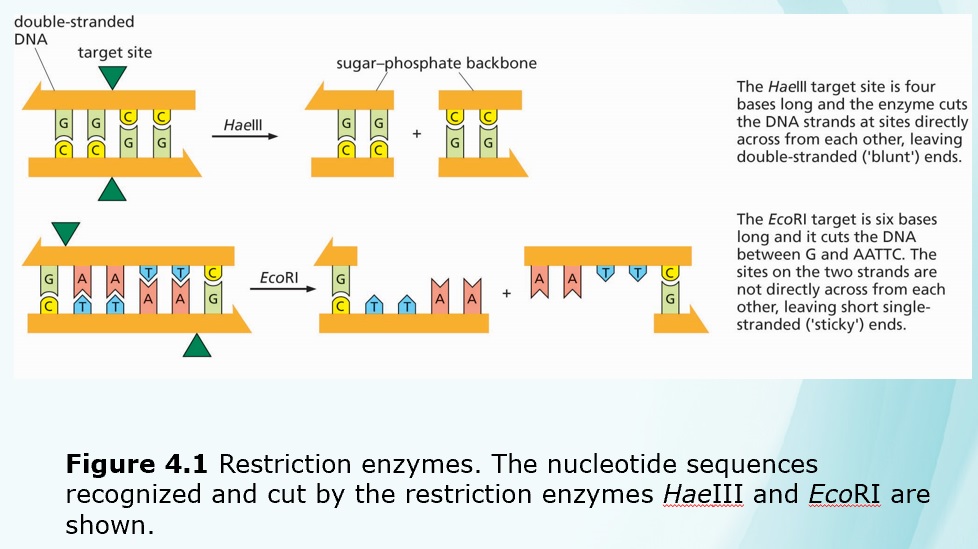
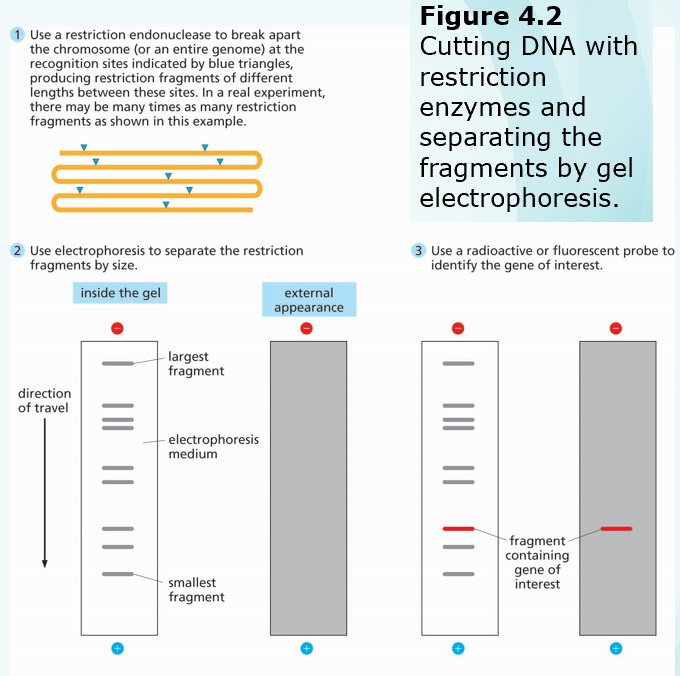
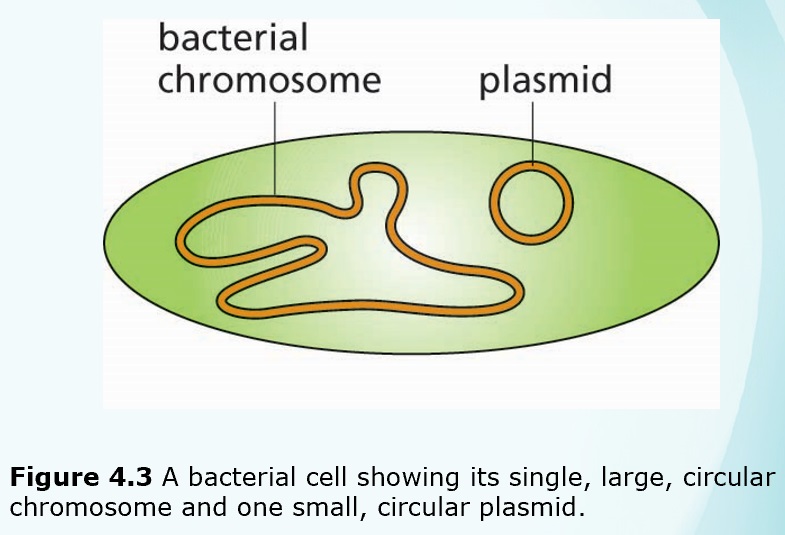
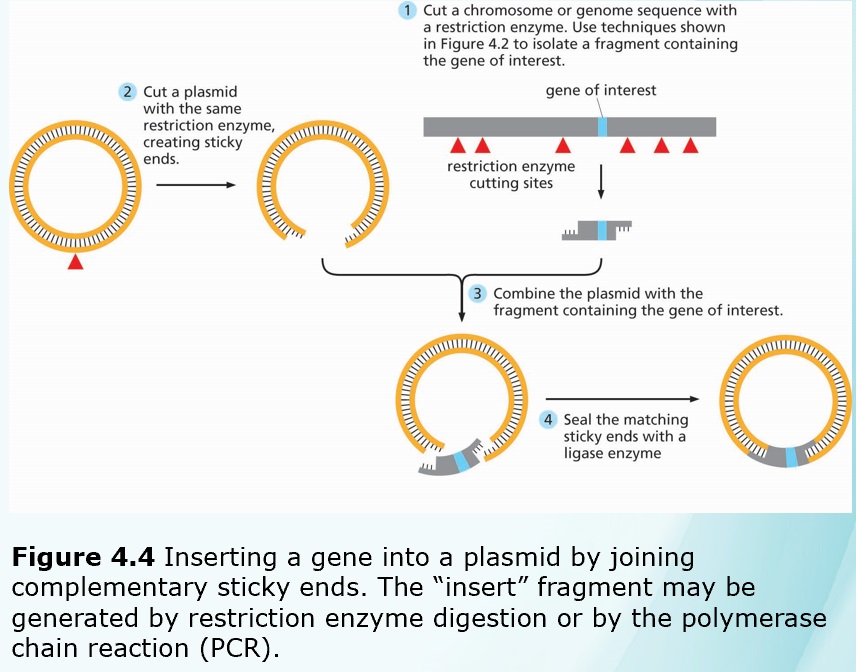
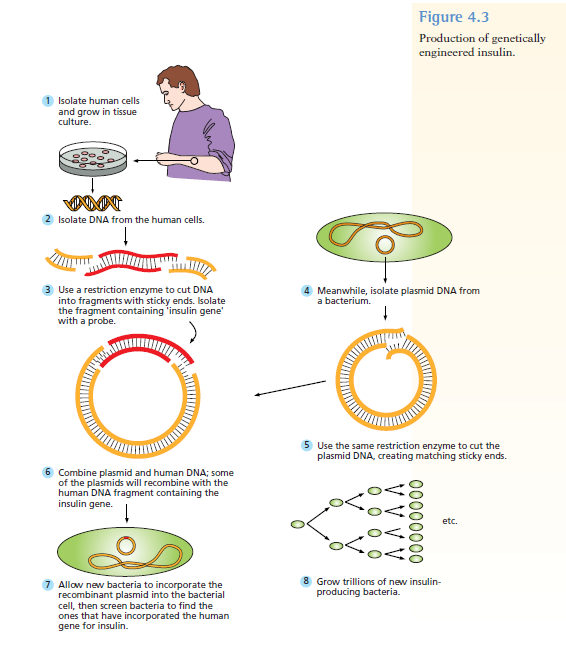
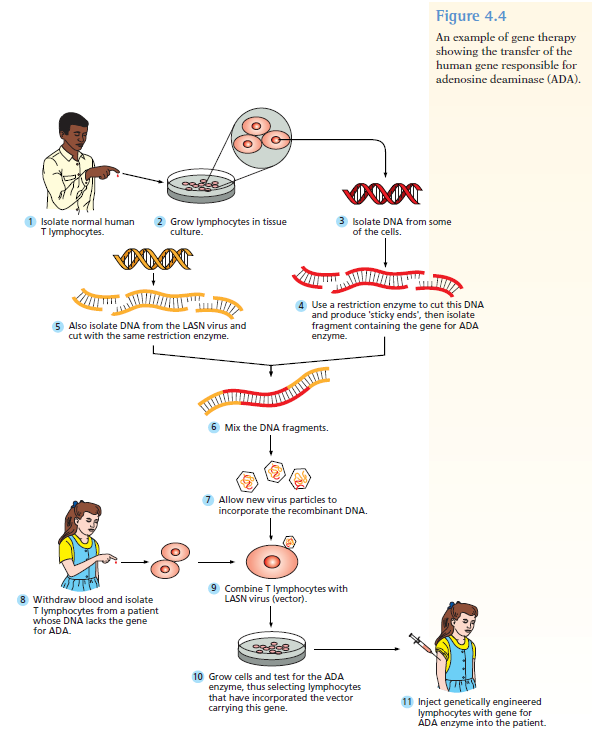
