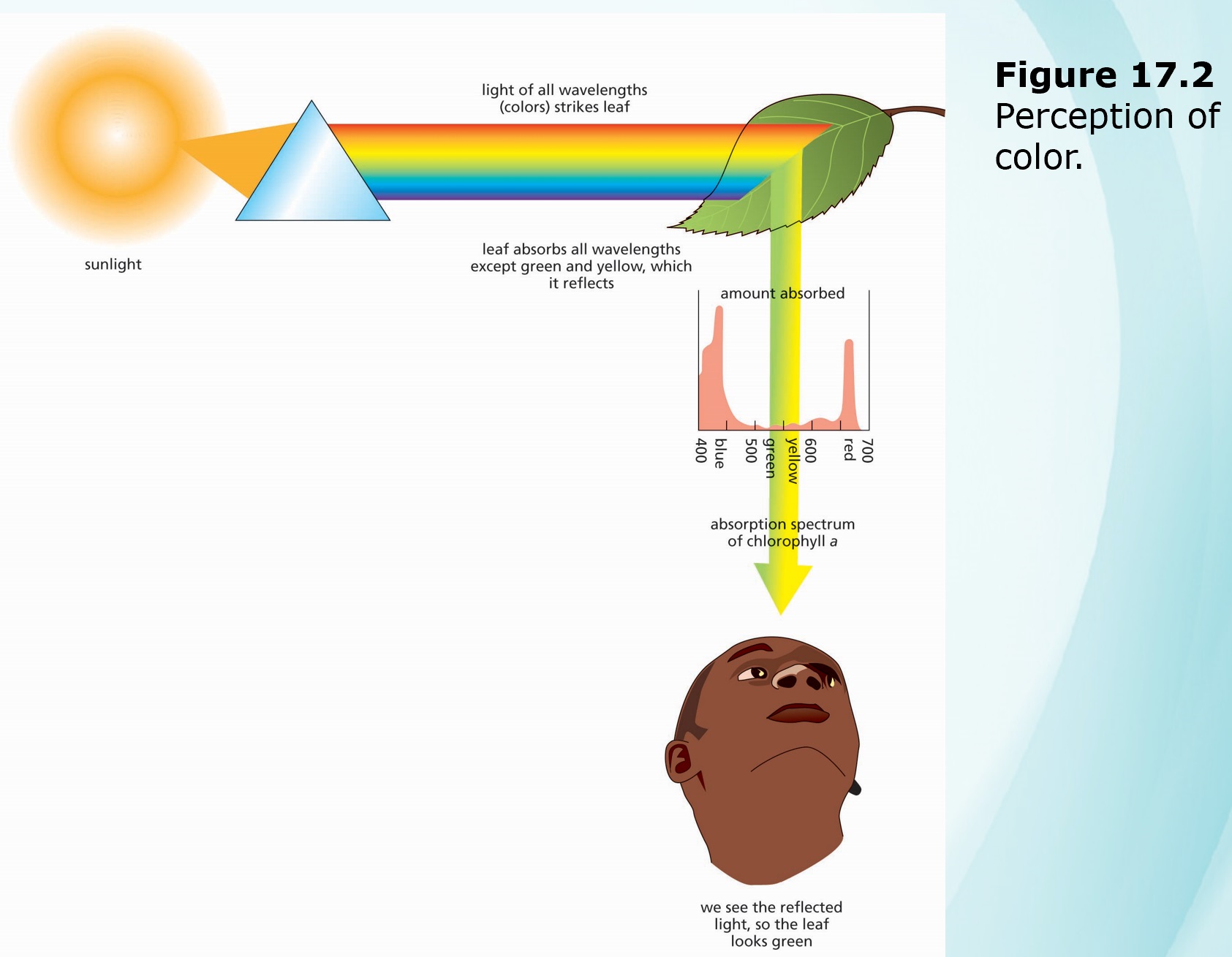
- Photosynthetic using chlorophylls a and b, plus several "accessory pigments," to capture solar energy.
- Generally non-motile, with some exceptions for male gametes.
- Presence of persistent embryonic tissue (meristem) capable of indeterminate growth throughout life.
