Eucaryotic cells have nuclei surrounded by double-layered membranes.
The several chromosomes each contain proteins as well as DNA. The cytoplasm
of eucaryotic cells contains many organelles not found in procaryotic cells.
Much evidence indicates that eucaryotic cells originated by symbiosis. In
particular, mitochondria and plastids were once separate organisms.
Procaryotic vs Eucaryotic cells:
Procaryotic vs Eucaryotic cell types
Eucaryotic cells are cells with true nuclei, each containing a nucleolus
and surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
- Chromosomes are usually separate, multiple, and linear; each contains protein
as well as DNA.
- Cytoplasm contains contractile proteins (actin, myosin), making possible
cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis), amoeboid locomotion using pseudopods, and
ingestion of food by phagocytosis.
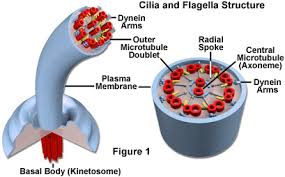
- Many types of cytoplasmic organelles are present, including membrane
organelles (like endoplasmic reticulum) and "9 + 2" arrangements of
microtubules. Mitochondria (and plastids in plant cells) contain
their own DNA.
Theory of endosymbiosis: Most biologists now believe that eucaryotic
cells originated when small, energy-producing procaryotic cells lived inside
larger cells and became mitochondria by intracellular symbiosis
(endosymbiosis). Plastids may have arisen the same way. Similar origins
for other cell parts have been proposed but are less widely accepted. Perhaps
host cells originally phagocytized the energy-producing mitochondria; then
natural selection favored those host cells that maintained the mitochondria
as an energy source instead of digesting them.
- Evidence for endosymbiosis comes from the fact that both mitochondria
and plastids have two membranes: the outer membrane resembles the
membranes of the eucaryotic host cell, but the inner one resembles
procaryotic cell membranes instead.
- Mitochondria and plastids possess their own DNA and are self-replicating.
- Bacteria are known whose metabolic abilities are similar to those of
the postulated host cell, while other bacteria have the enzymes of the
Krebs cycle and are thus comparable in ability to mitochondria.
REVIEW:
Study guide and vocabulary
|