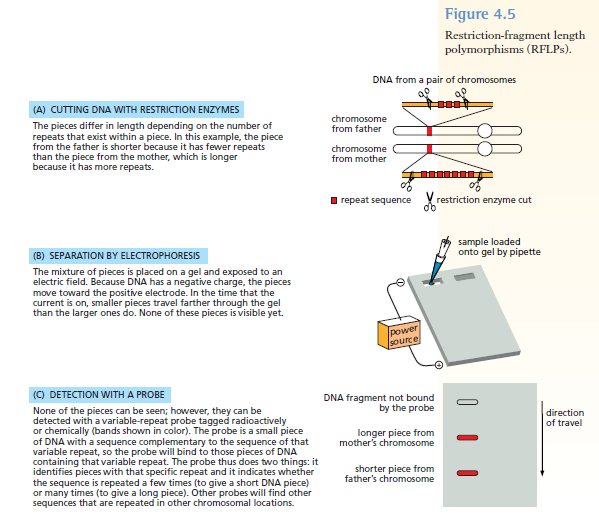
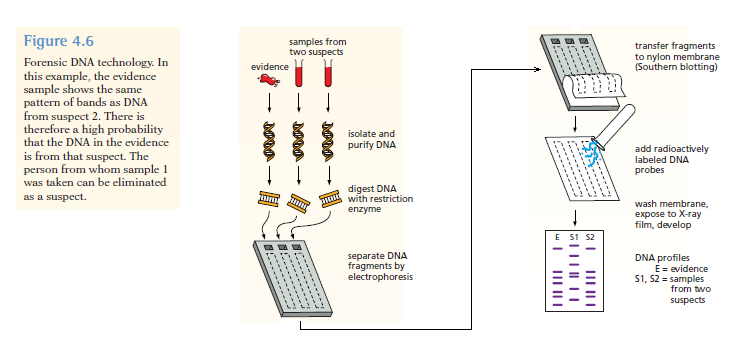
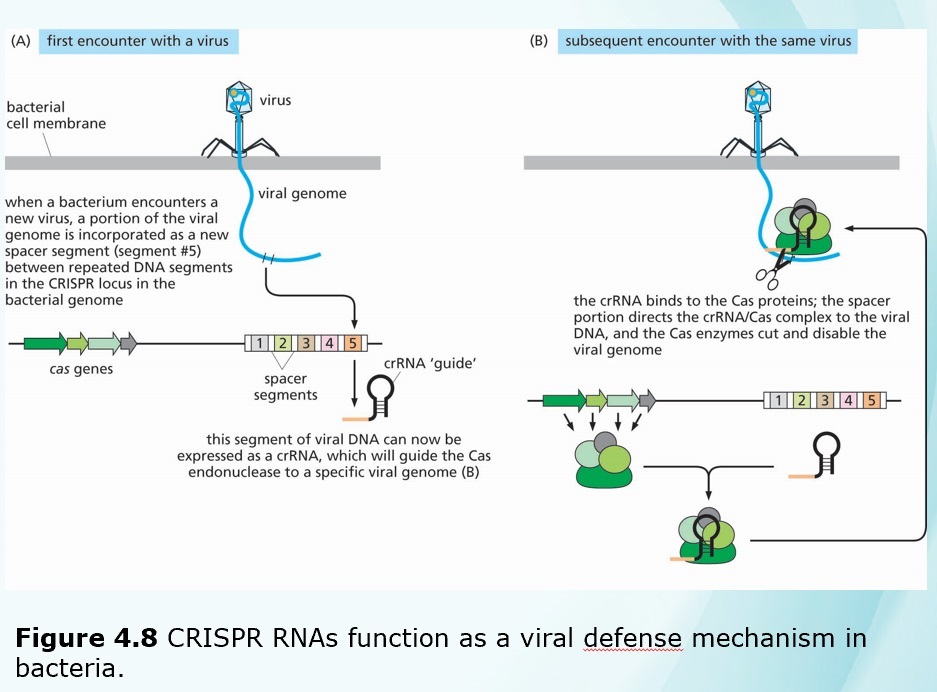
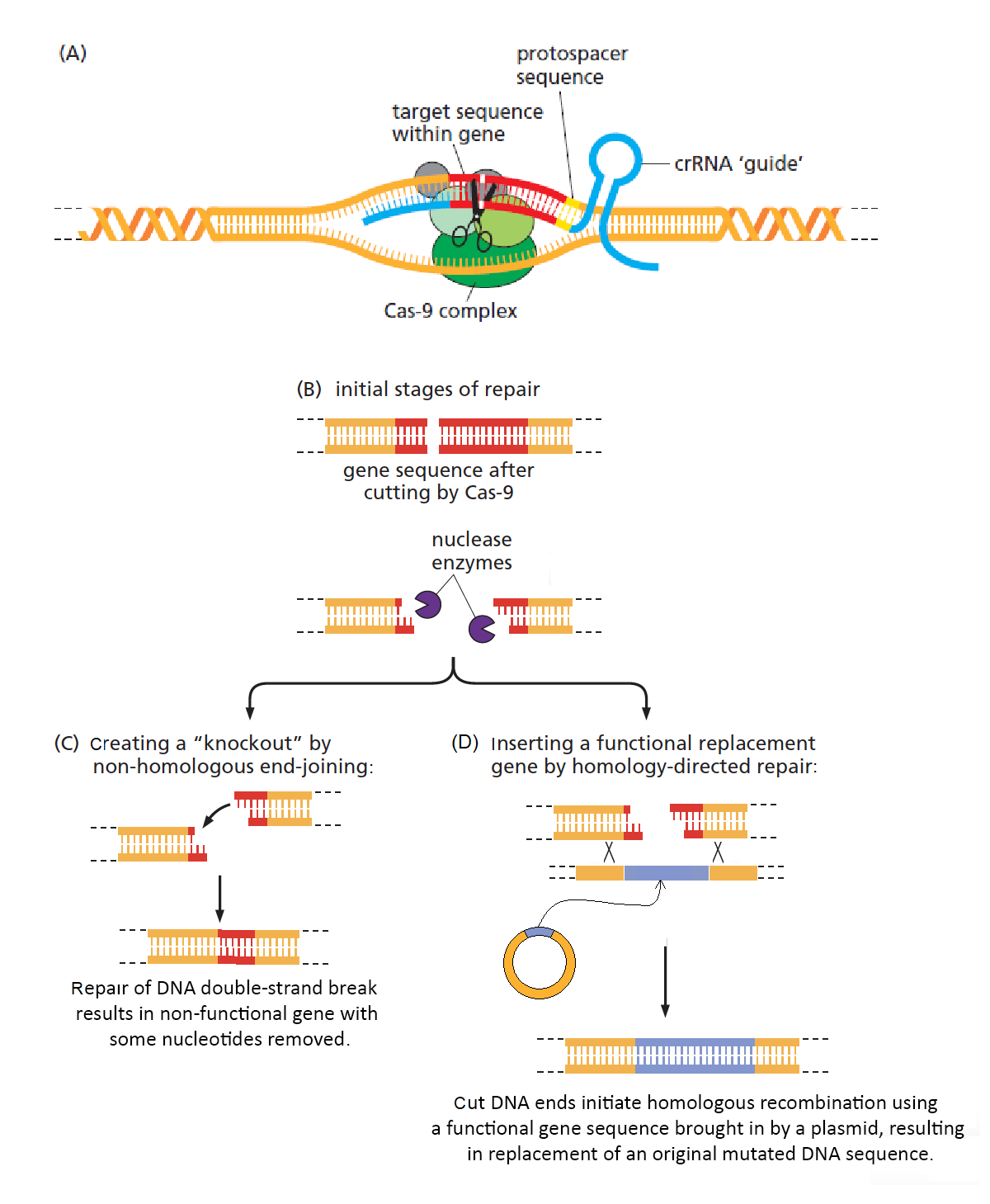
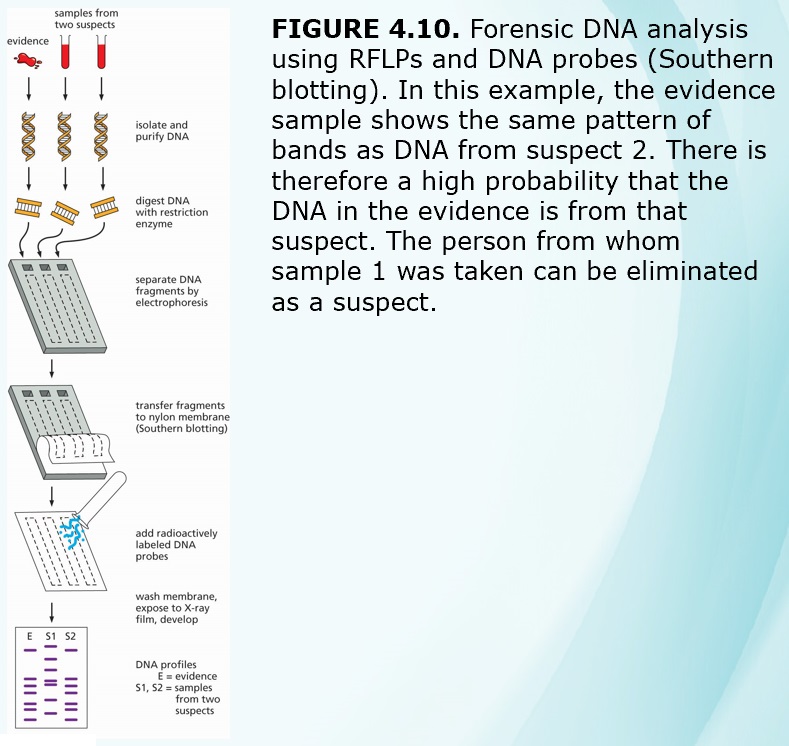
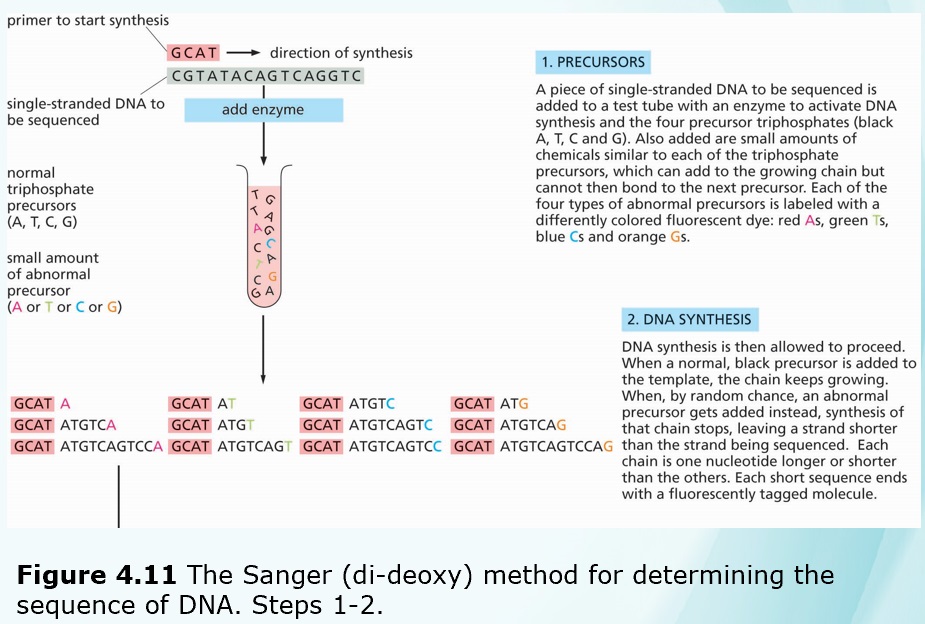
