- LAYERS and FOLDS:
When layered rocks are not horizontal, their angle of incline is called a dip.
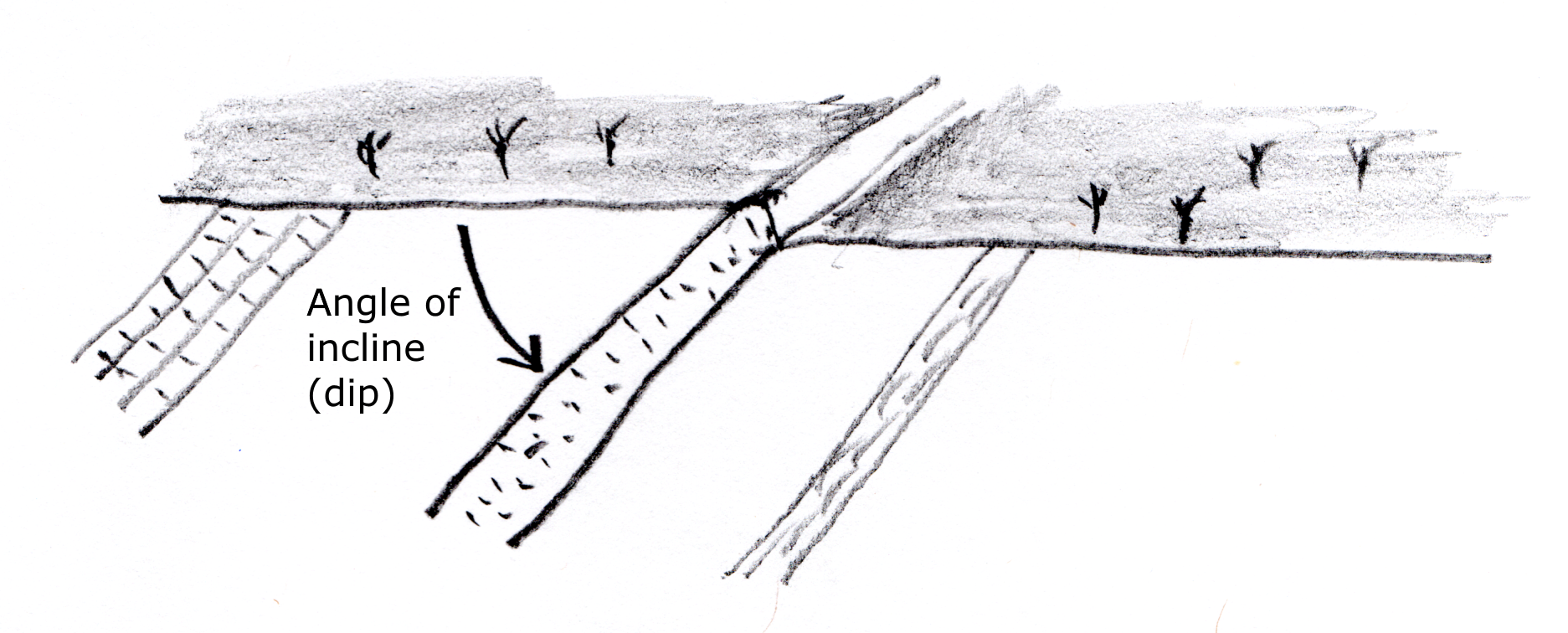
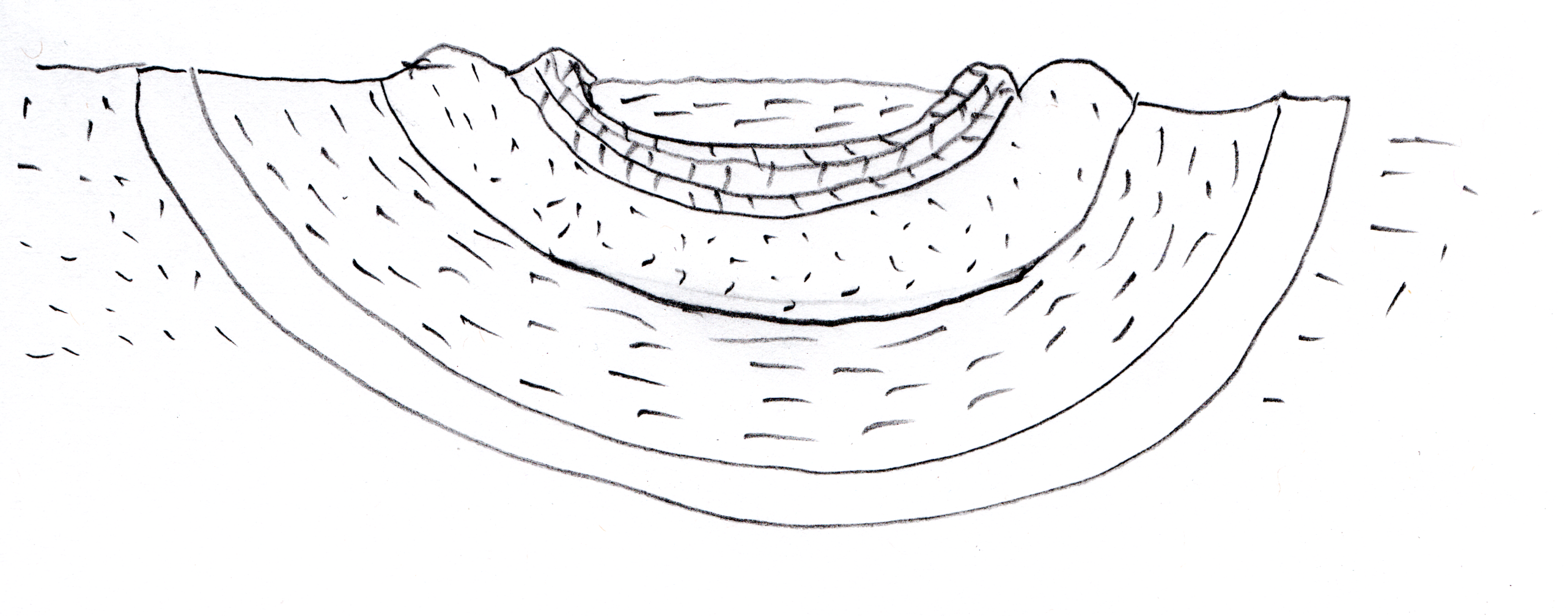
When rock layers are folded so that the inclines
(or dips) run together, it is called a syncline