- Development from multicellular embryos in which a reproductive cell (ovum) is surrounded by nonreproductive tissue.
Origin of Plant Kingdom = origin of multicellular embryos.

- Plants Capture the Sun’s Energy and Make Many Useful Products
- All our food comes from plants, or from animals that eat plants, etc.
- We also get many other useful products (medicines, dyes, wood, paper, etc.) from plants
- Photosynthesis
- Agriculture and other plant uses
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
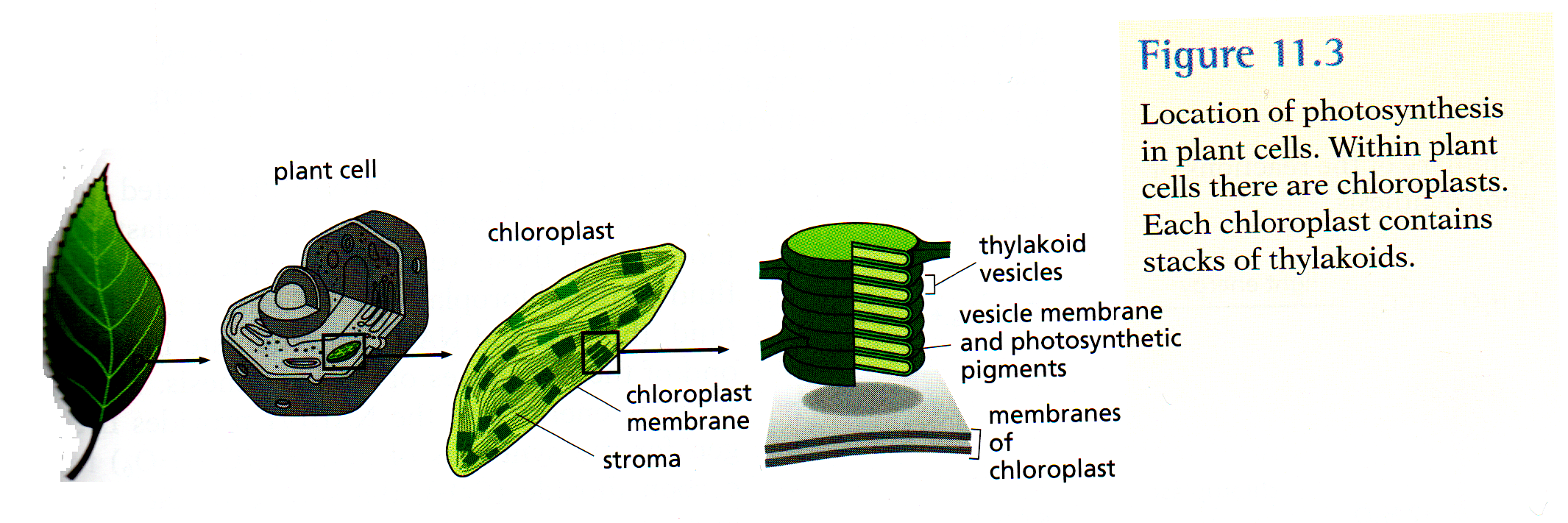
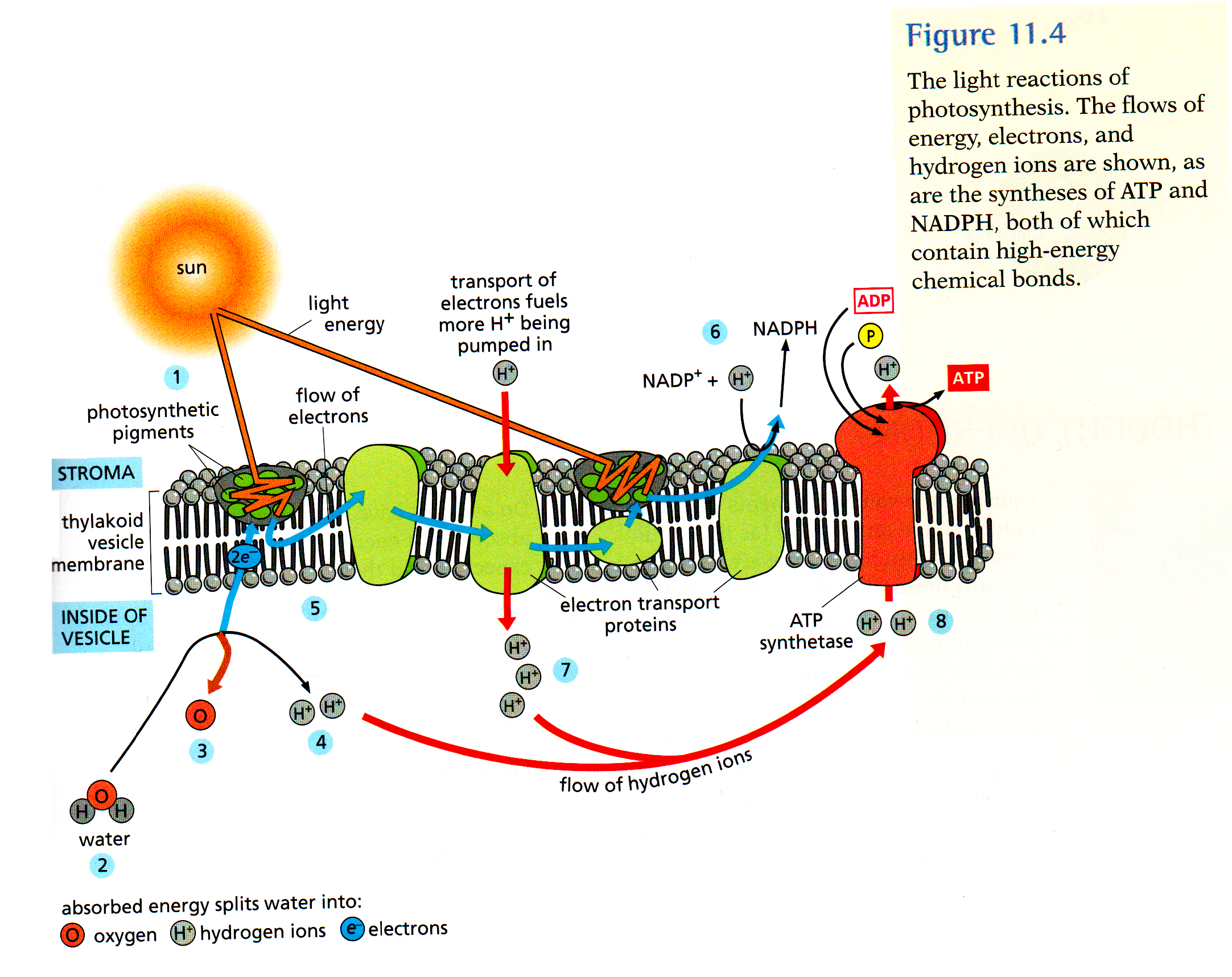
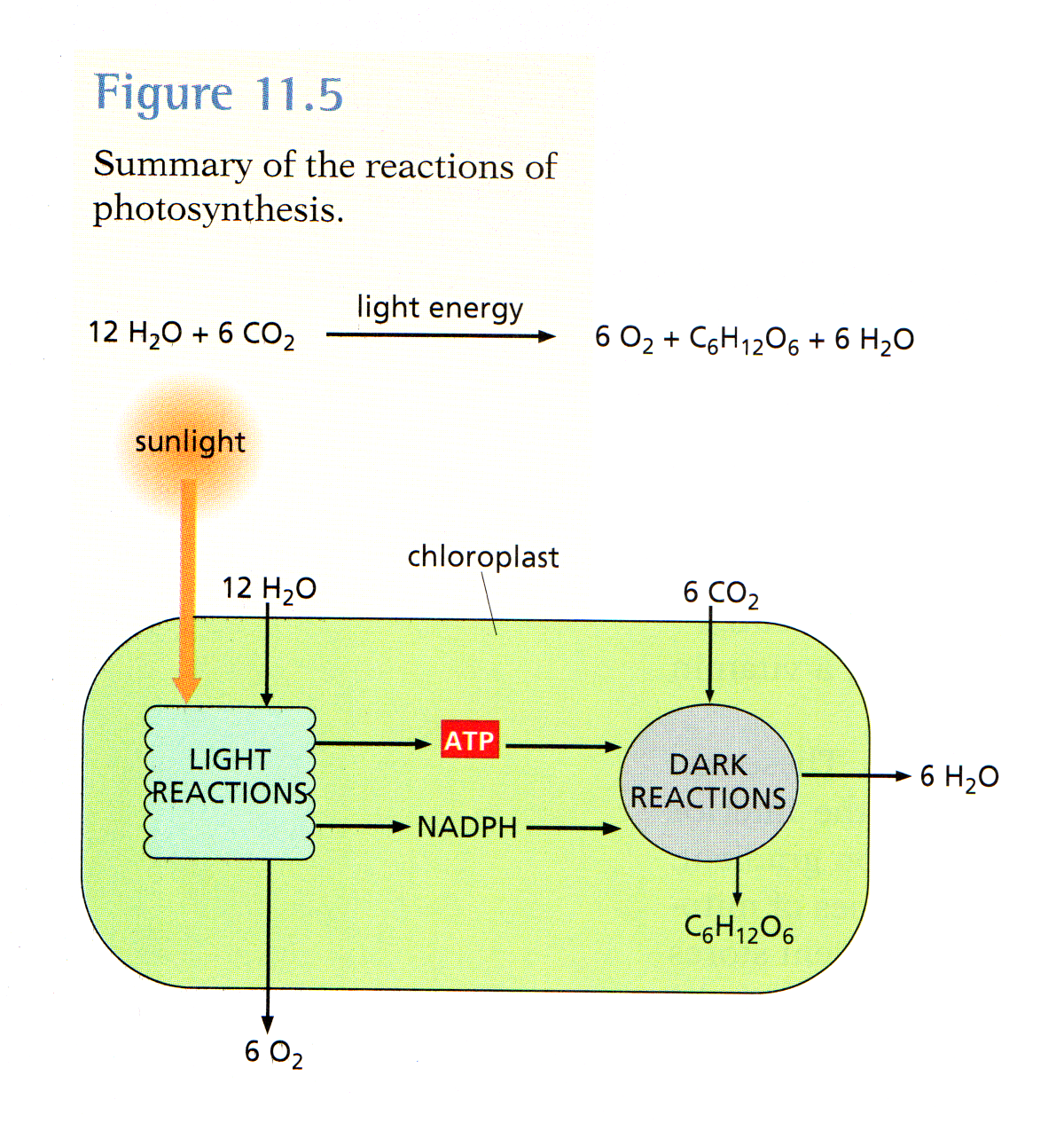
- Plants Use Specialized Tissues and Transport Mechanisms
- Tissue specialization in plants