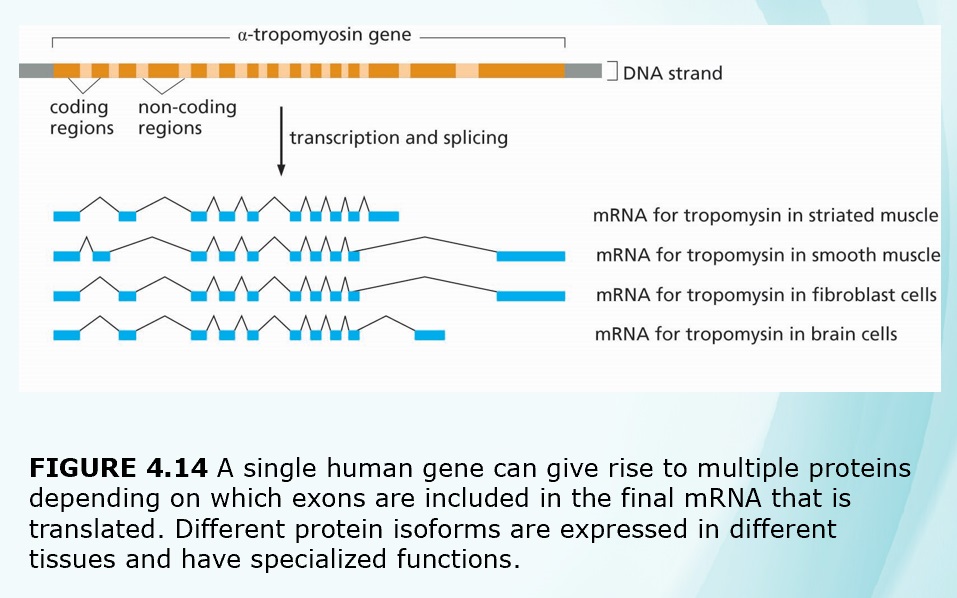
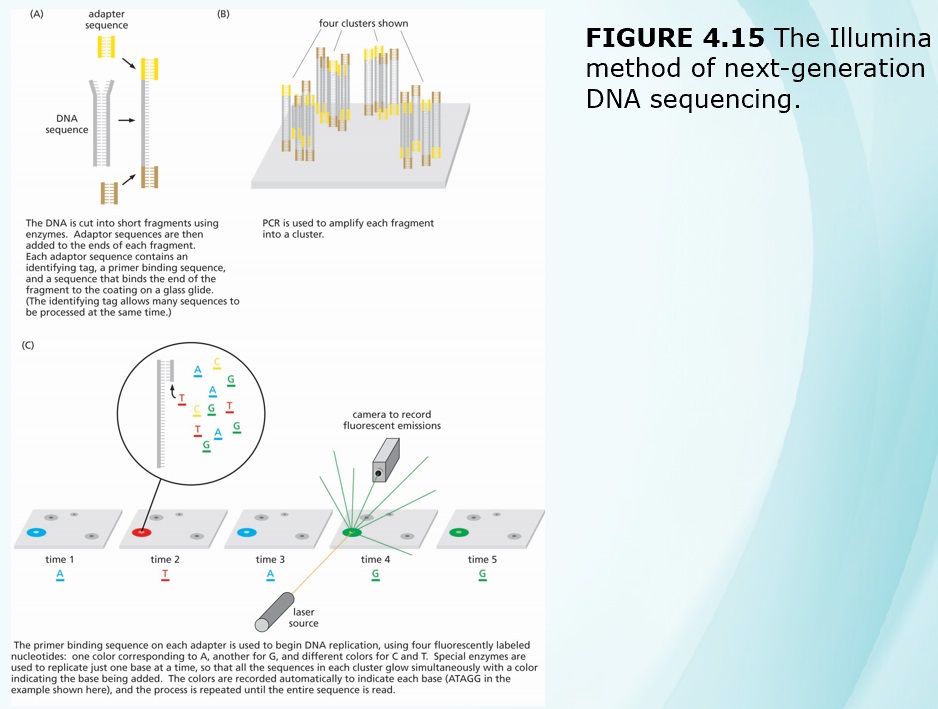
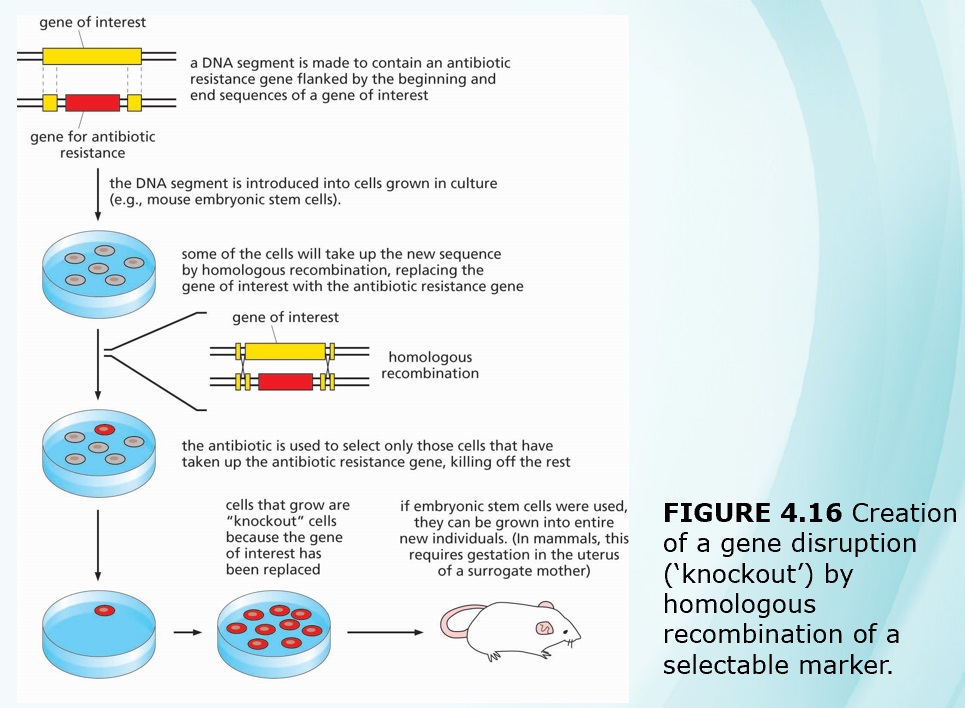
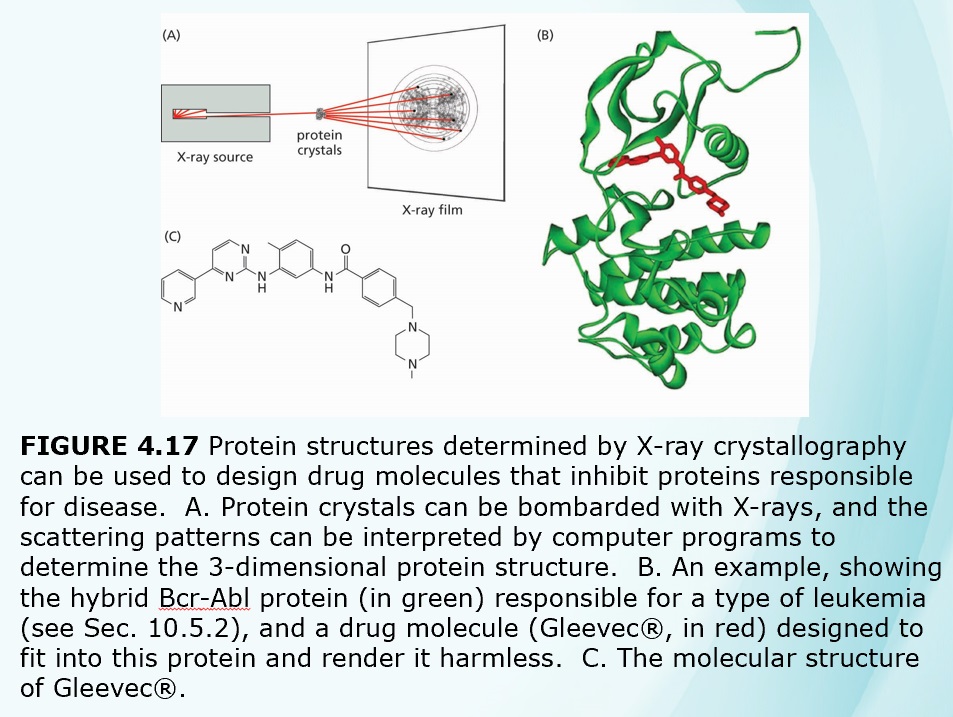
Chapters 3-4 (Genetics)
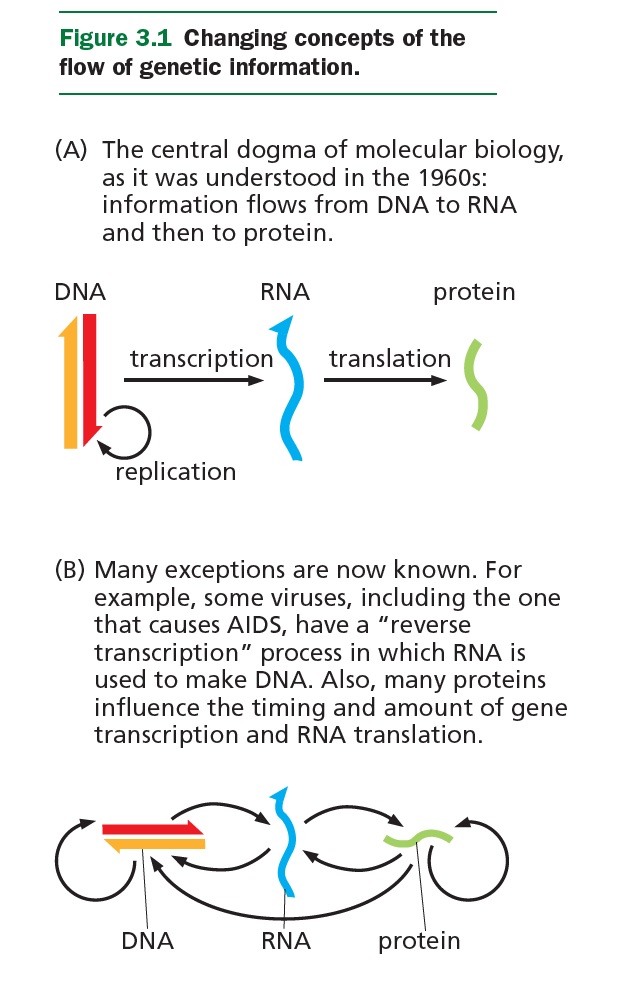
How do genes work? What do they do?
