Biological Concepts — Lab 11 online
ANIMAL DIVERSITY part I:
Non-coelomates and Protostomes
|
Instructions: Study all the visual information in this online lab, plus the accompanying explanations. Be prepared to answer a few "check-in" questions to show that you were paying attention. YOU ALSO SHOULD REVIEW pages 183-200 in the text, as well as THIS CLASSIFICATION, for this lab and the next. |
Phylum Porifera (sponges)
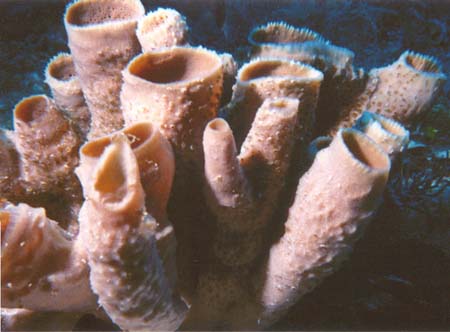 sponges in a colony  Grantia (class Calcarea) |  Venus flower basket Euplectella (class Hyalospongea =Hexactinellida) 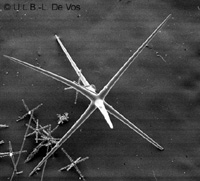 spicules of a glass sponge (class Hyalospongea)  bath sponge Spongea (class Demospongea) |
Phylum Cnidaria
Class Hydrozoa 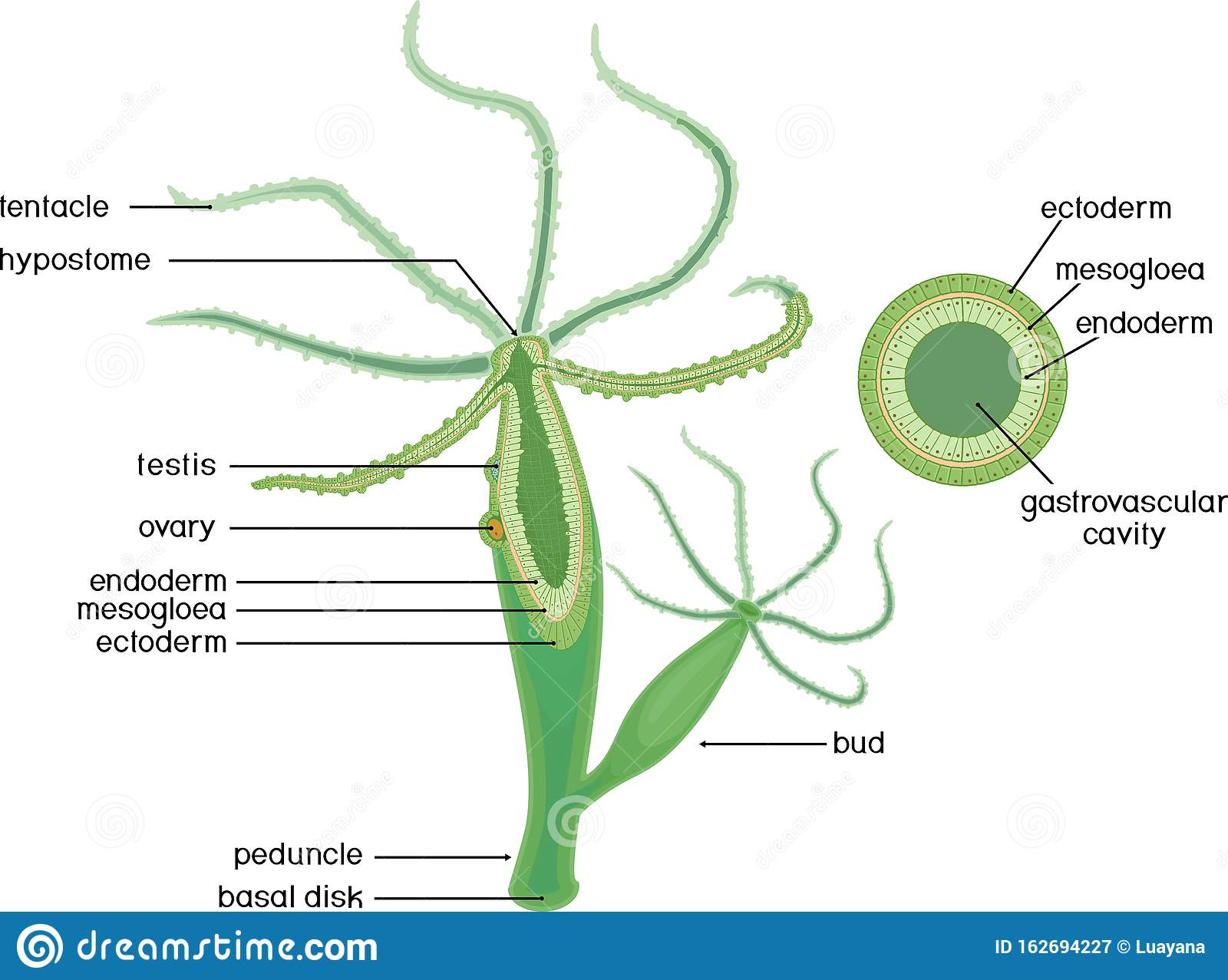 Hydra |
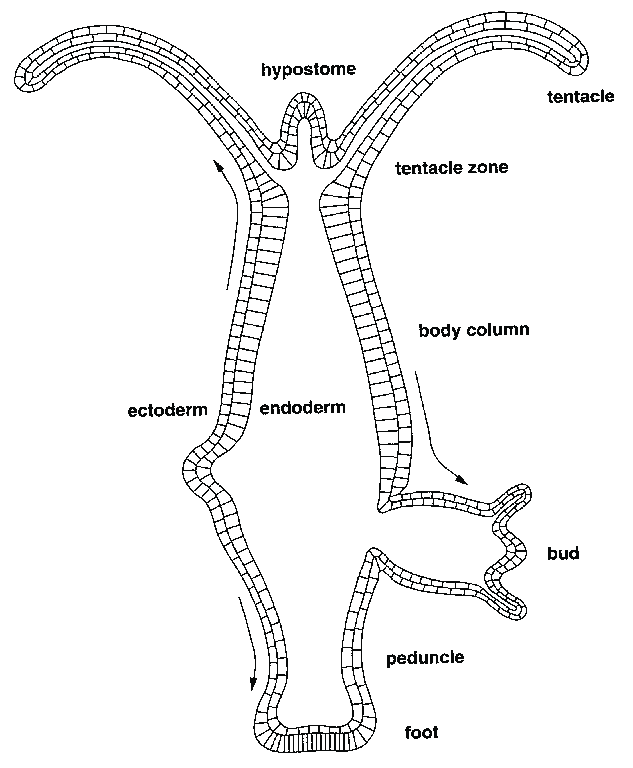
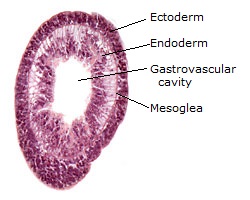 Hydra (details) |
 Obelia: feeding individuals in a colony . |