(from Greek, 'syn'=together, 'cline'=incline or slope).
|
| 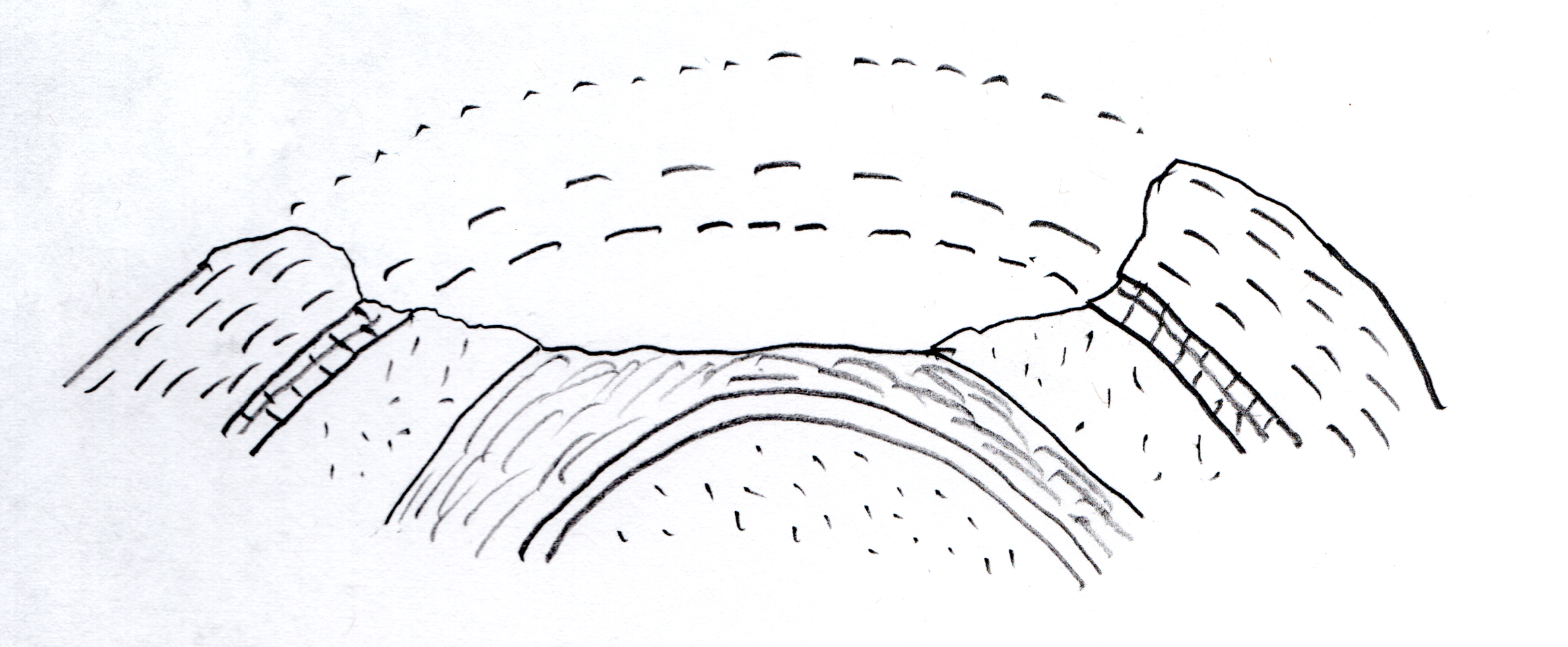
Rock layers folded in the opposite direction make
an anticline; the layers appear to lean against
one another (Greek 'anti'=against).
|
- FAULTS:
Faults are cracks (or fracture planes) within the Earth's crust along which movement takes place.
Movement along a fault causes Earthquakes (Topic 48).
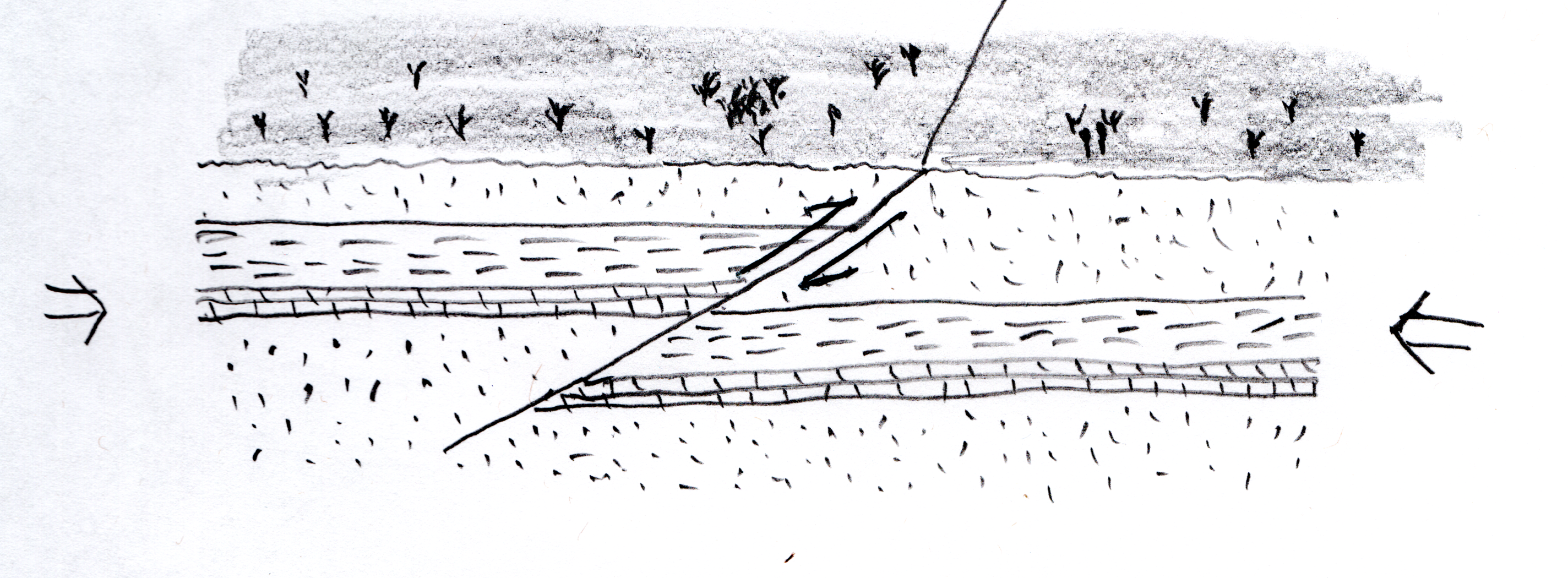
Compression faults are generally at a low angle (typically 30o) to the direction of maximum pressure.