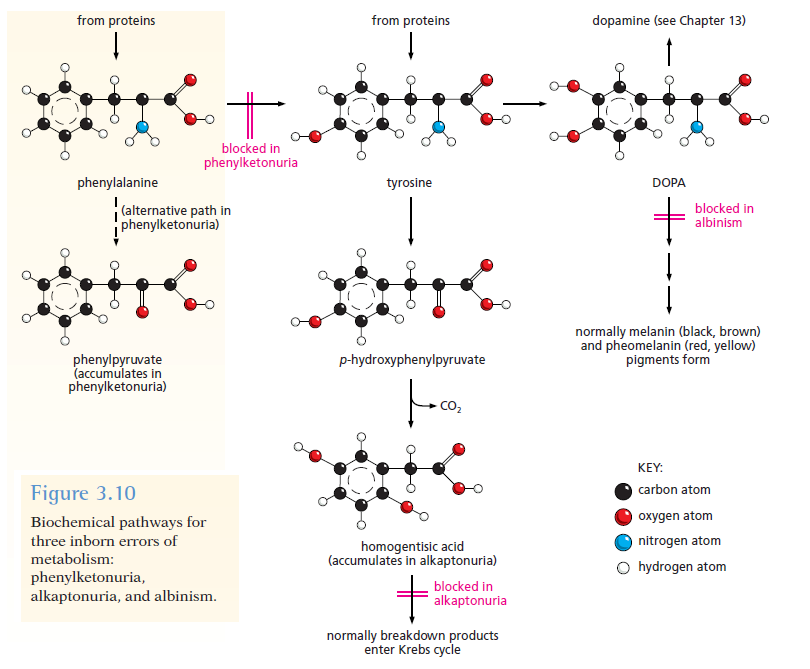
Archibald Garrod: "Inborn Errors of Metabolism" (1906)
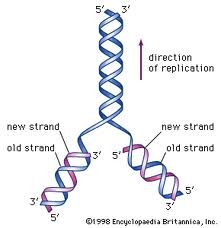
REPLICATION
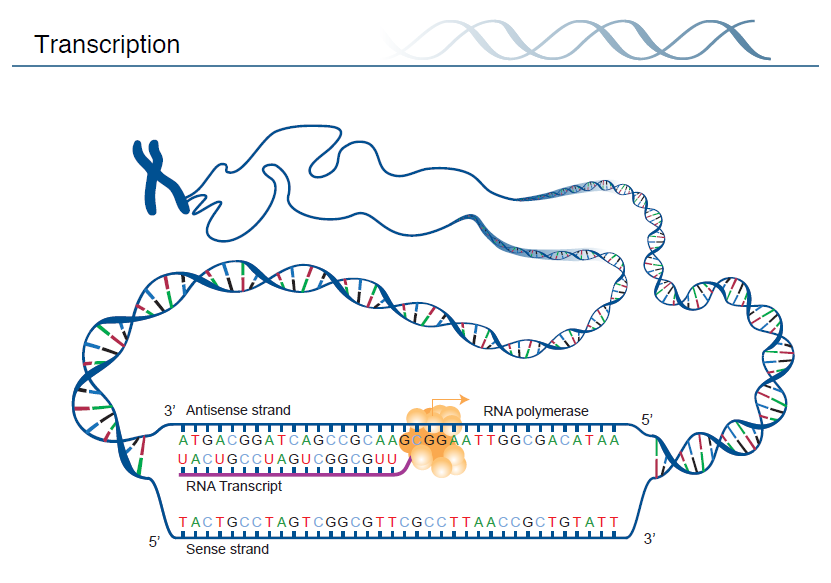
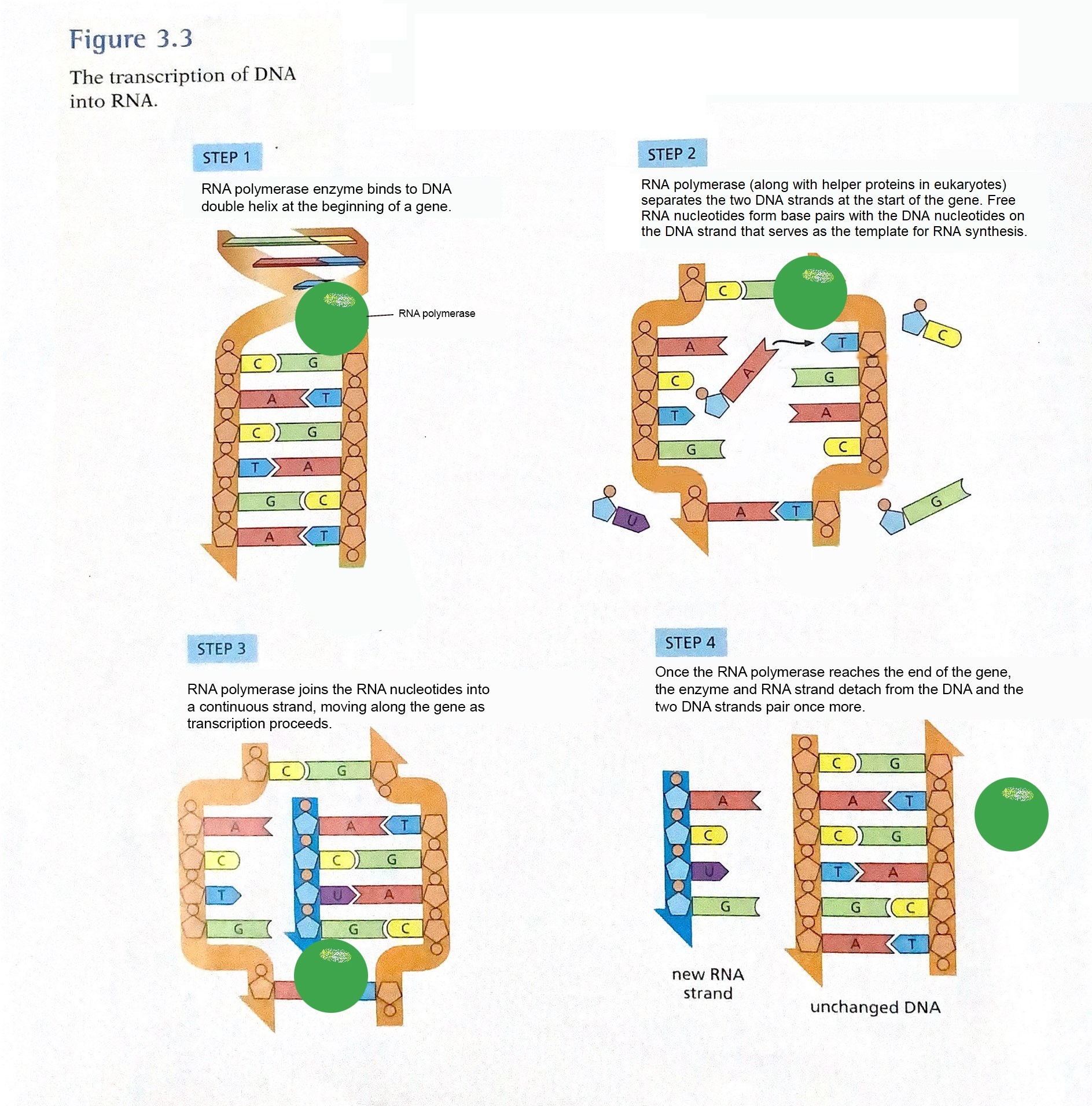
TRANSCRIPTION
