ADOLESCENCE:
- Physical maturation, puberty
- More sudden and dramatic for girls--
Reproductive system, incl. monthly cycles
- Menarche (onset of menstruation) usu. occurs around 100 lb (45 kg) weight
- Age has been declining historically (~age 18 in 1890s); younger in many African Americans
- Many girls anticipate and look forward to this
- Hastens privacy; emotional connections to other girls with similar experience
- As breasts develop-- more interest in appearance, attractiveness;
wanting boys to be interested in them
- In boys, more gradual, less to discuss (maybe shaving or growing a mustache)
- Growth spurt: Earlier in girls (girls taller than boys ~age 15) but lasts longer in boys
- Physical growth: larger appetite (protein, calcium needed); some nutritional problems emerge or get worse:
obesity, anorexia, bulimia
Anorexia
- Physical ability and sports skills increase
- More risk-taking, so more accidents, incl. death (autos, guns, suicide), also alcohol abuse, unwanted or unprotected sex
- Brain growth: More abilities but less inhibition-- more impulsive, risk-taking (esp. boys)
- Memory skills improve; also logical skills and problem-solving--
Better understanding of math, science, philosophy, politics
- Kohlberg and moral reasoning:
Preconventional
(based on punishment & reward)
| 1. Obey authority | | 2. Be nice; get rewards, not punishment
| Conventional
(based on social norms)
| 3. Do what others expect | | 4. Follow rules that maintain social order
| Postconventional
(based on moral codes)
| 5. Social contracts (when valid); ~Kant's "categorical imperative"
| | 6. Moral system based on abstract principles
|
- Criticism of Kohlberg: doesn't account for divided loyalties (to group vs principles),
esp. among adolescents: clubs, gangs, other group loyalties
- To promote moral reasoning:
- Discussion
- Religious groups and communities
- Choose your friends wisely-- Parents should ask about friends and
encourage those who are good influences while discouraging those who are bad influences.
- Rites of passage (transitions to more adult roles):
- Menarche ceremonies in a few societies (Apache)
- Bar/Bat Mizvah
- "Work papers" for legal employment
- "Quinzeana" in Latin America
- "Sweet sixteen" or "Coming out"
- High School prom
- Graduation
- Driver's license
- Drinking age
- Voting age
TEENS BECOMING ADULTS:
- Teenage identity and self-esteem:
- General characteristics:
- Wants adult privileges (own initiative), but still wants parental support (as child)
- Internal conflict (turbulence) and self-doubt; "Storm and Stress" ("Sturm und Drang")
(This is minimized by loving family support)
- "Adolescent egocentrism": feels empowered, oblivious to negative aspects (dangers) and long-range prospects
- Feels invulnerable, invincible; willing to take risks
(Common risks: drinking, smoking, drugs, unsafe sex, unsafe driving, extreme sports)
- Personal fable: "I'm the only one who has ever experienced this or felt this way"
- Imaginary audience: "They're all watching me", "Hey, look at me!"
Girls as "beautiful princess"; boys "showing off", "death-defying" stunts
Boys as "rock stars" or star athletes; girls as the preferred choices of rock stars or star athletes
- Self-esteem: affected by parents, peers, social or ethnic identity;
Girls often more sensitive; low self-esteem may lead to depression and suicide
- Ethnic identity (important for many teens but not all): connecting with traditions
- Parenting of teenagers is hard:
Demands and needs keep changing from dependent to independent and back.
Often rebellious: can be harmless (clothing choices, music)
or harmful (drugs, alcohol, unsafe sex, etc.)
Authoritarian parents often lose control at this time (esp. if teen moves away)
- Building an adult identity-- Four approaches (statuses):
- Diffusion-- plays games and puts off decisions
- Foreclosure-- conforms to long-standing parent wishes and expectations
- Moratorium-- changes mind frequently among alternatives
- Achievement-- Having explored alternatives, "I found what I really want, what I'm good at"
- Romance and sexuality:
- Dating and romance: begins earlier if family ties are weak; varies ethnically, also individually
Girls are often socially more mature; boys are awkward at first
Couple alone (or "double-dating") vs "hanging out" in a large group (not paired)
- Sexual behavior varies:
- Boys: seek and report positive enjoyment (seldom any regrets, no long-range plans)
- Girls: seek love, intimacy, long-range commitment; often disappointed or conflicted
- Alcohol use and poverty both predispose to earlier sexuality
- Good grades, good social adjustment predispose to later sexuality
- Teen pregnancy (usually improper use or no use of birth control): multiple bad outcomes
- Date rape, dating violence: All outcomes bad
- Same-sex (homosexual) attraction:
Reasons and consequences poorly understood. A few differences in brain structure
have been reported, but it is unclear if these are the causes or the consequences.
- Seeking employment
- Often starts with casual part-time or summer work (easy entry if family runs a restaurant or farm)
- Career choice-- Donald and Super-- 3 phases:
- 1. Crystallization ("What am I good at?)