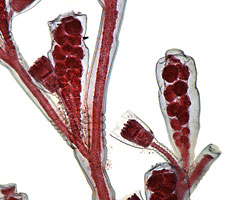 Obelia: reproductive members of a colony |
Class Scyphozoa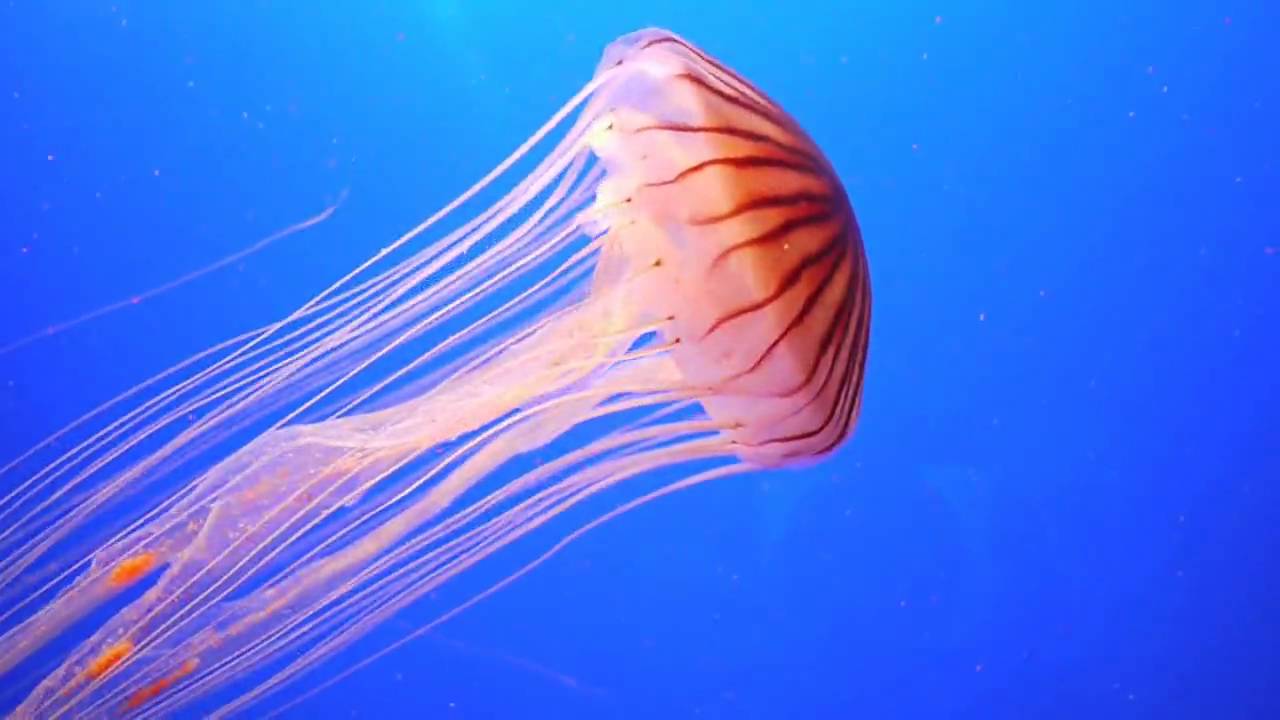   |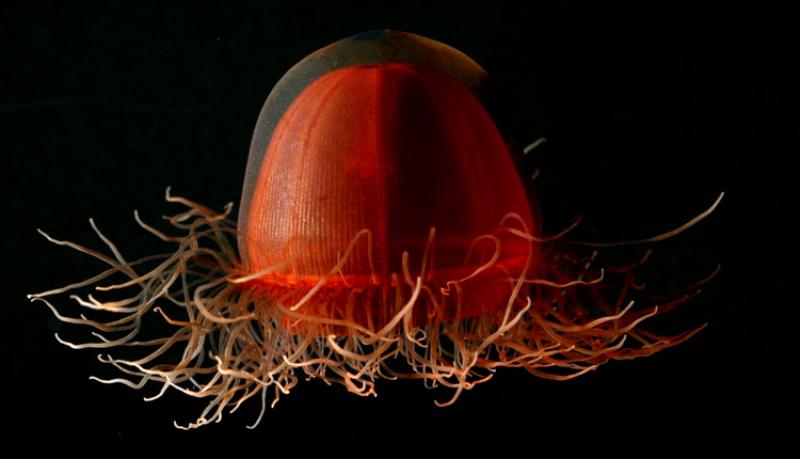  Crossota  |
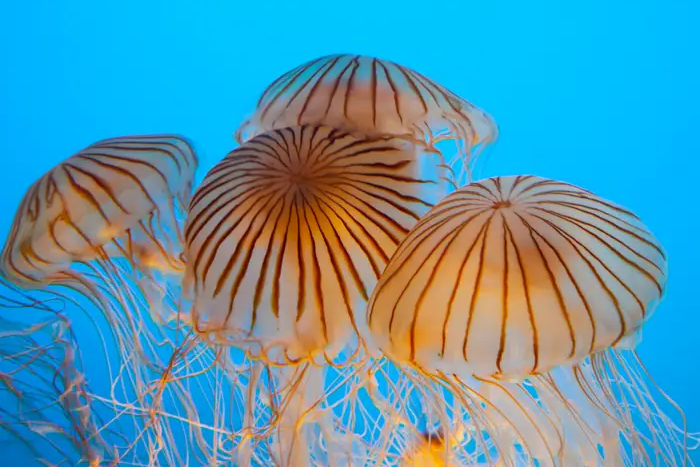 | |
Class Anthozoa  Sea anemone (Actinia)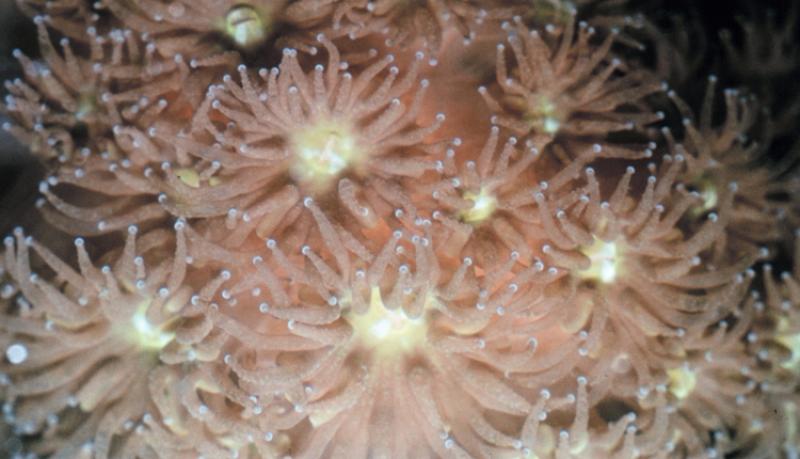  