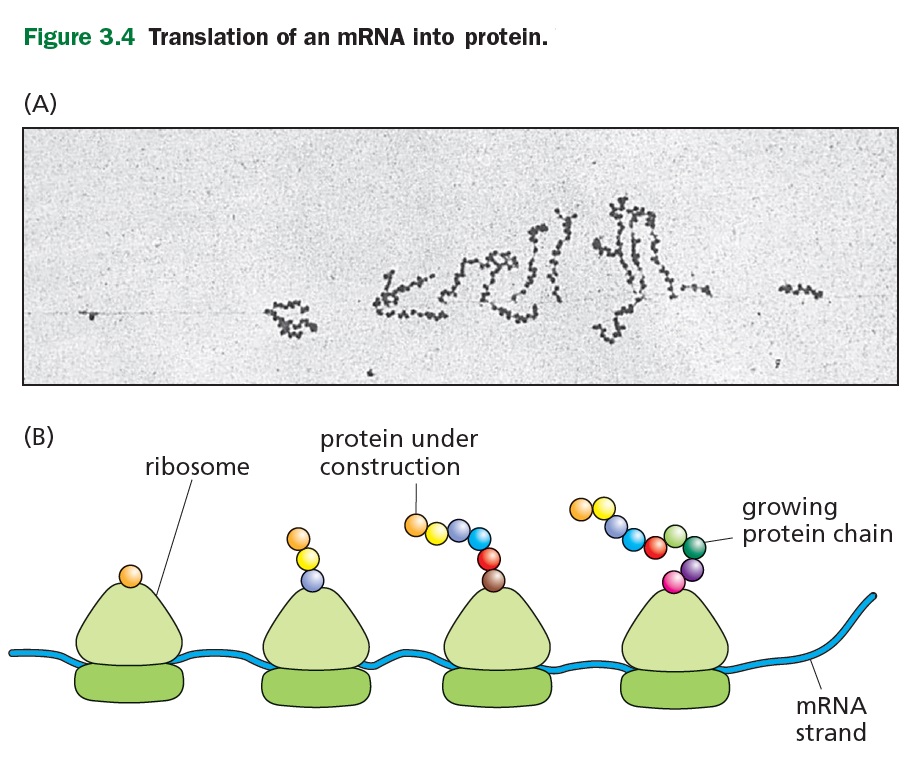
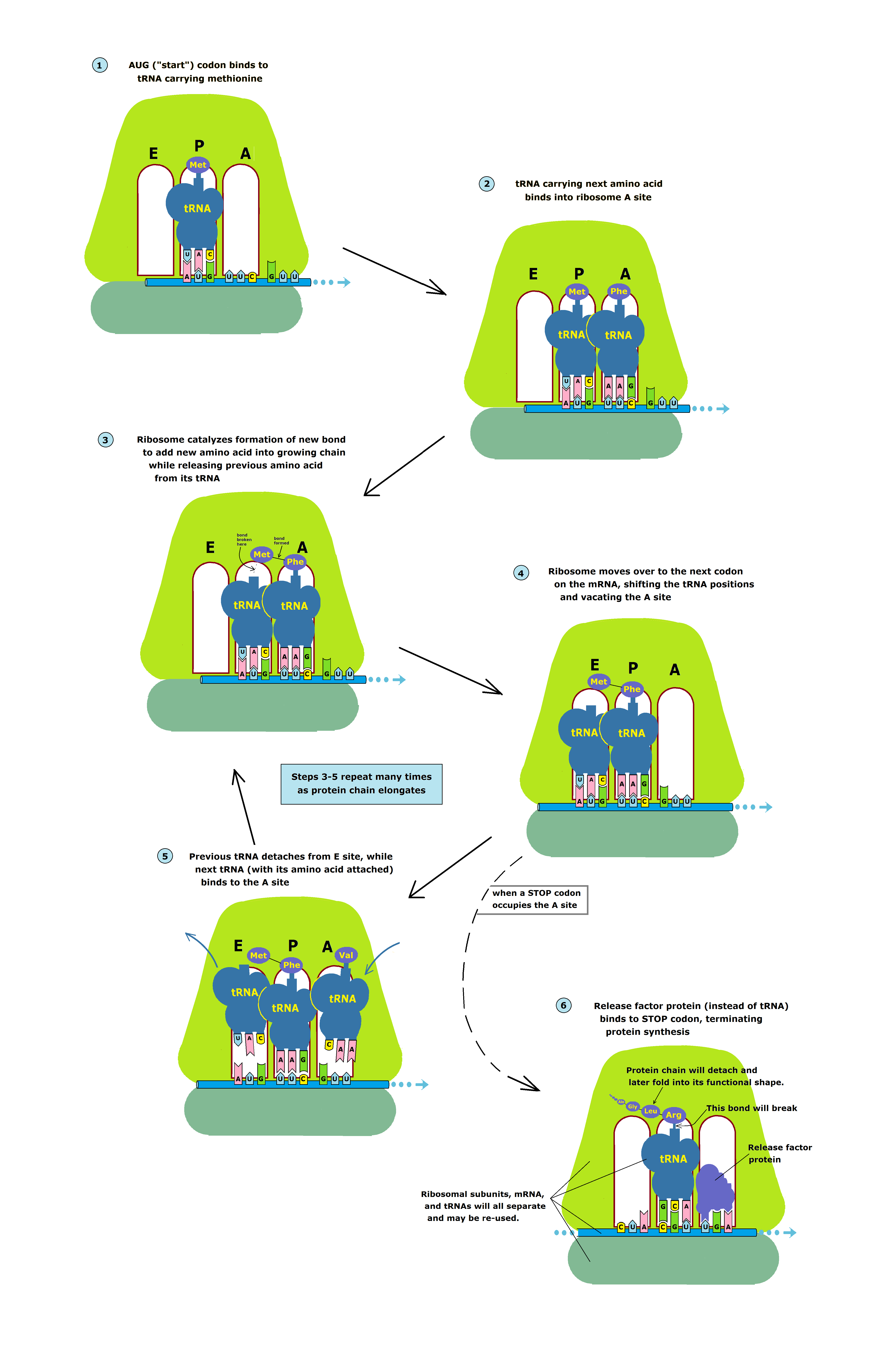
TRANSLATION

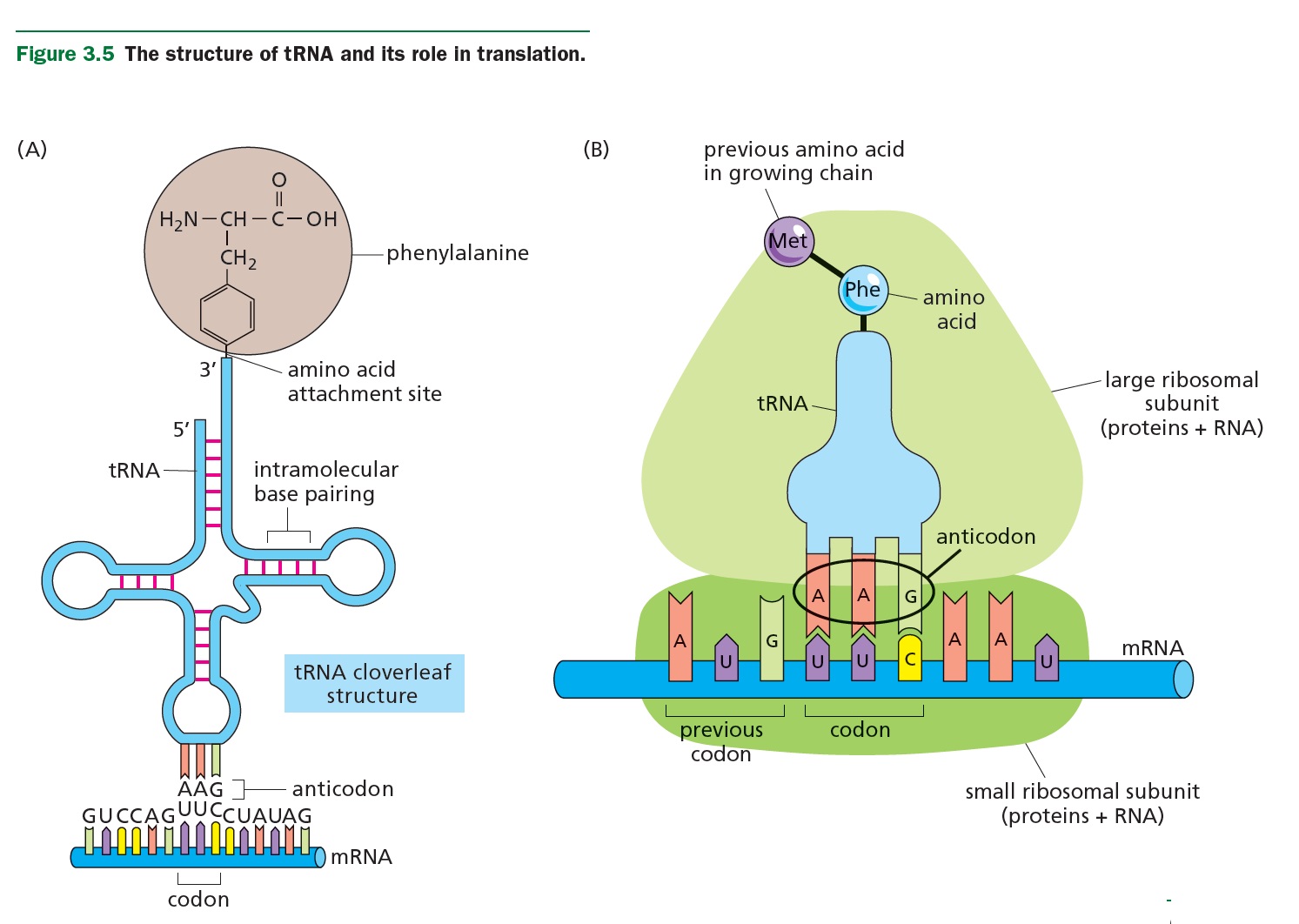
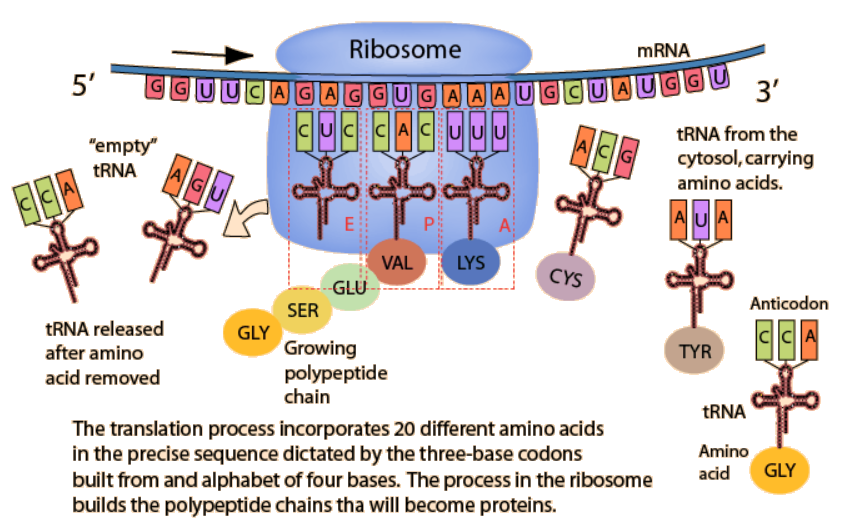
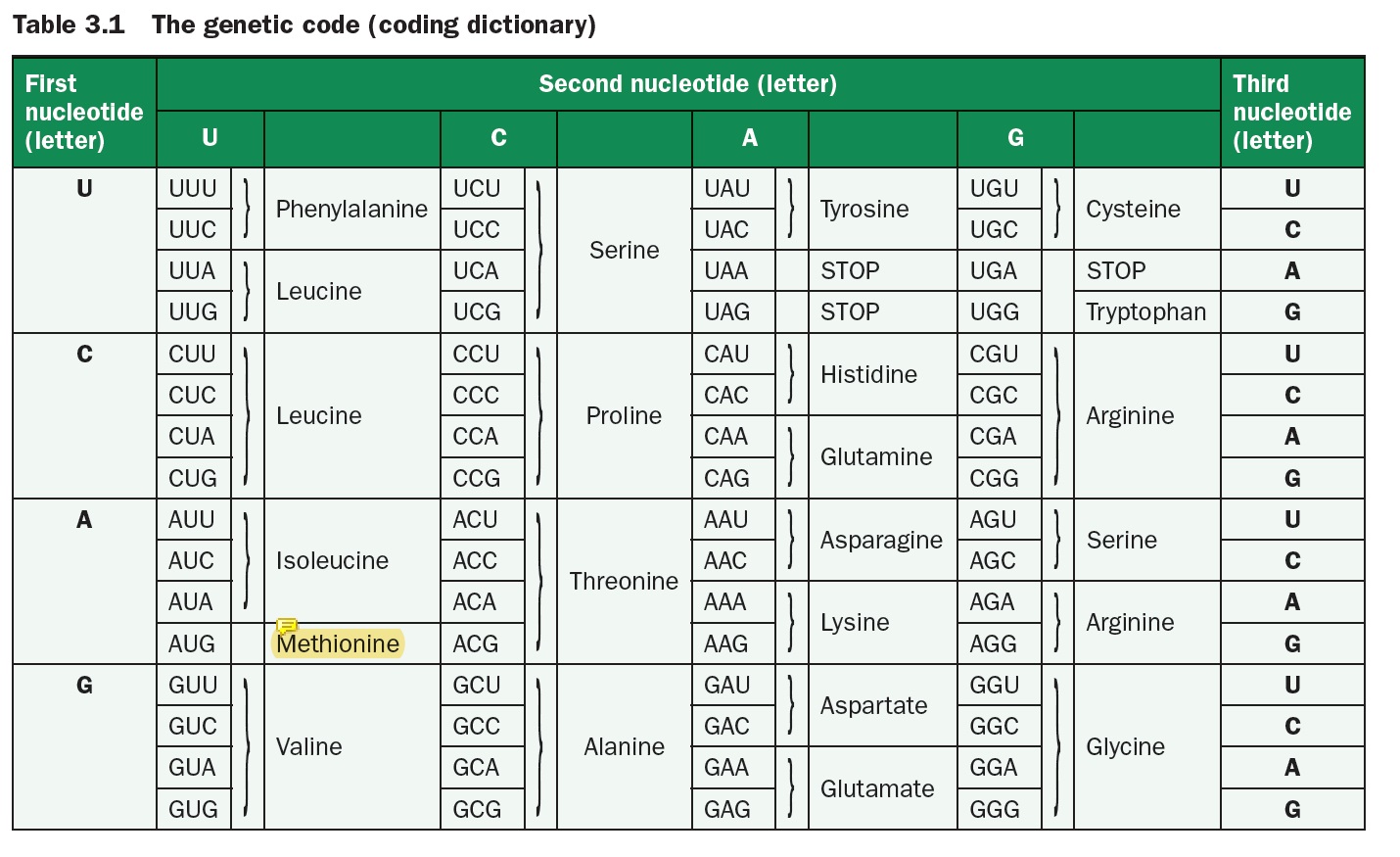
QUESTION:
What is the difference between
a CODON and an ANTICODON ?
