In order to show that you studied this lab carefully, please email me at
eminkoff
 bates.edu bates.edu
with your NAME and the answers to these 5 questions:
(No need to repeat the questions; the answers alone will do.)
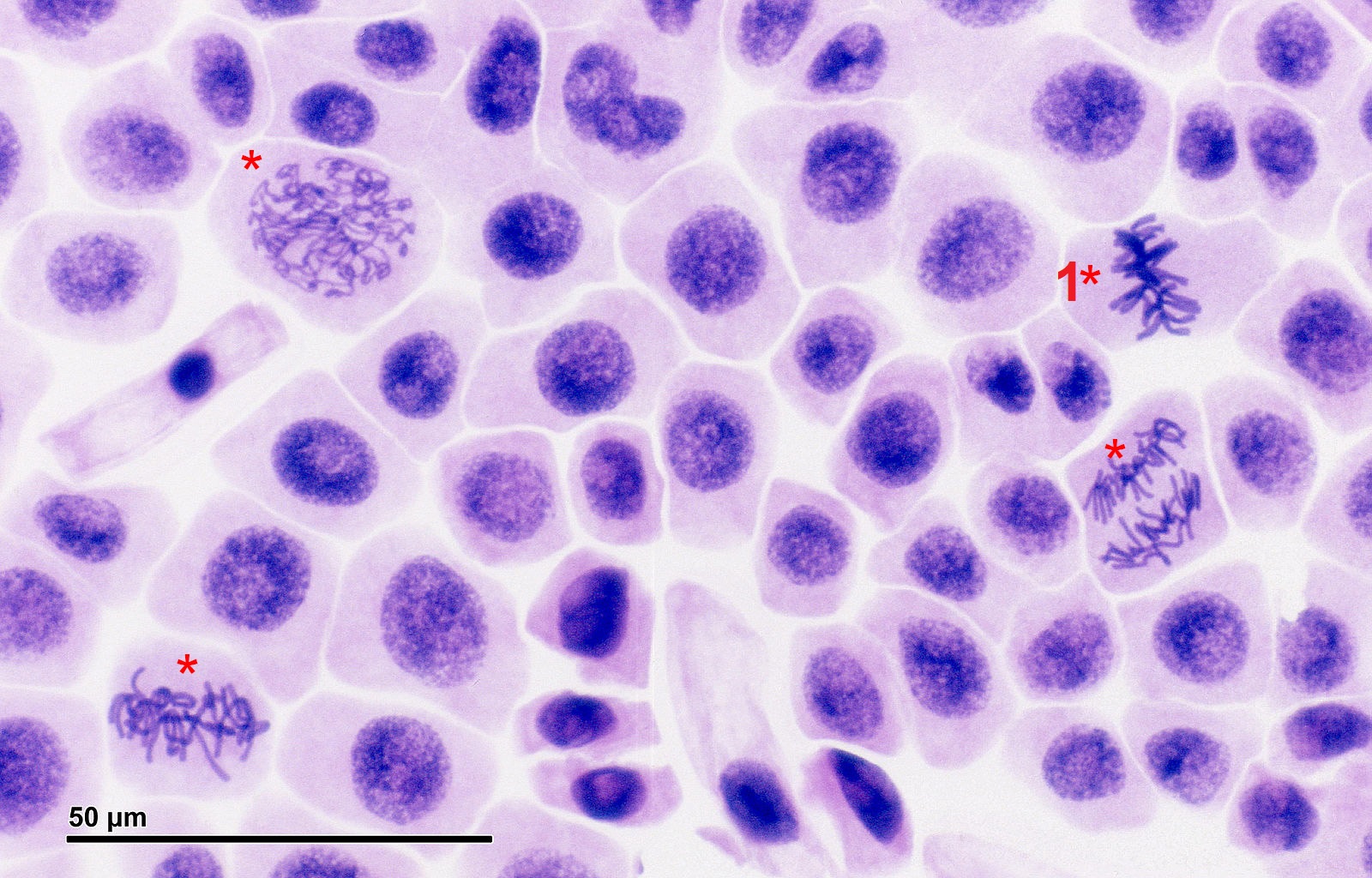
- 1. Cell #1 in the photo above is in what phase of mitosis?
- 2. What important structure breaks down and disappears during prophase of mitosis?
- 3. Fruit flies (Drosophila) have a diploid chromosome number of 2N=8 (i.e., four pairs).
How many centromeres
could a scientist hope to see during anaphase I of meiosis?
(Study the diagrams of meiosis carefully.)
- 4. A plant is heterozygous for a gene determining flower color. At what phase
of meiosis, and in which meiotic division, do the two alleles separate? (Your
possible choices are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, or telophase, of division I,
or prophase, metaphase, anaphase, or telophase of division II.)
- 5. Genes located on the same pair of chromosomes do not obey Mendel's law of independent assortment.
In fruit flies (2N=8), a scientist studies several different genes that all assort independently, meaning that no two of them are on the same chromosome pair.
What is the maximum number of genes that she could be studying?
(It's a deceptively simple question: Two genes on the SAME chromosome
pair are "linked," meaning that they do not assort independently. Two genes must be on DIFFERENT
chromosome pairs in order to assort independently. So, what is the maximum number of genes that can
each be on a different chromosome pair than all the others?
This was the reasoning that led Walter Sutton to predict 'linkage' of some genes in 1902.)
|
