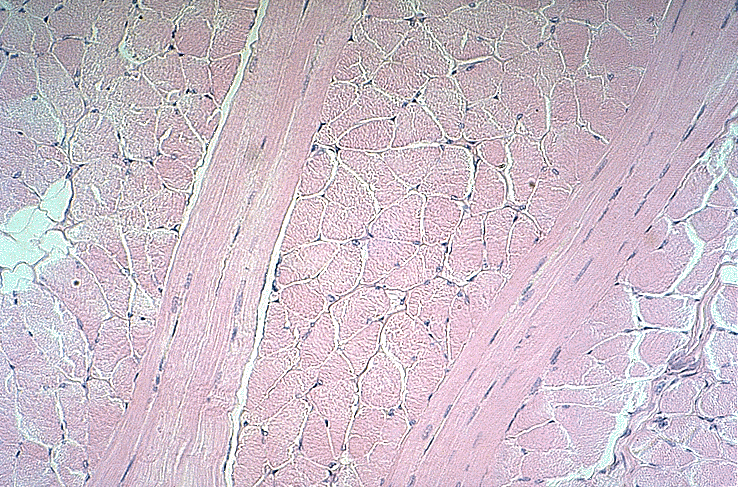
Smooth muscle tissue.
Skeletal (striated) muscle tissue. Some fibers are cut
longitudinally, others transversely.
Muscle tissue striations.
Cardiac muscle tissue: In this slide and the one to the right,
notice the striations and the cell boundaries (intercalated disks) running
perpendicular to the fiber direction; also notice the centrally located nuclei.
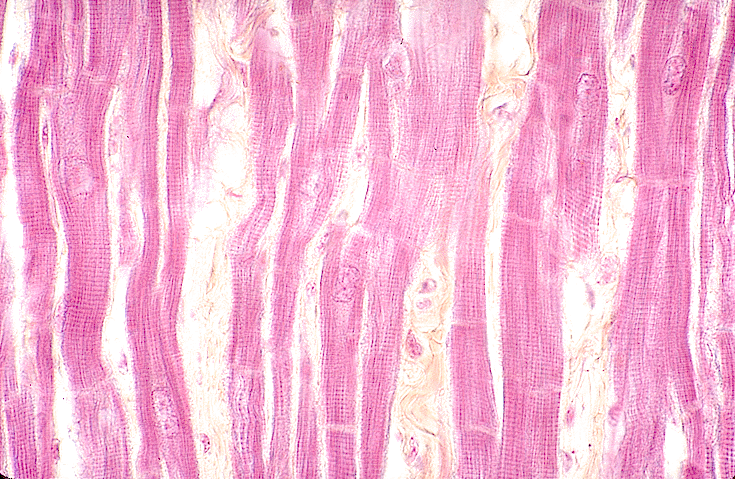
Cardiac muscle tissue
nervous tissue
Cerebral hemispheres (cross-section)
Spinal cord: gray matter (left) and white matter (right)
Motor neuron cell bodies in ventral horn of spinal column
Cell body of motor neuron
Neuron cell body, with neurofibrils
Peripheral nerves in cross-section
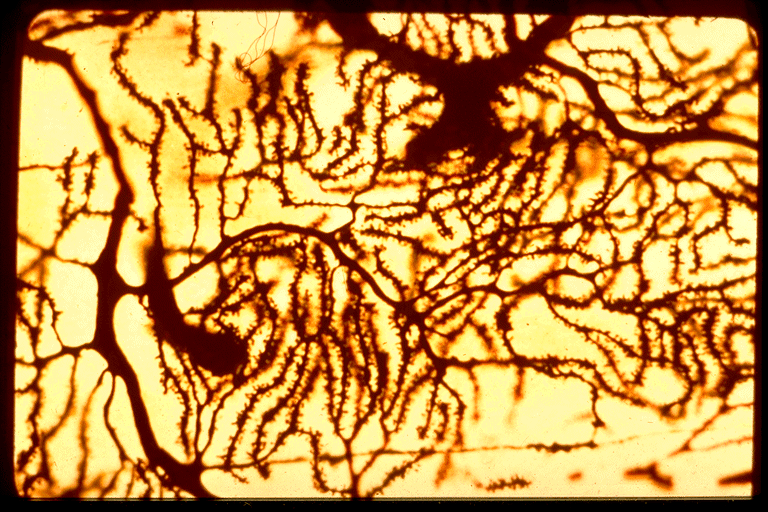
Dendrites
Astrocytes
Fibrous astrocyte
Oligodendroglia
Basket cell (large, right of center) and granule cells (smaller,
with fewer branches)