coral polyps  coral: skeleton of a small colony  detail of coral skeleton |
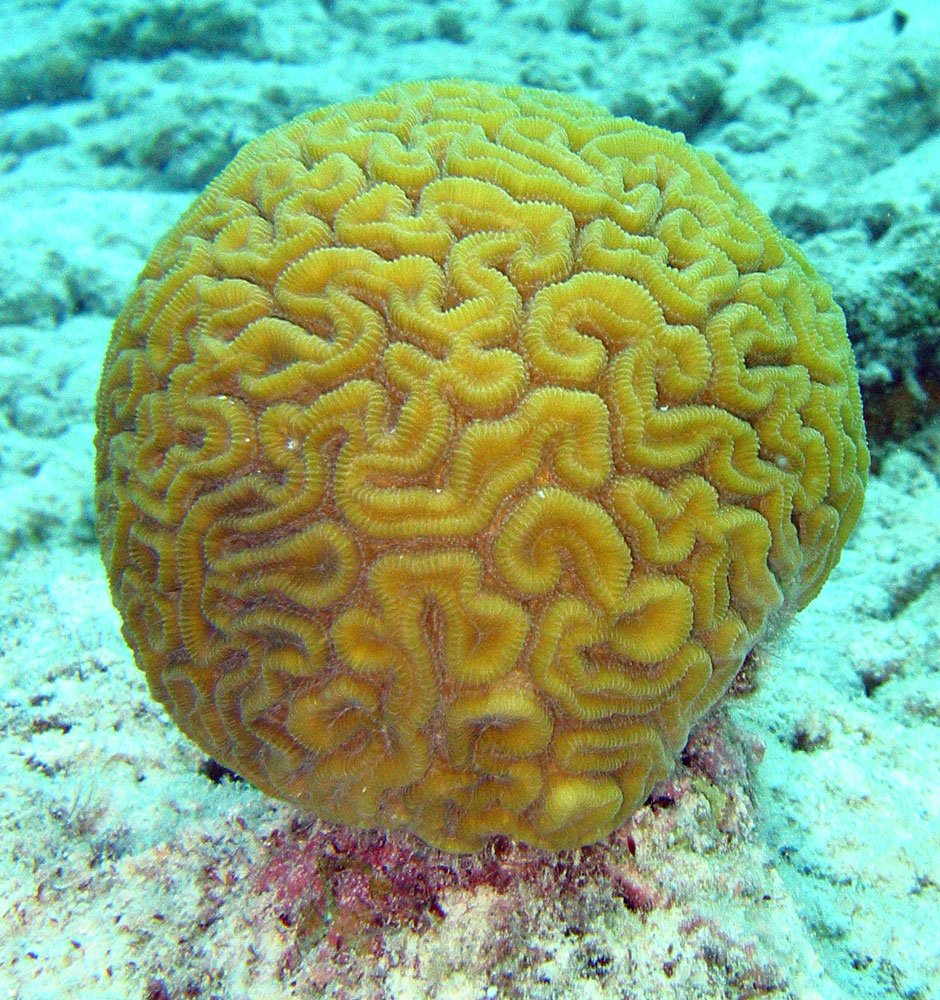 Stony coral (Diploria) 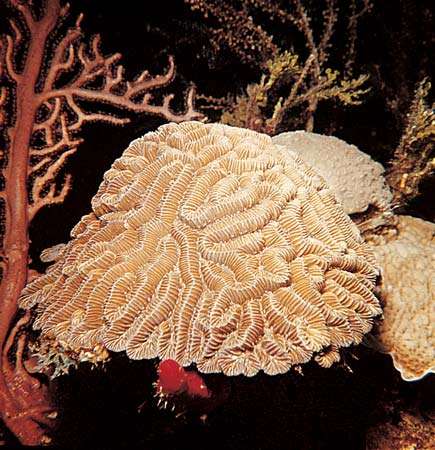 Stony coral (Diploria)  Staghorn coral (Acropora)  Sea fan (Gorgonia), supporting a diverse local ecosystem |