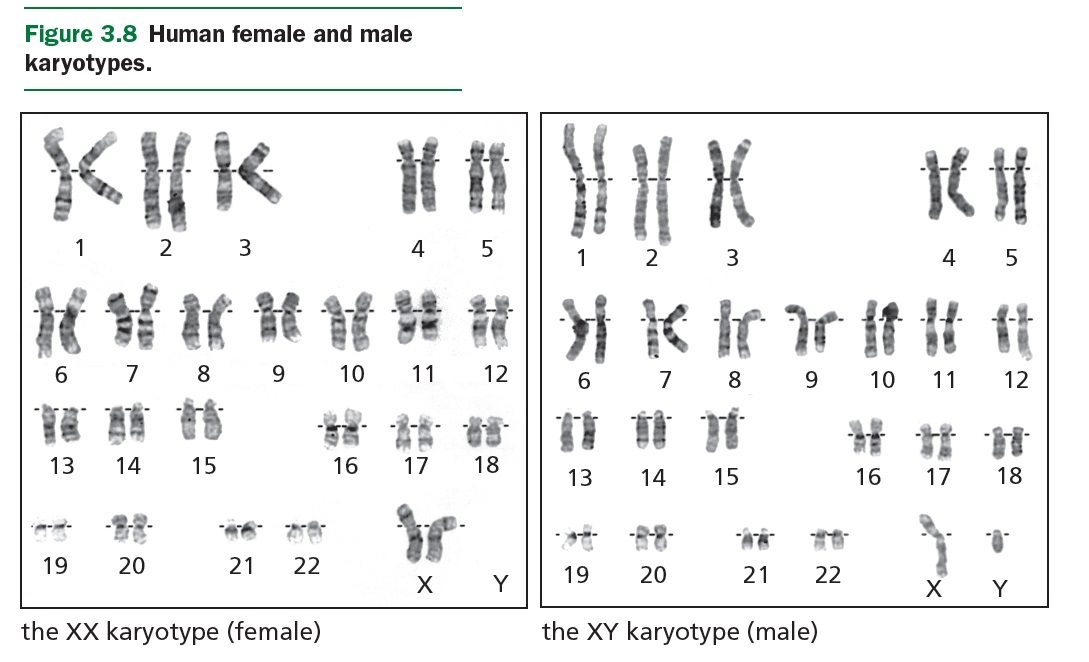
Chromosomes and Sex-linked traits
|
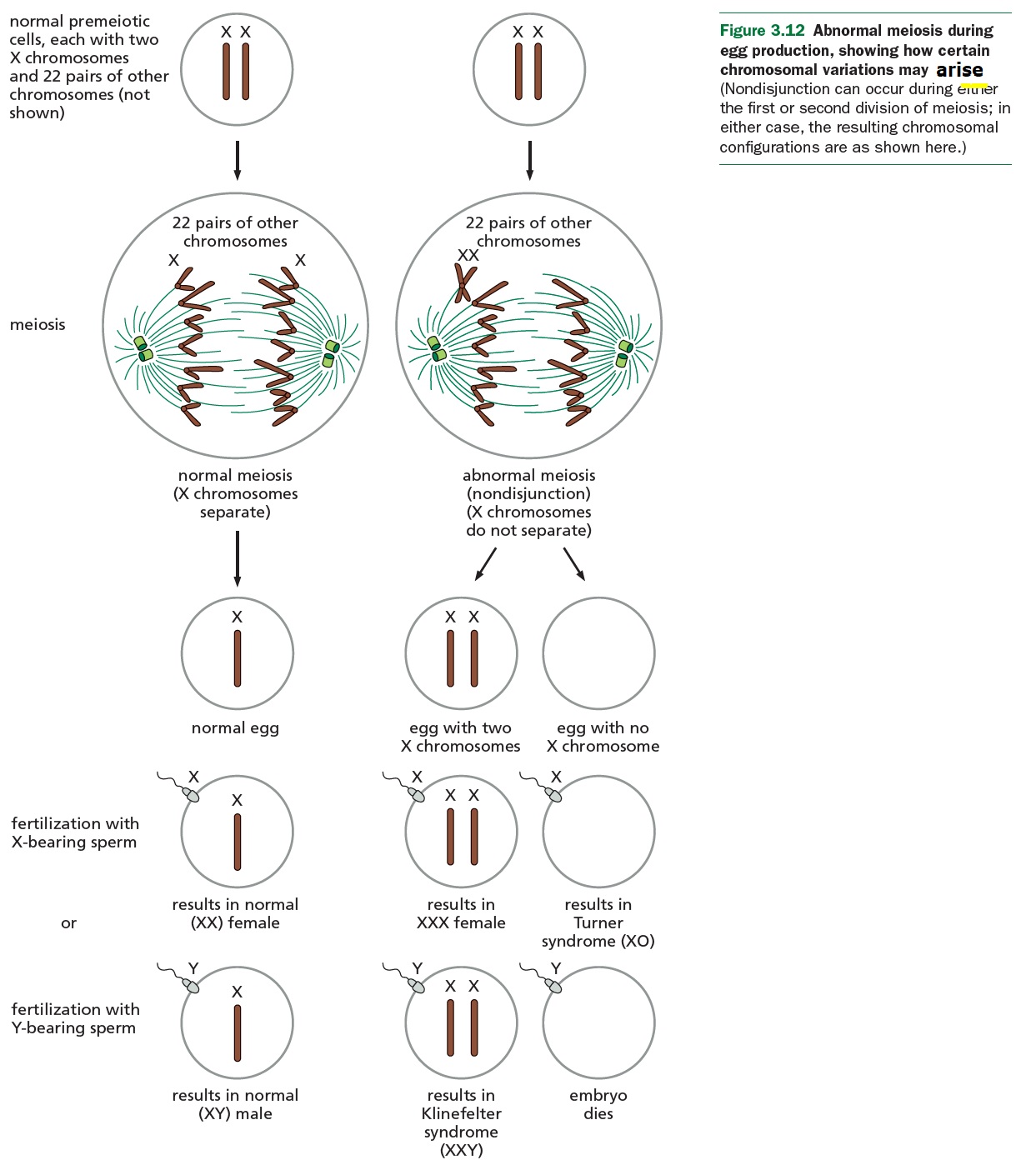
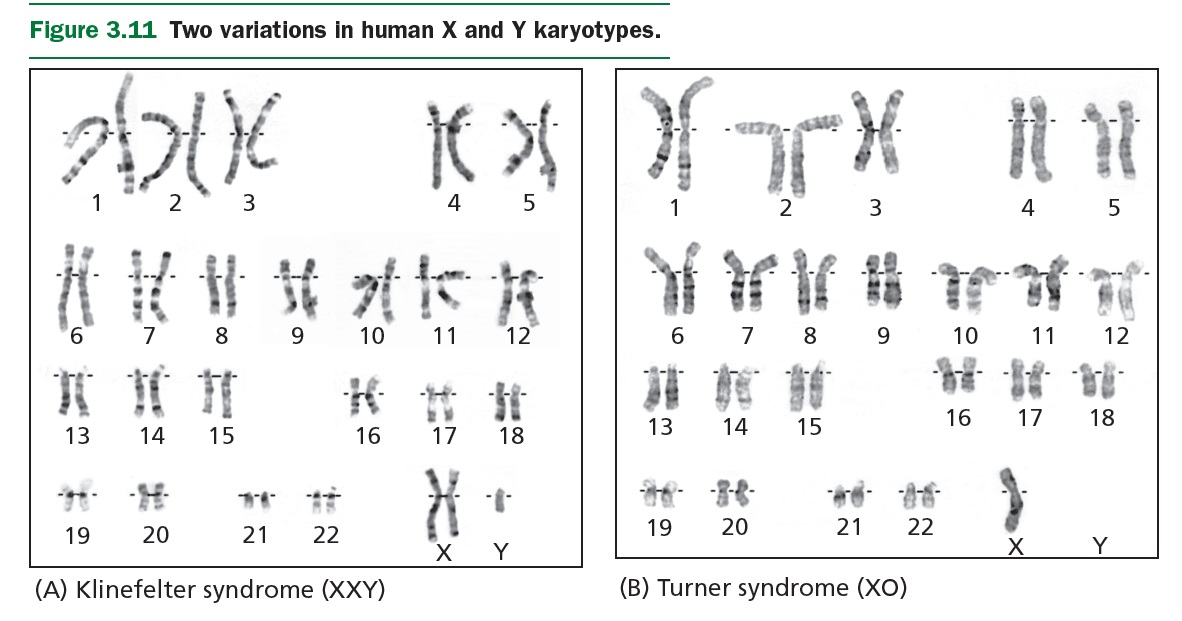
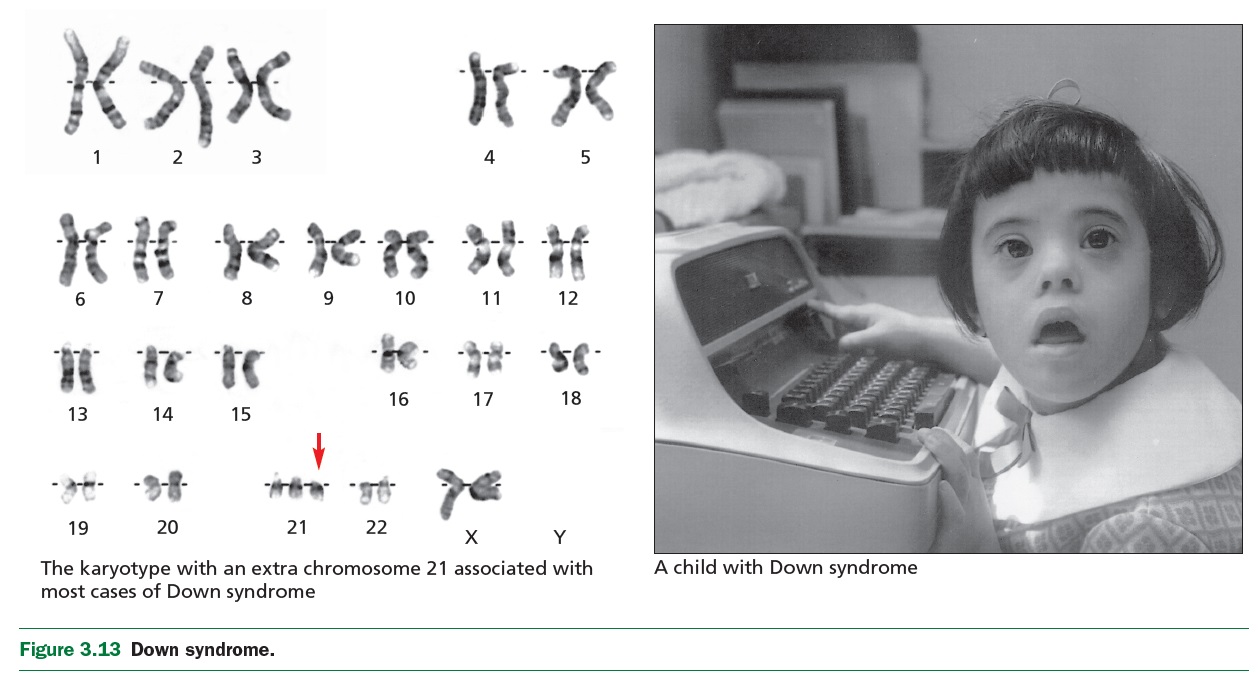
Sex determination: XX vs XY also X0 (Turner), XXX; XXY (Klinefelter), XYY Sex-linked traits: males are hemizygous for these traits Chromosomal variations (e.g., Down syndrome, etc.) Social and ethical issues (incl. sports, discrimination, dysphoria, etc.) |
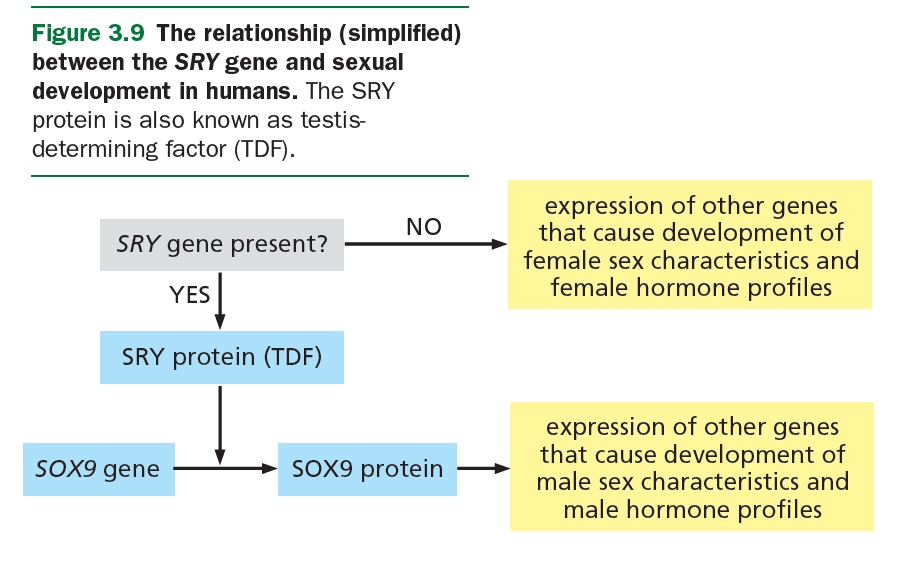
ANOTHER UNCOMMON ANOMALY:
XY individuals with androgen insensitivity
QUESTION:
Why are the numbers of baby boys and baby girls approximately equal?