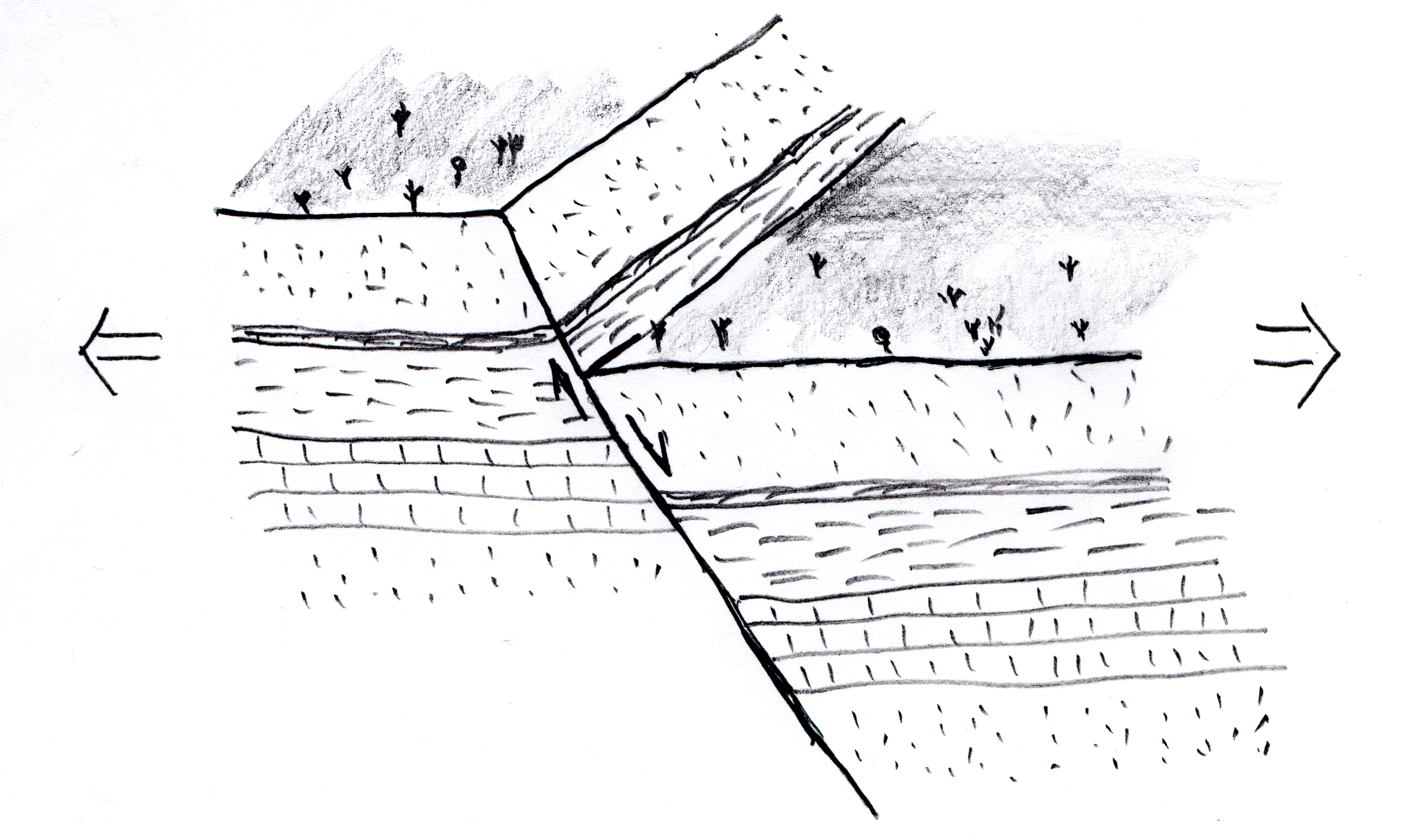
Tension faults are generally at a high angle (typically 60o) to the axis of maximum tension (where the Earth's crust is pulling apart).