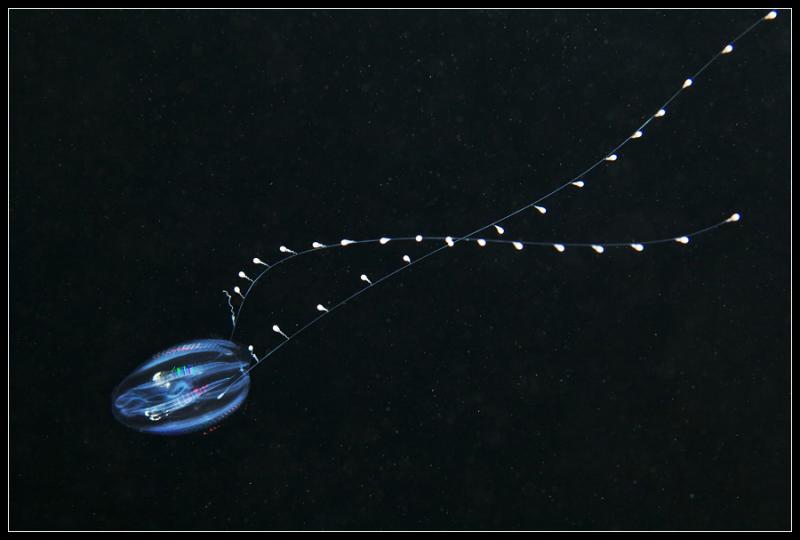 Dryodora |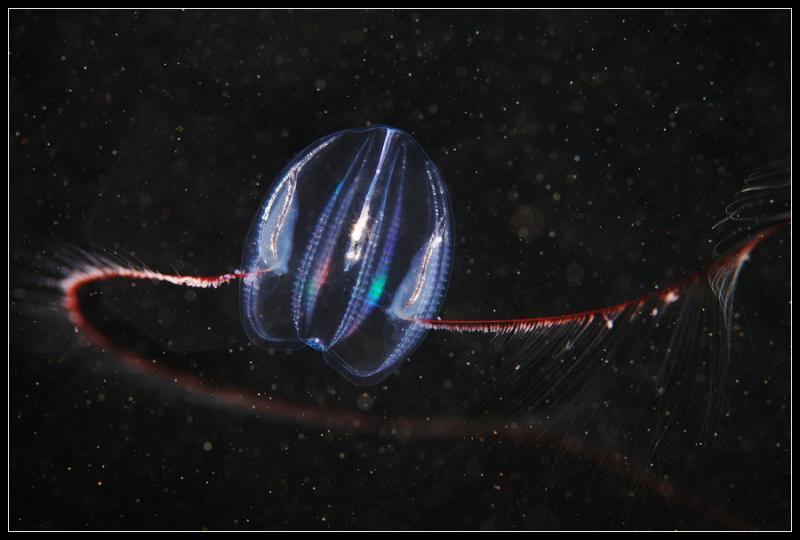  Mertensia |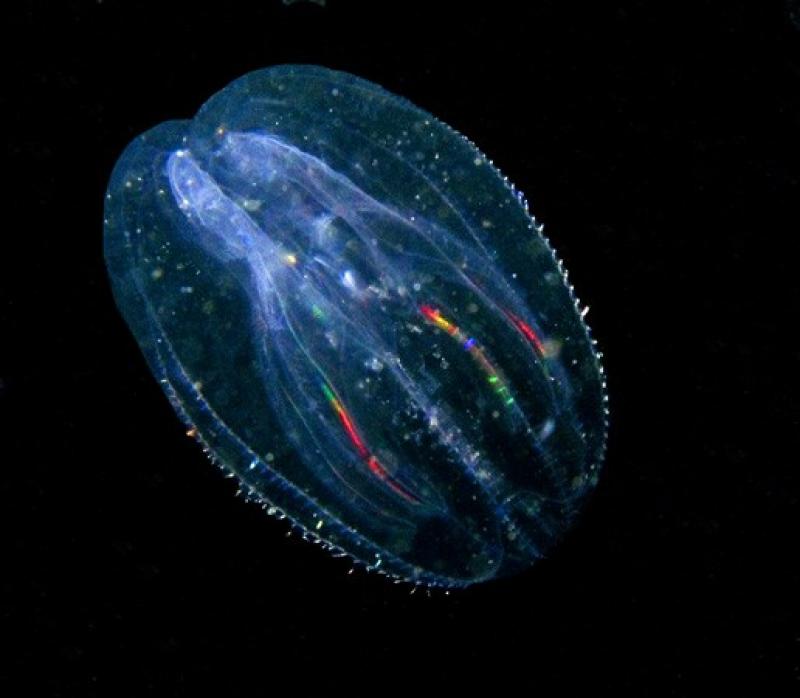  Mnemiopsis |
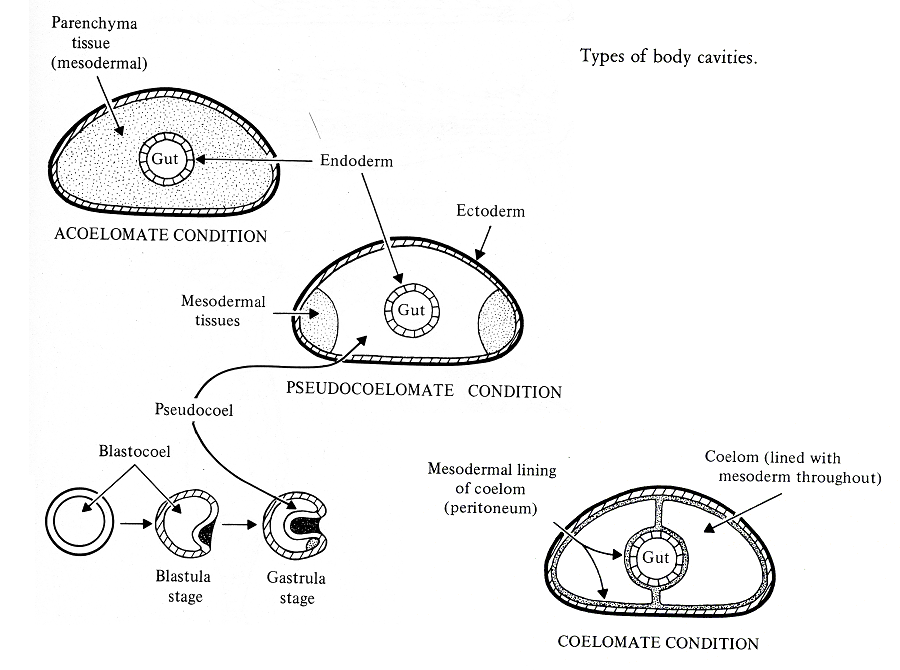
Evolution of body cavities
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Class Turbellaria 