HINT: Think about meiosis in fathers
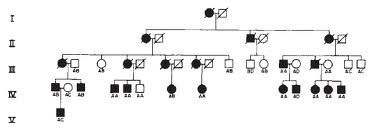
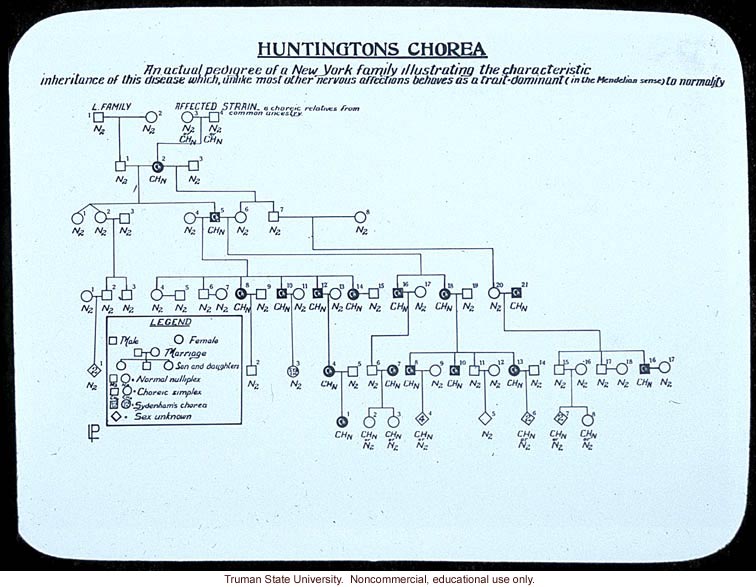
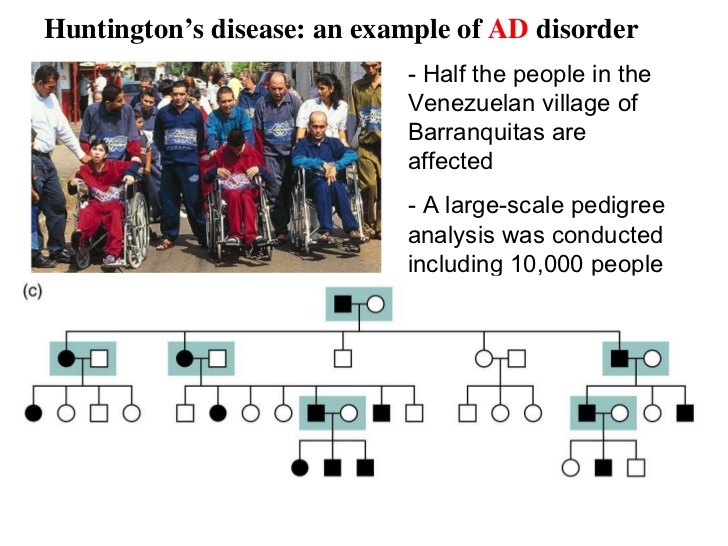
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT TRAITS


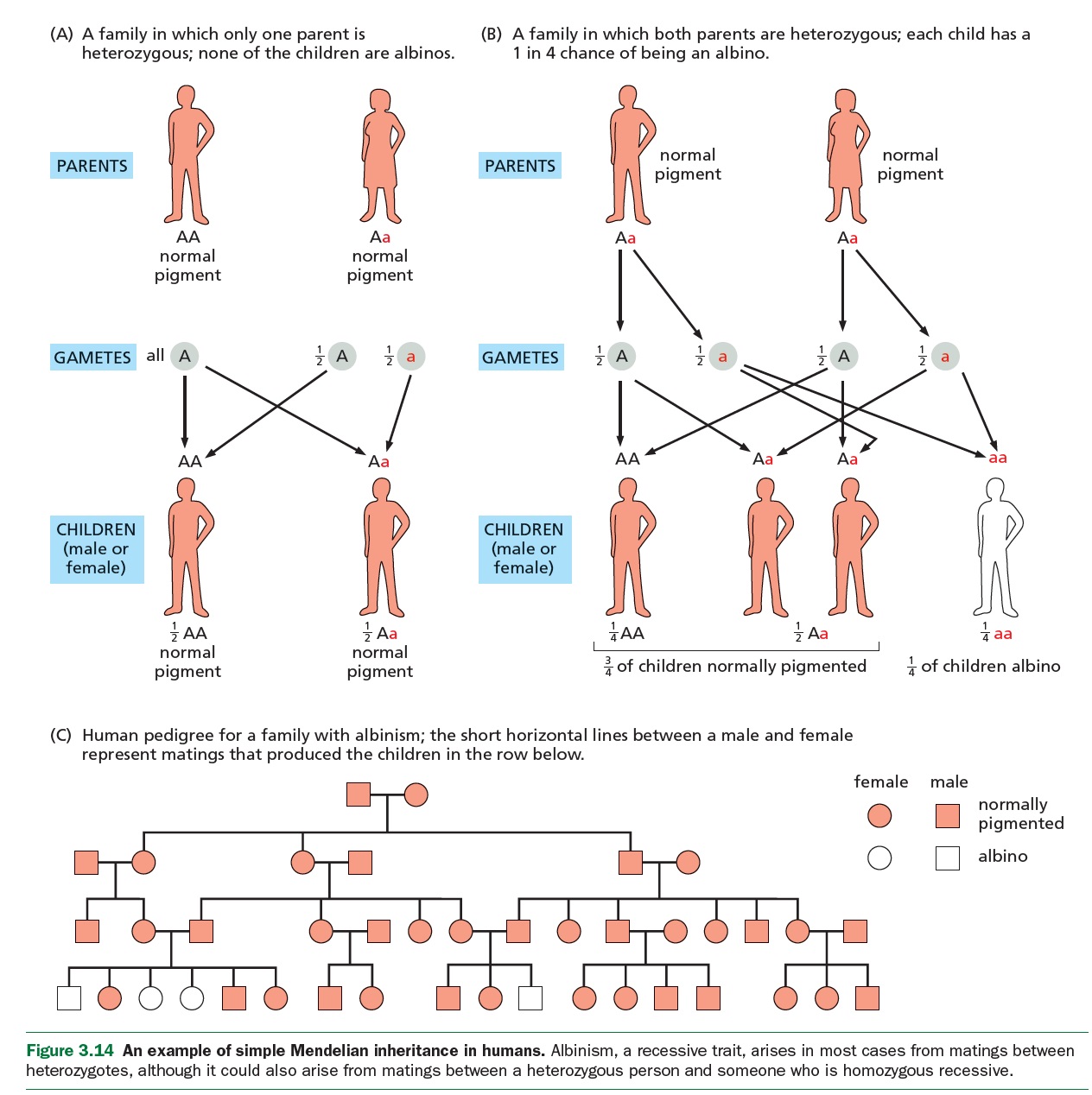
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAITS

REMINDER: Reseccive because of a nonfunctional protein (such as an enzyme)
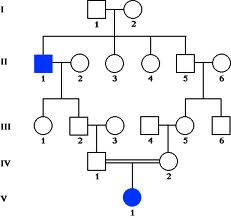

DOMINANT OR RECESSIVE?