- 2. Specification (seeks training)
- 3. Implementation (get a job, or decide to change jobs)
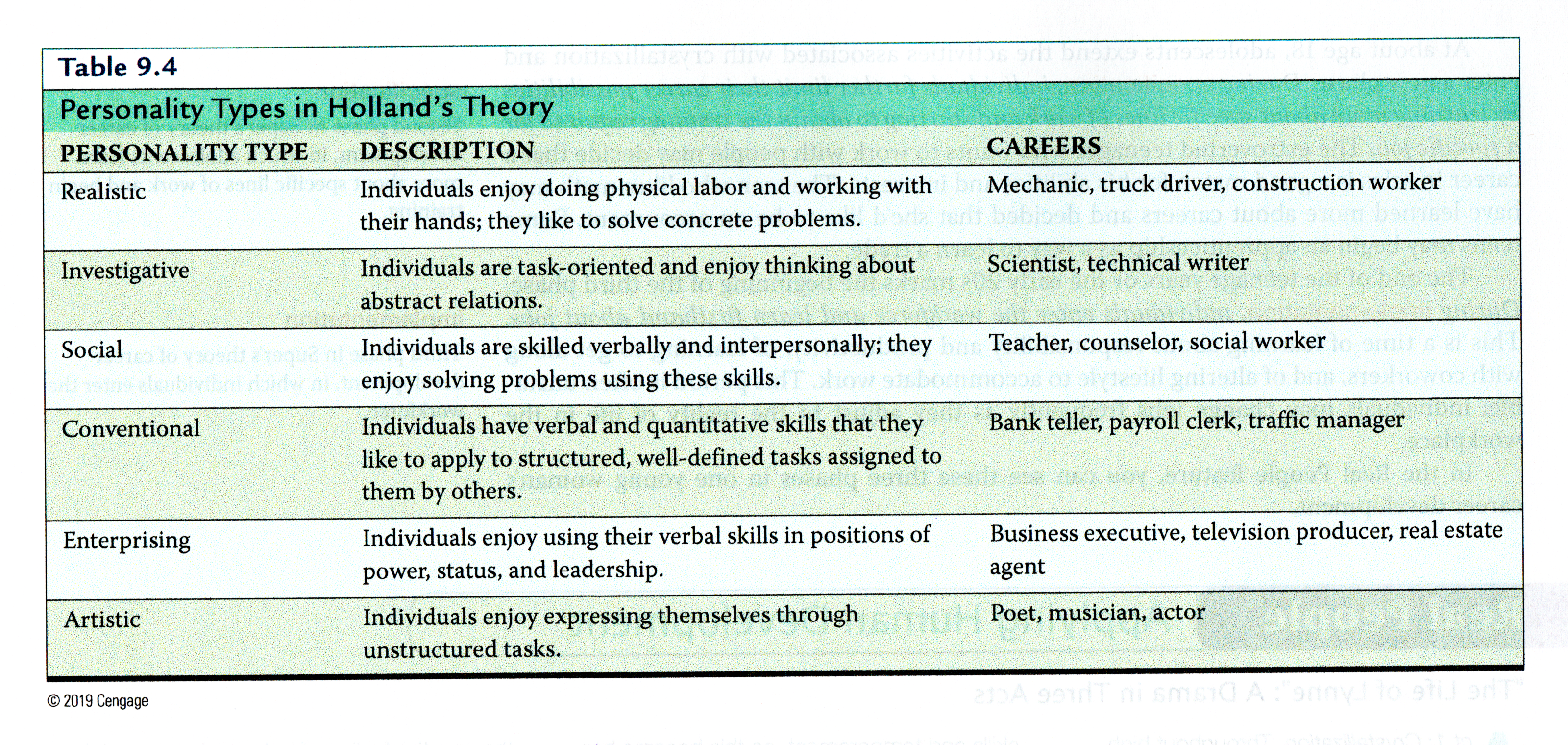
- Personality-type career theory (John Holland, see table page 304 top):
"Work is fulfilling when it fits my personality"
- Social-cognitive career theory-- Repeated (iterative):
Interests, goals ——> Try it out ——>
Success/failure ——> Beliefs about self & outcome⤵
🡑—— New interests/goals <————————————————(repeat)———————⤶
- Some career choices based on "What I want to avoid" (gravitate to what I see that avoids it)
- Part-time work (OK if only occasional or summer, otherwise interferes with school)
Often long hours or inconvenient times-- schoolwork suffers
Frequent behavioral and mental health problems, also sleep problems, poor health outcomes
Some immaturity at spending money quickly for self-gratification (not saving for future)-- this varies
- Teen problems:
- Alcohol: leads to bad coping skills, traffic accidents, sometimes date rape
- Smoking and vaping: often by succumbing to peer pressure; also leads to bad coping sklills, poor lung health (incl. cancer, bronchitis, emphysema)
- Depression and suicide-- Major cause of death among teens!
- Girls: casual sex as an outlet, or as imagined control of boys
- Delinquency, truancy, crime
- Risky and destructive behaviors:
- Alcohol
- Smoking (incl. vaping)
- Drugs
| - Unsafe sex
- Unsafe driving
- Extreme sports
|
|