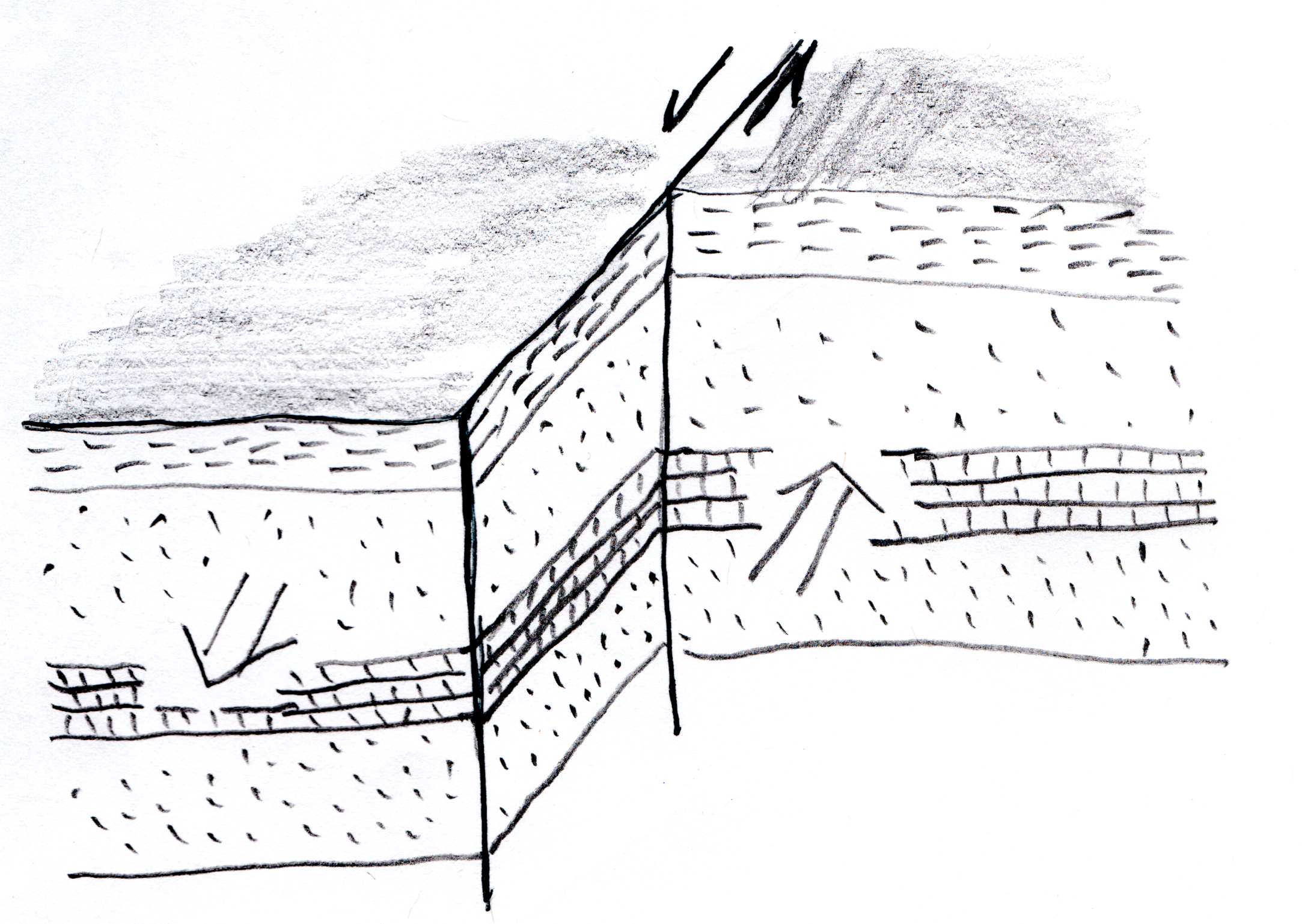
Strike-slip faults are faults in which the major movement is horizontal, usually along a vertical or high-angle fault plane.
|