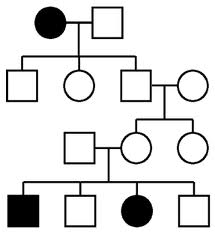

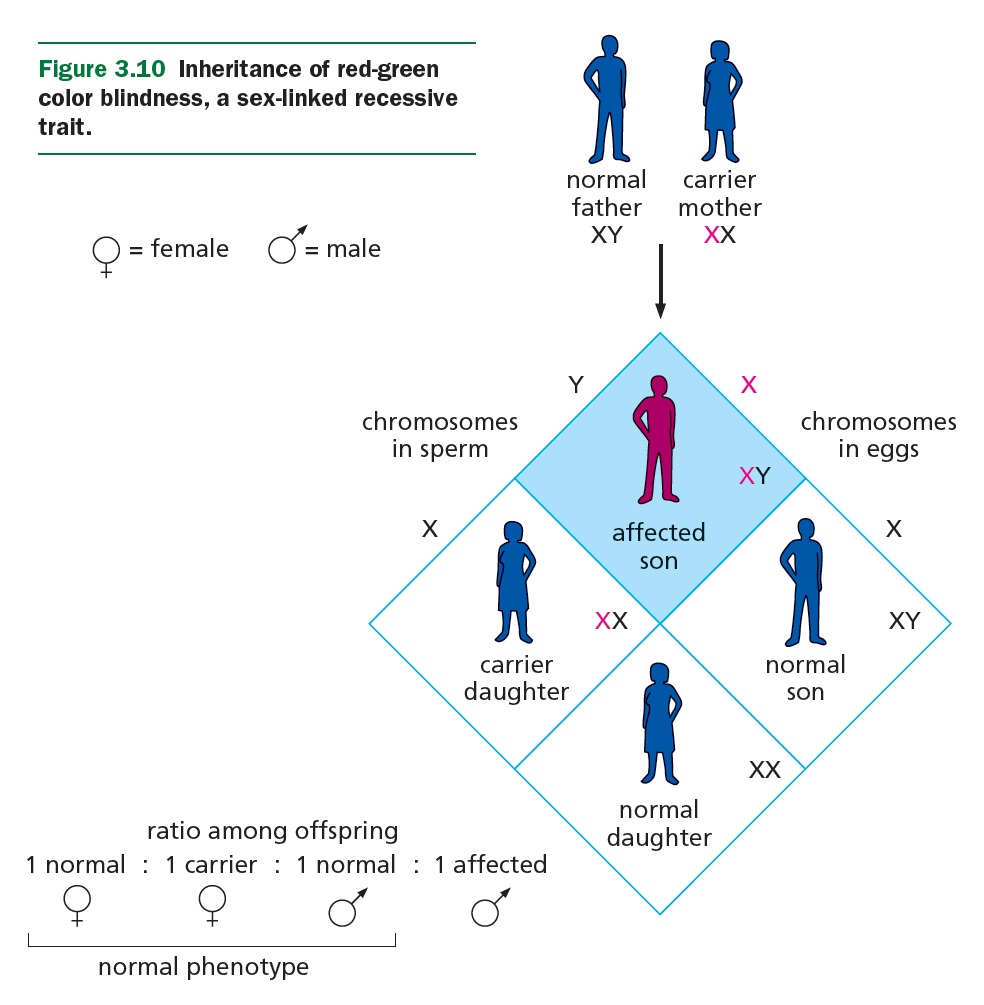
SEX-LINKED RECESSIVE INHERITANCE

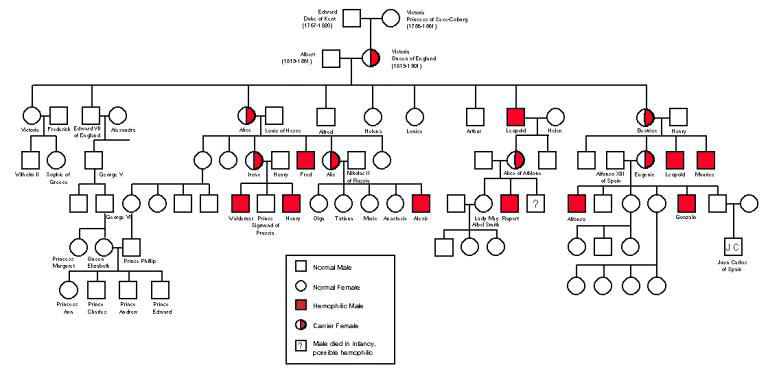
===================================
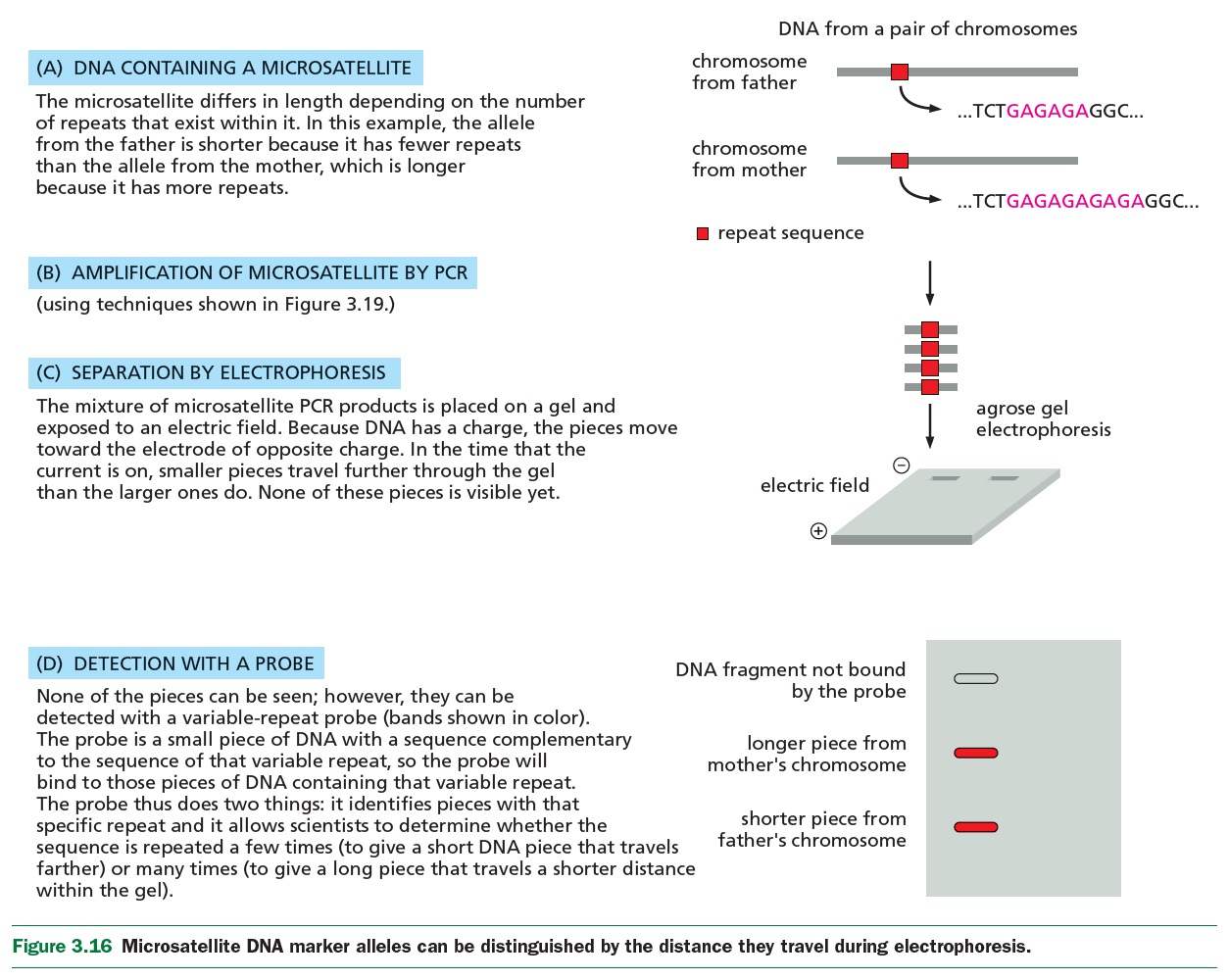
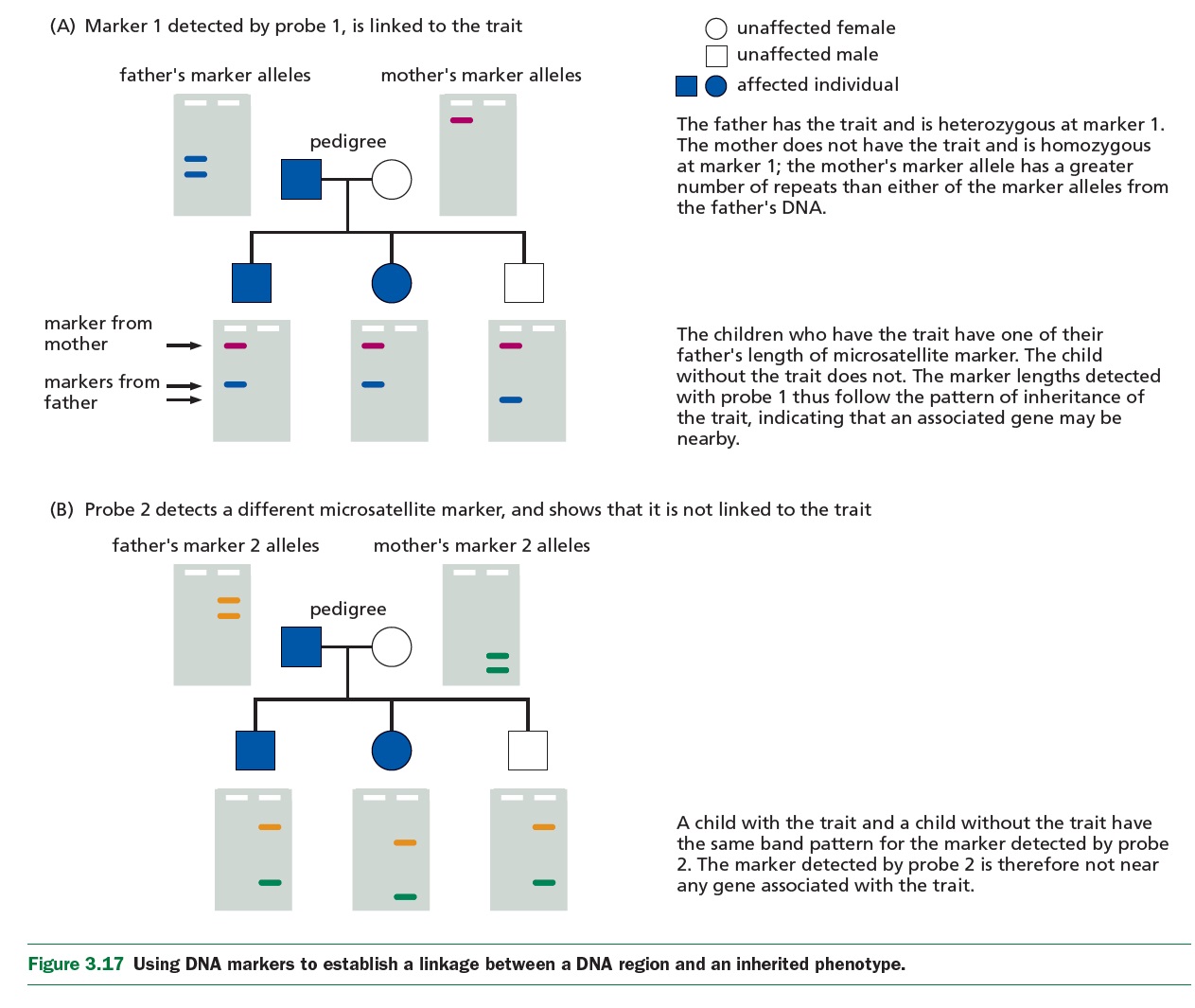
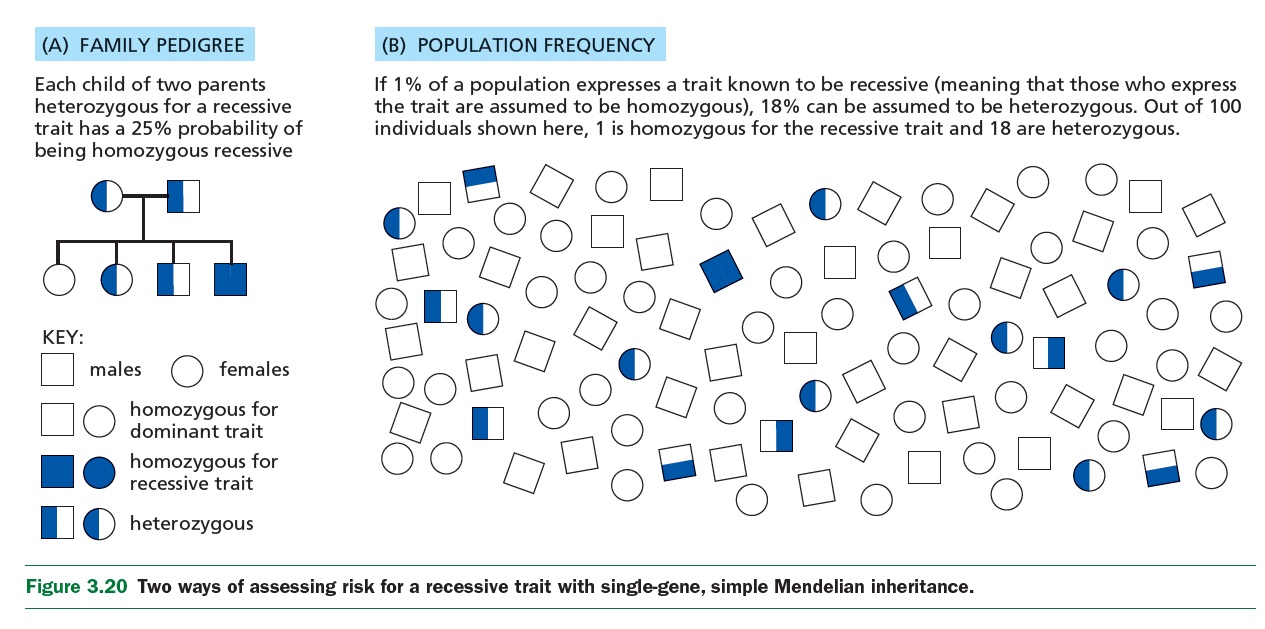
|
Altering the gene pool: positive eugenics; negative eugenics Altering individuals (euphenics); Altering physical environments (euthenics) Altering social environments (eupsychics) |