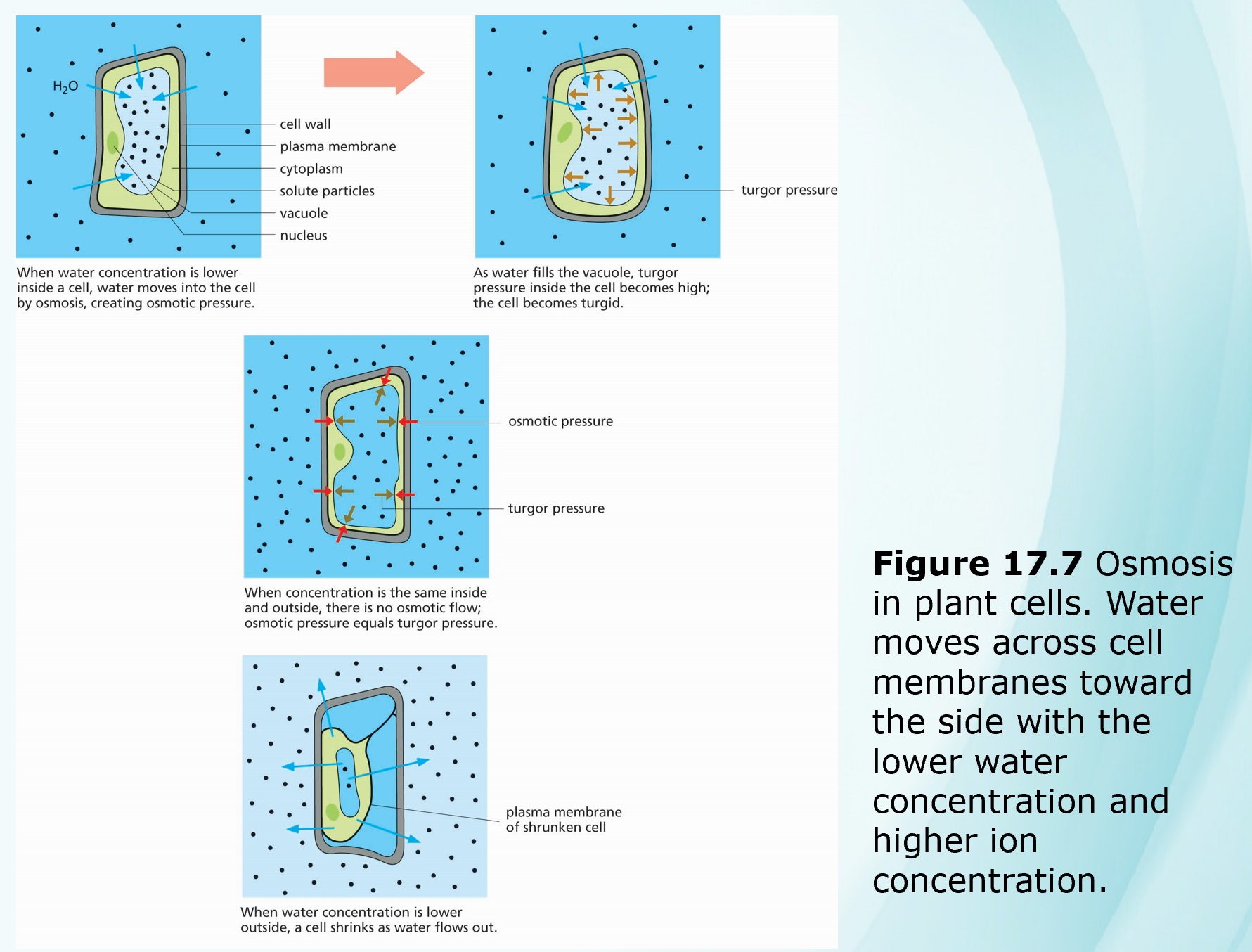
- Water transport in plants
VASCULAR PLANT PARTS

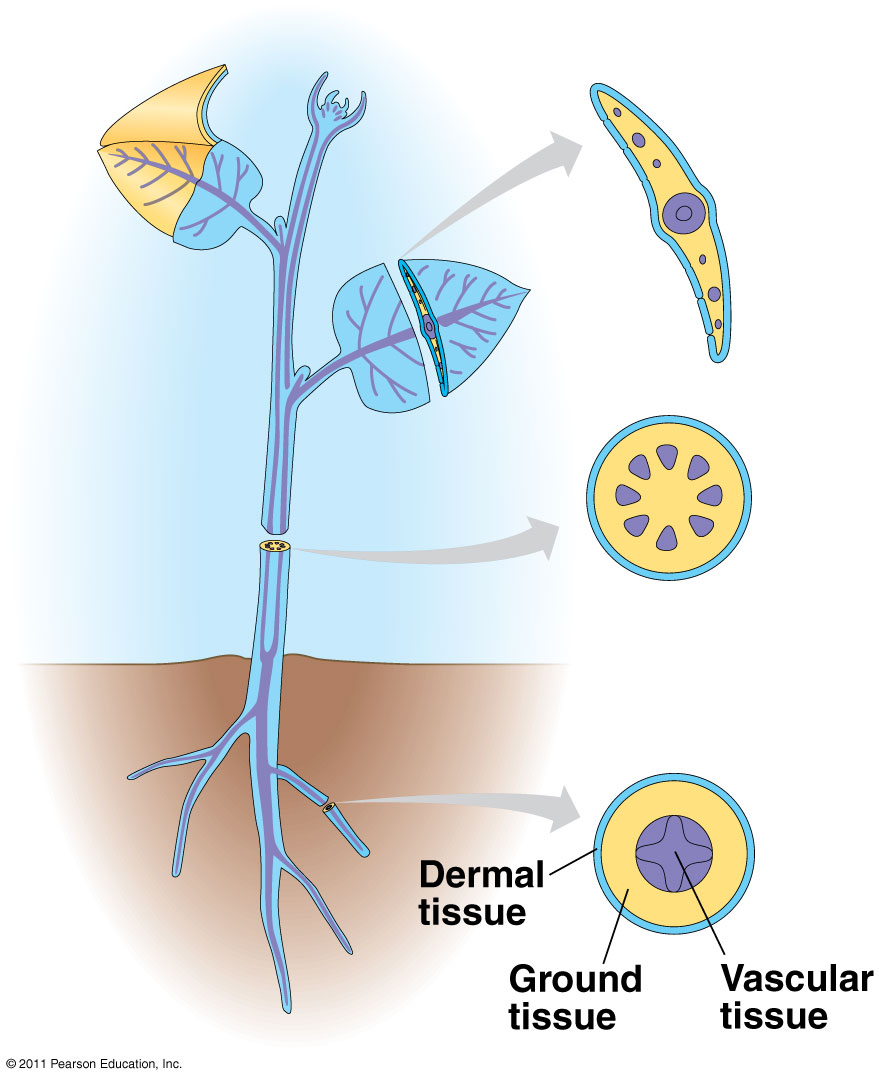
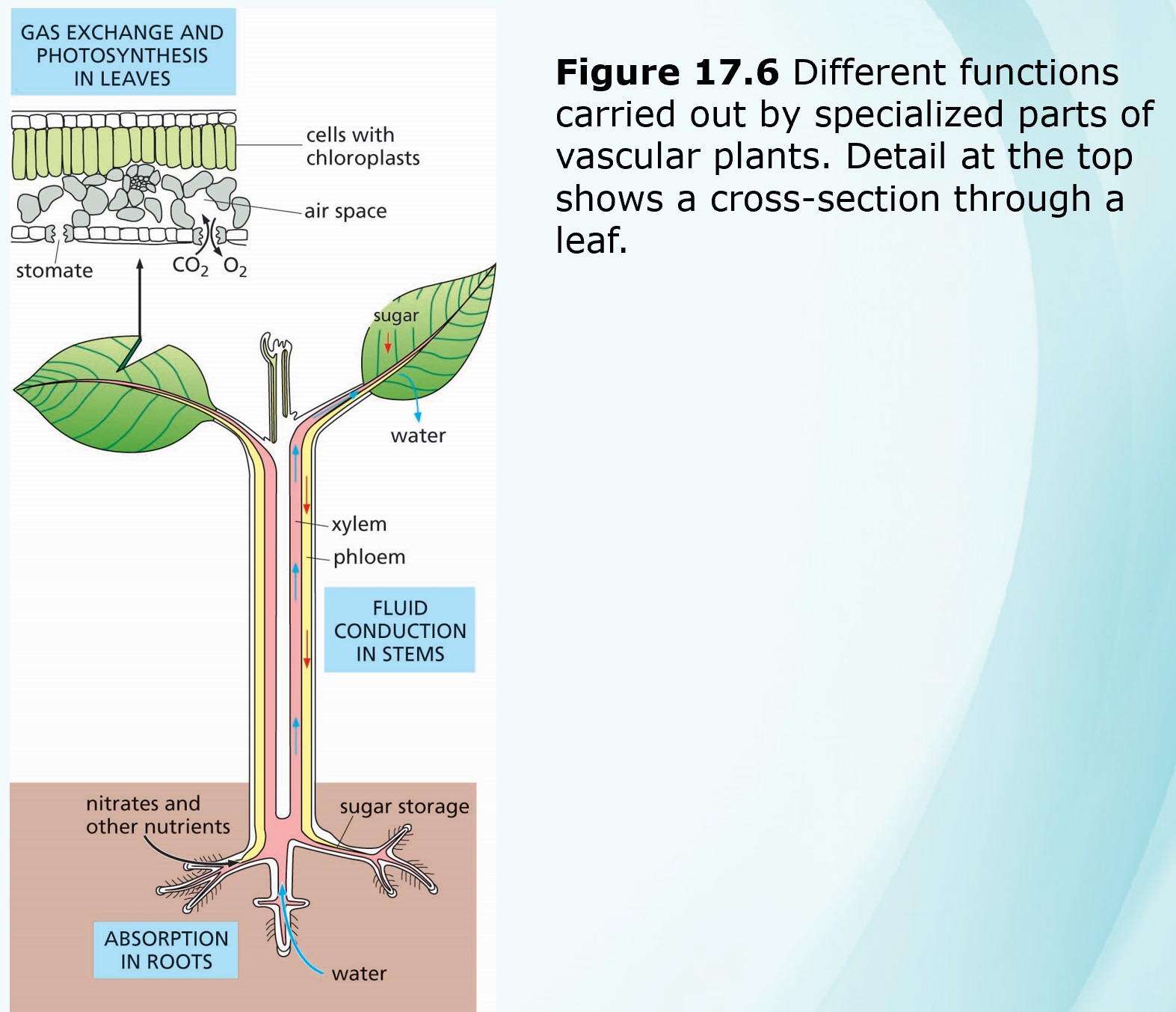
XYLEM
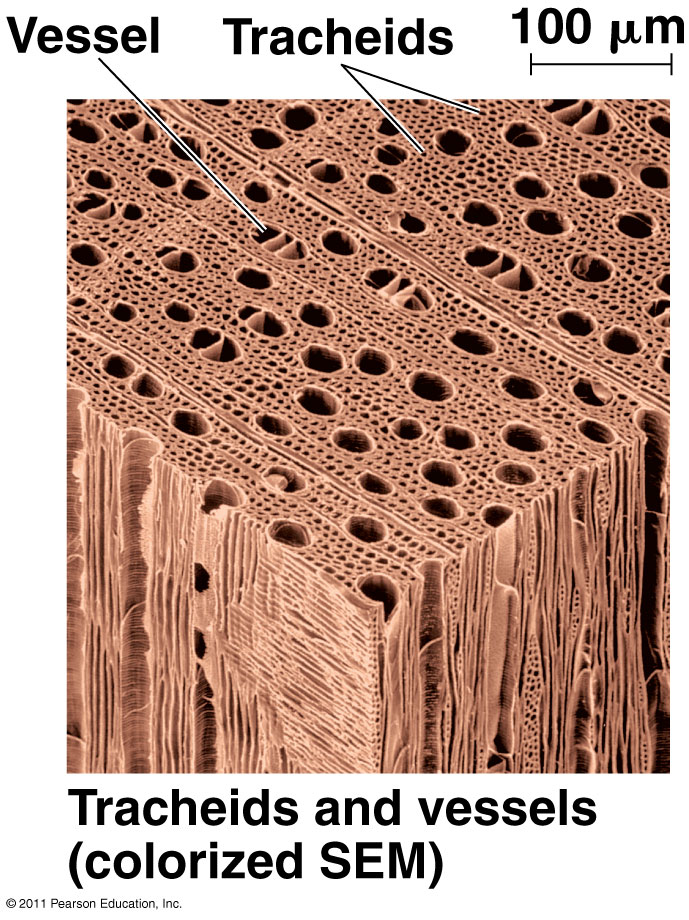
PHLOEM
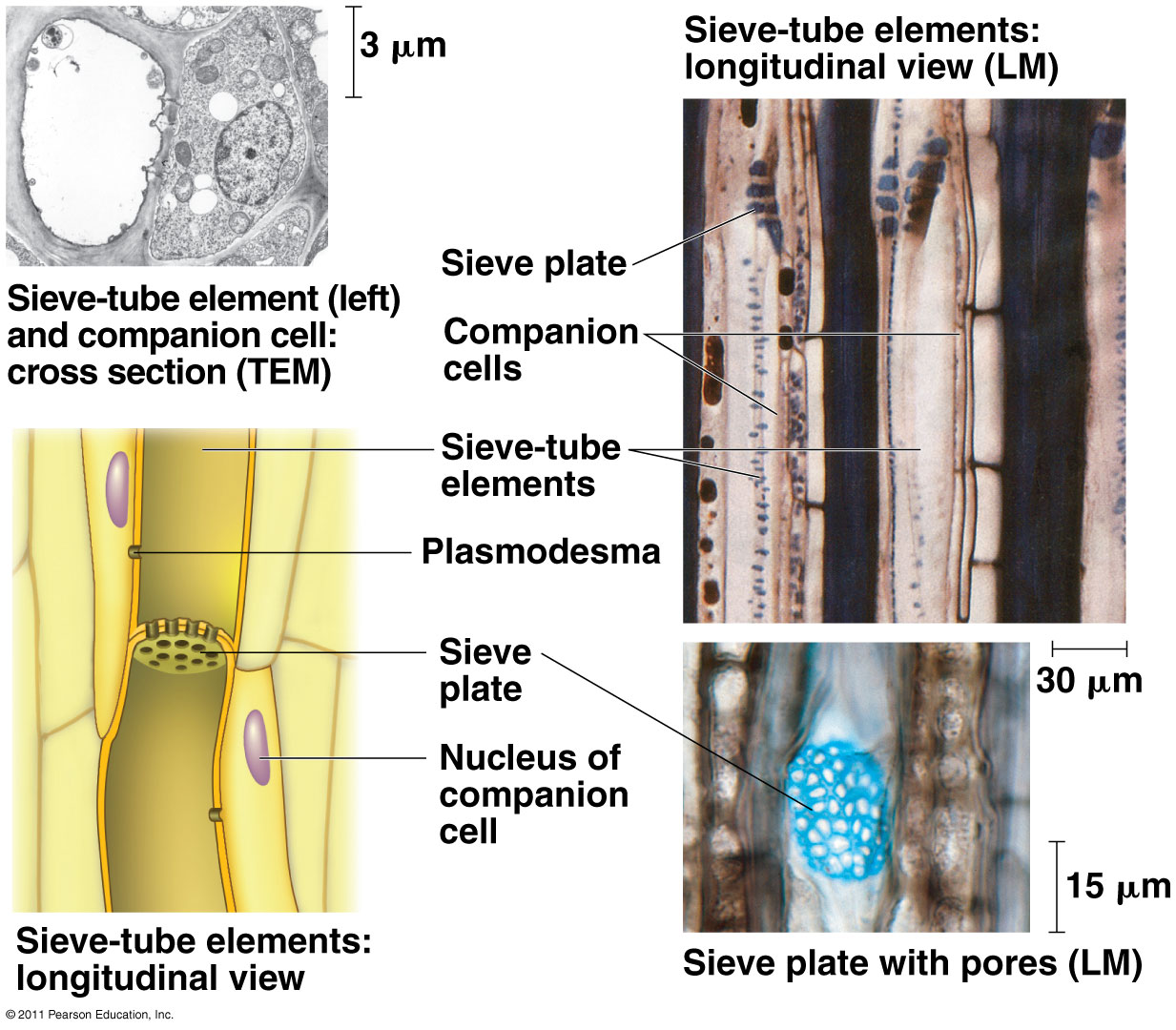
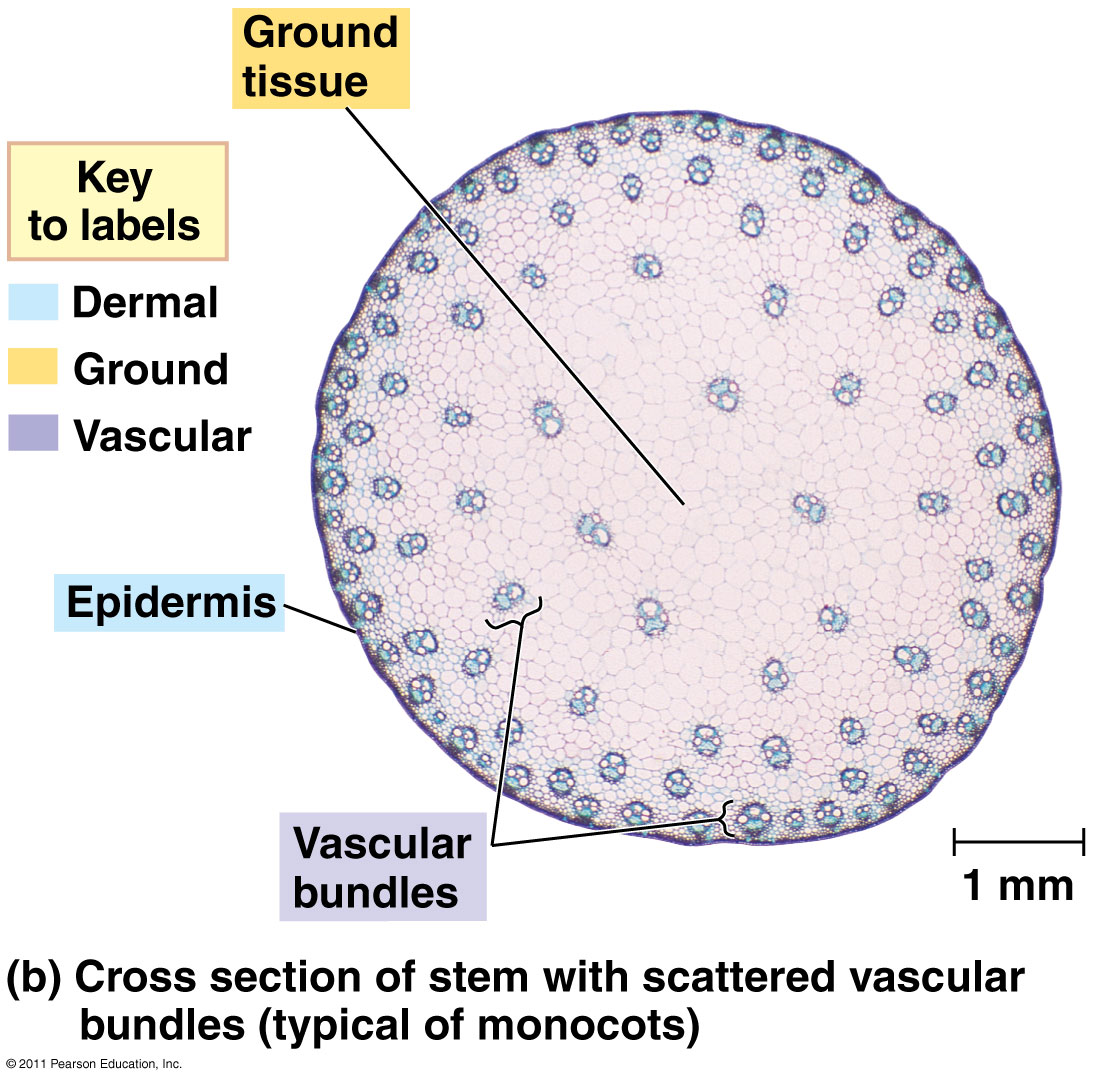
STEMS

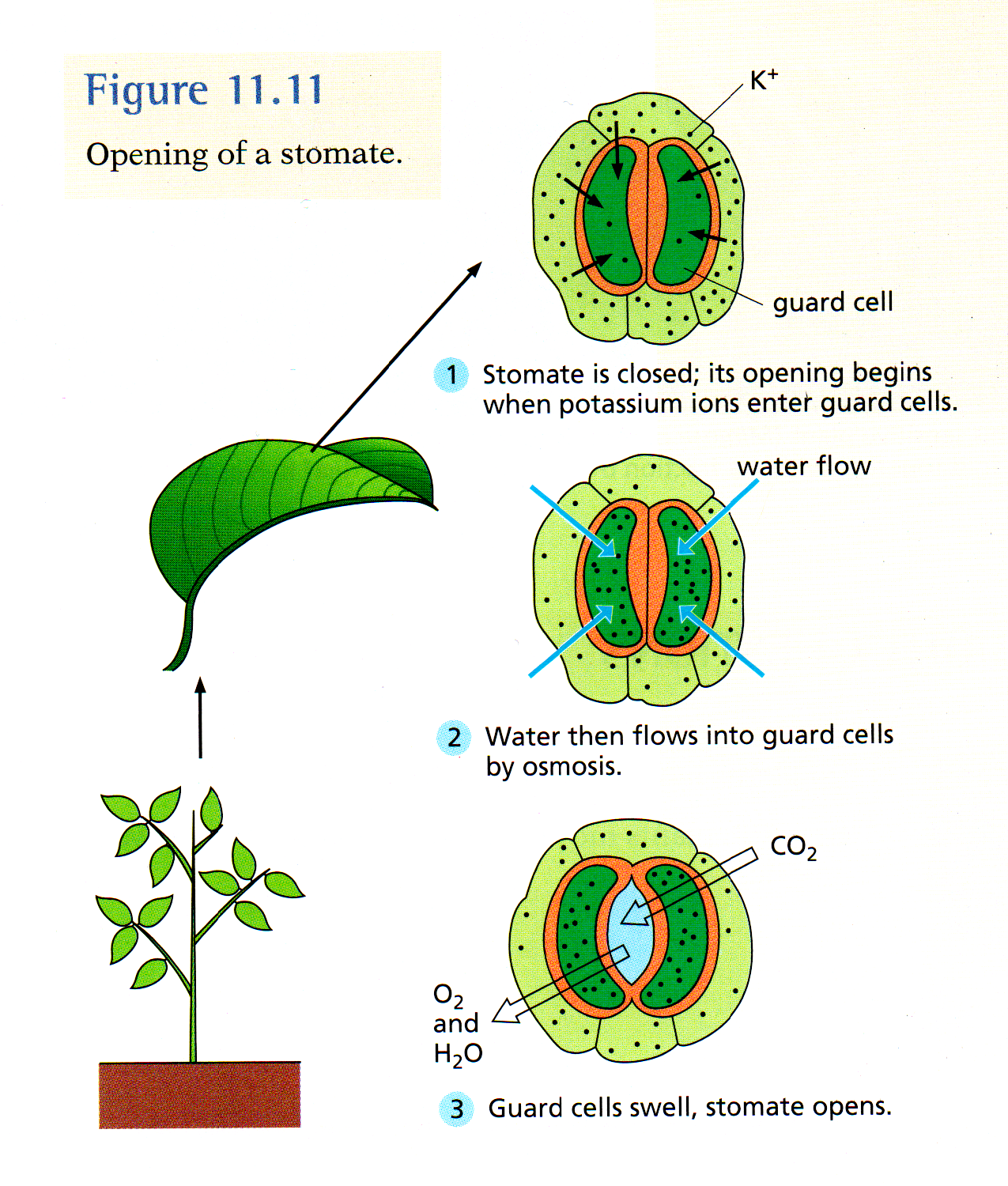