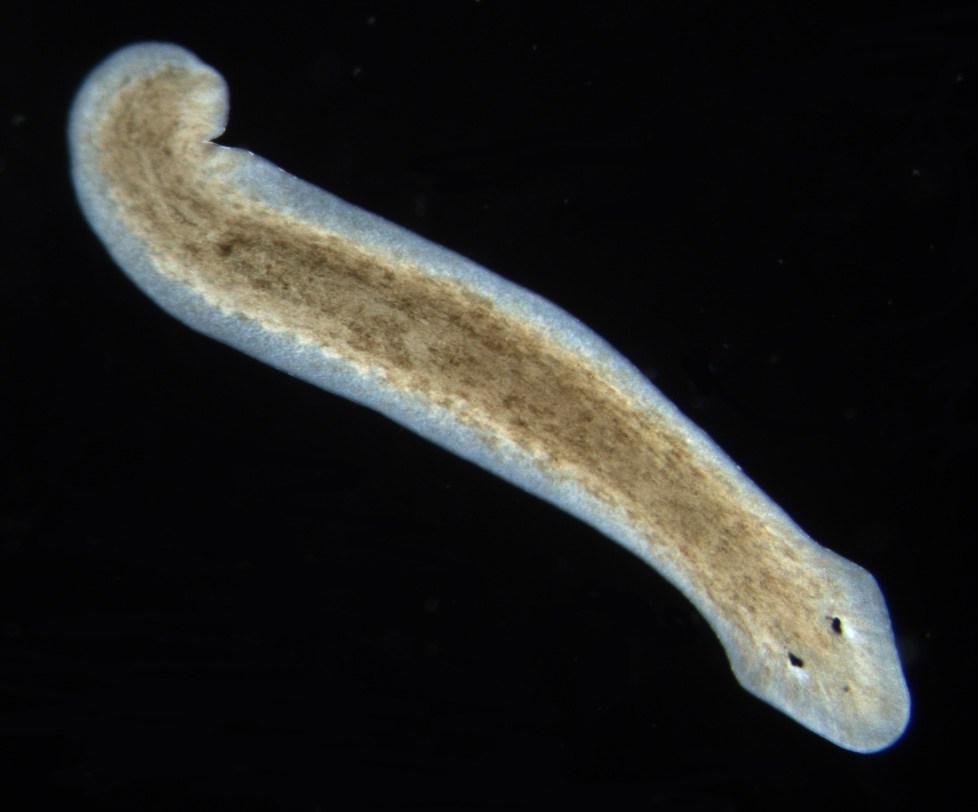 |  | 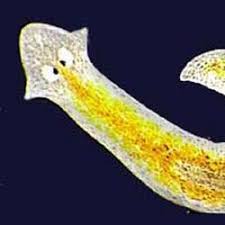 |
Class Trematoda (flukes) 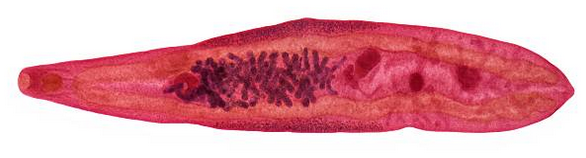 Chinese liver fluke (Clonorchis) | 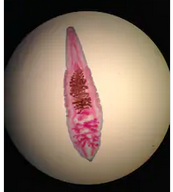 | 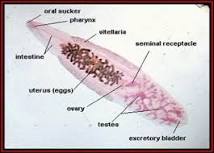 |