LEAVES

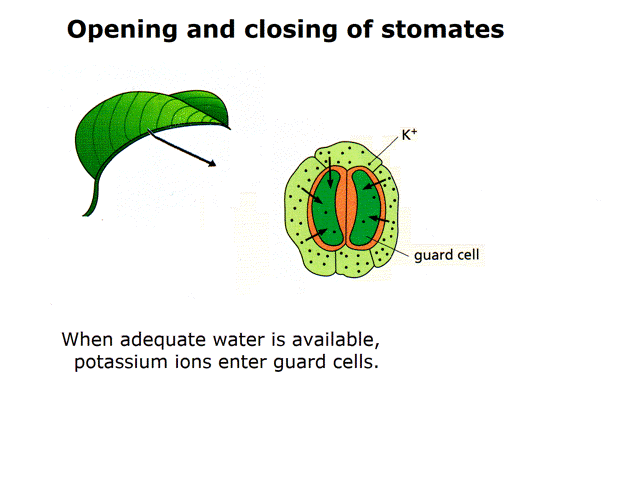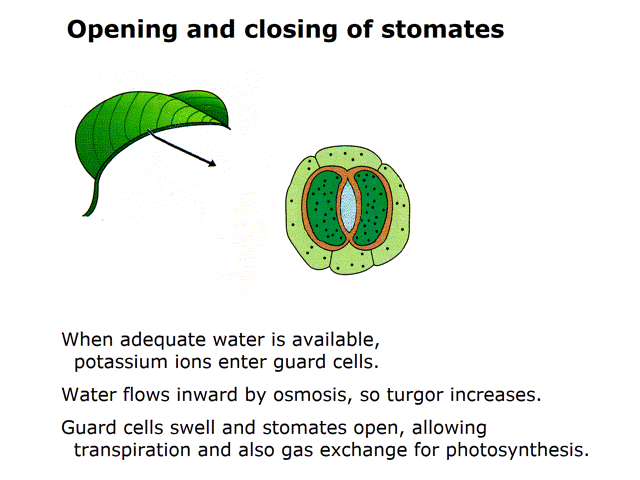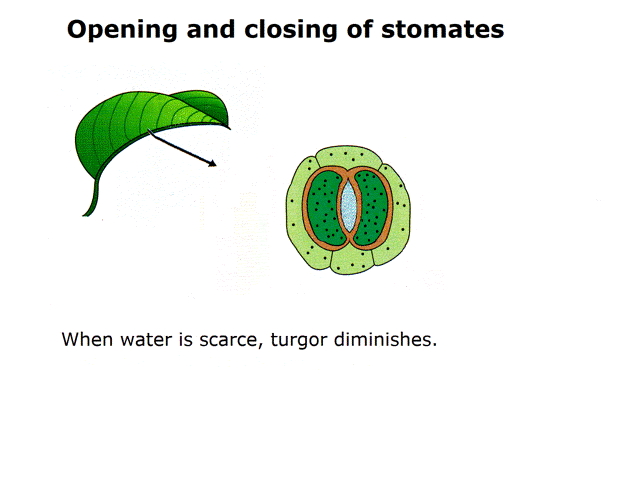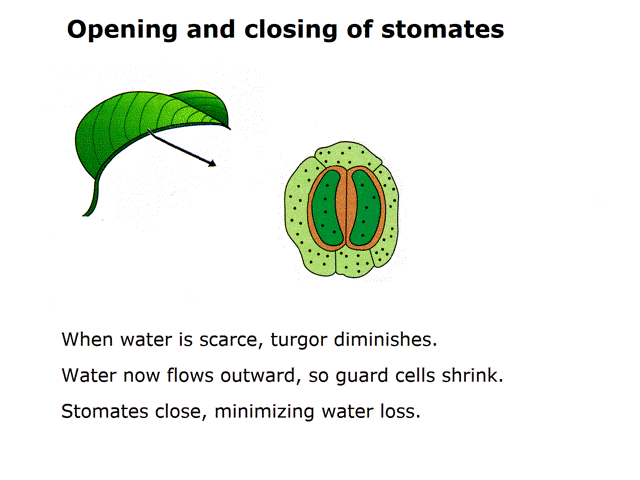

Question 1:
What are TISSUES?
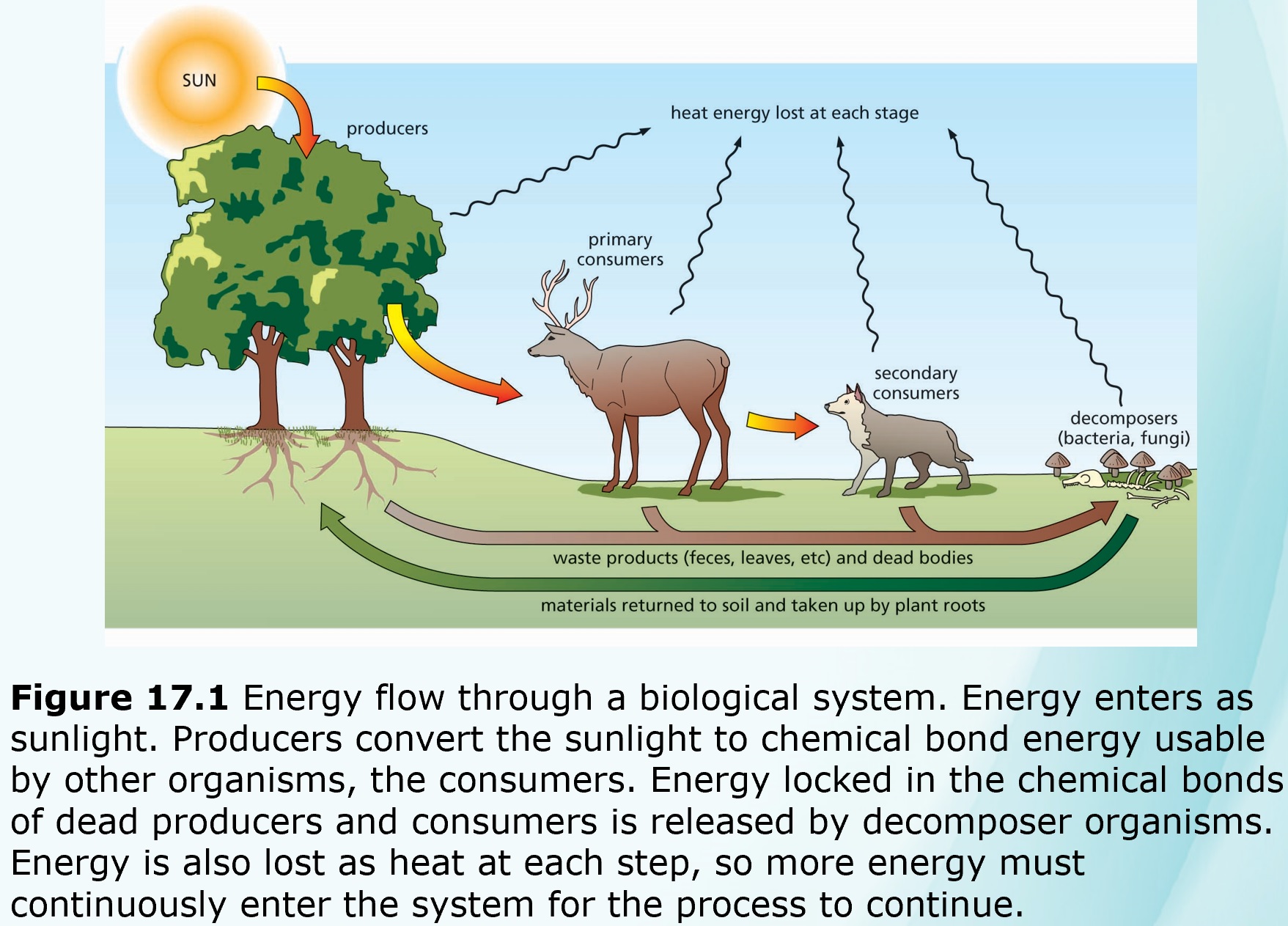
PLANTS IN ECOSYSTEMS
-
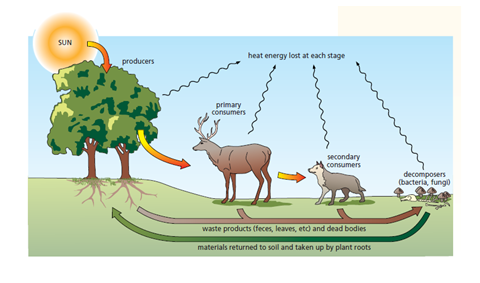
Nutrient materials circulate through all ecosystems:
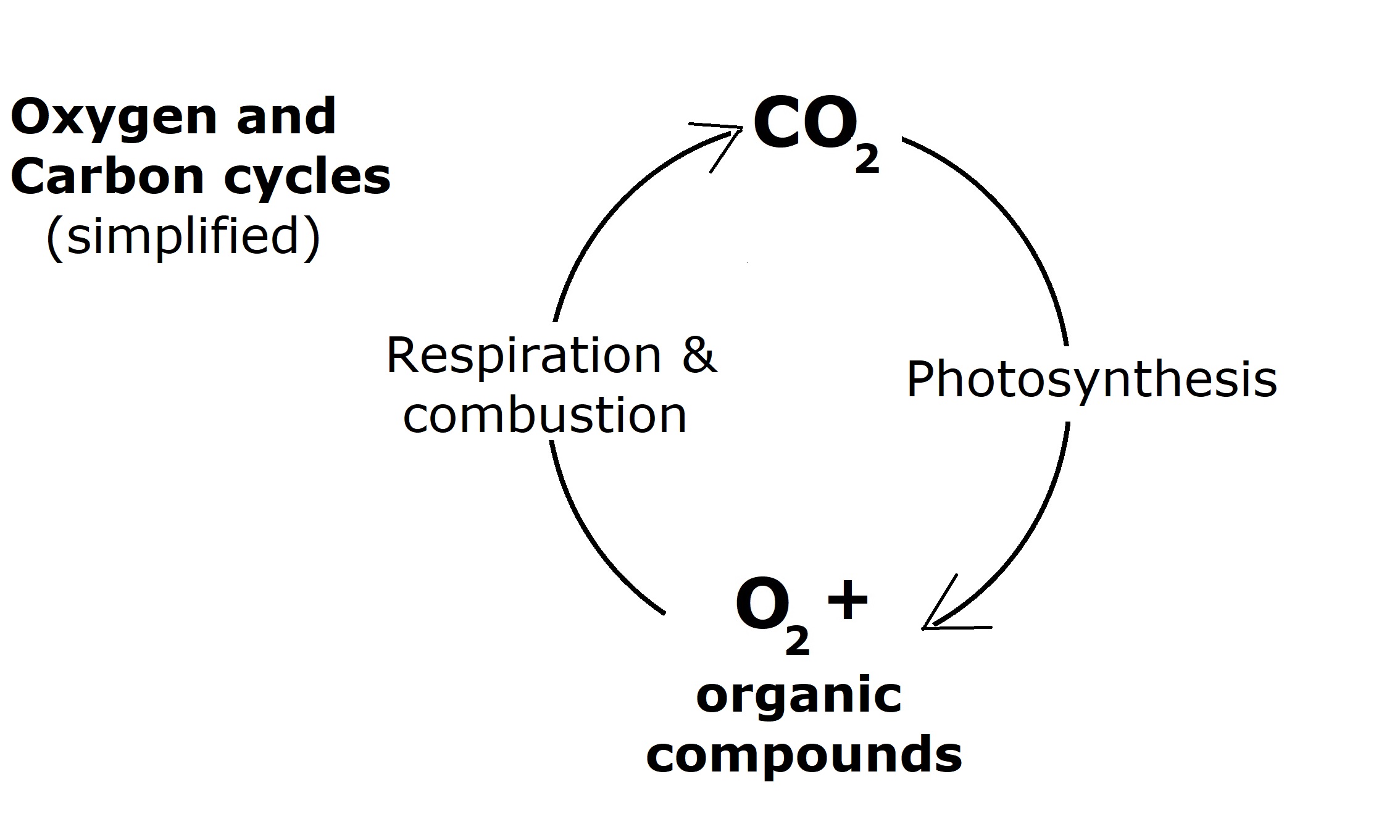
- Oxygen and Carbon follow very simple cycles
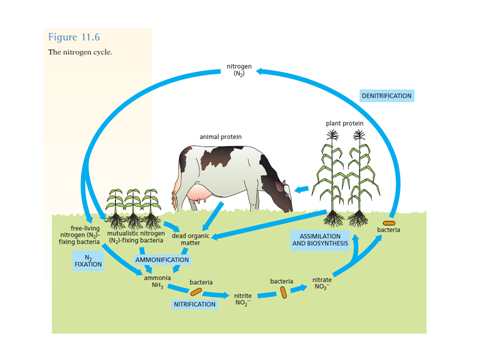
- Nitrogen for plant products
- Plants living in nitrogen-poor soils
- Mutualistic relationships, incl. bacteria in root nodules
|


Question 2:
Why are ROOT NODULES important?
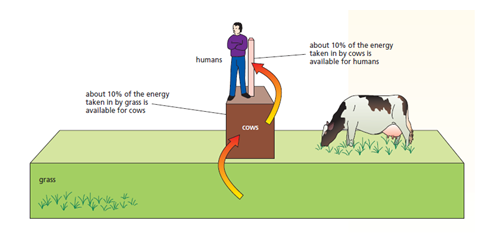
TROPHIC LEVELS, RUNOFF, and BIOMAGNIFICATION
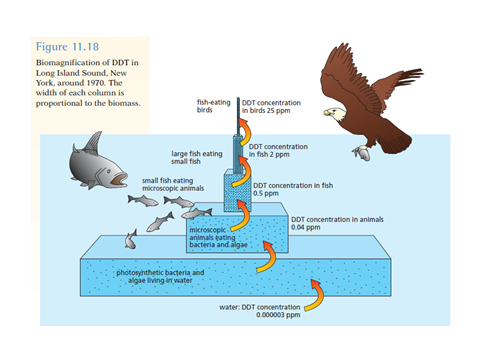
INCREASING CROP YIELDS: Overcoming various limiting
factors, while minimizing runoff and pesticide use
- Fertilizers:
- Chemical fertilizers and runoff
- Organic fertilizers and slow release
- Soil improvement and conservation
- Irrigation (incl. drip agriculture)
- Hydroponics
- Chemical pest control
- Integrated pest management




A cautionary tale: Cane toads
- Increasing Crop Yields Further by Altering Plant Genomes:
Question 3:
a. What is INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT?
b. What are some of its techniques?
|
· · · • • • • •
· · ·
—— Rev. Nov. 2023 ——
|