Class Cestoda (tapeworms) 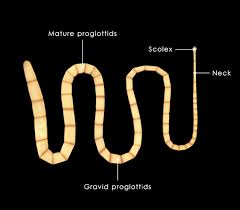 |  | 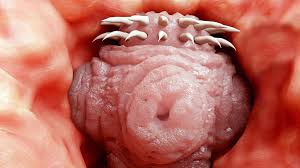 Scolex (head) of a tapeworm |
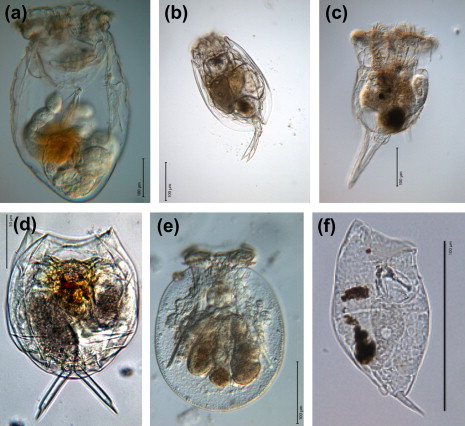 |  | 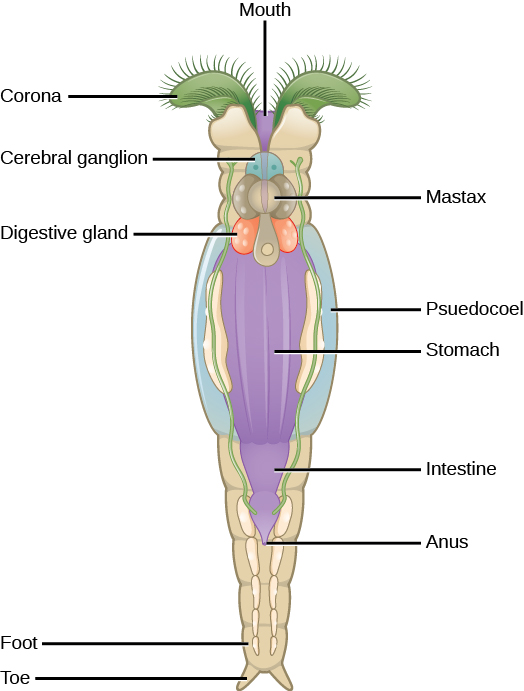 |
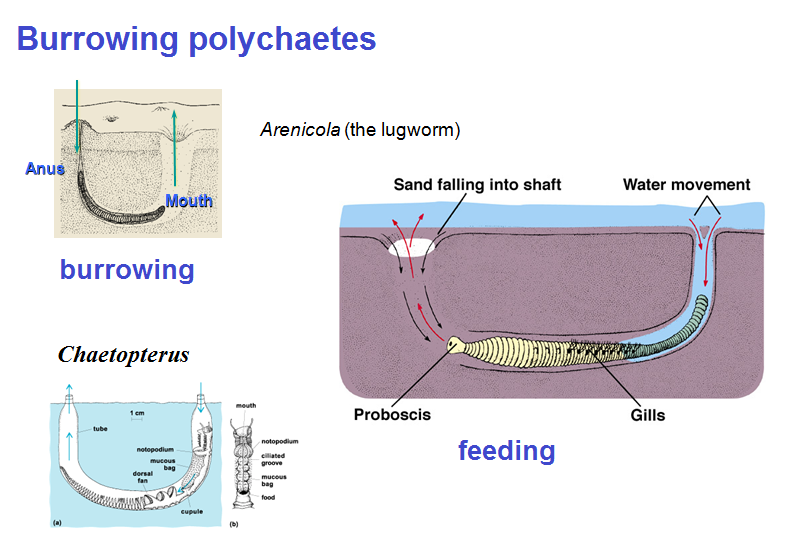
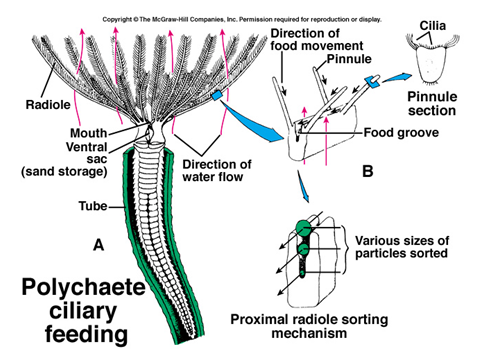
Phylum Annelida (segmented worms) 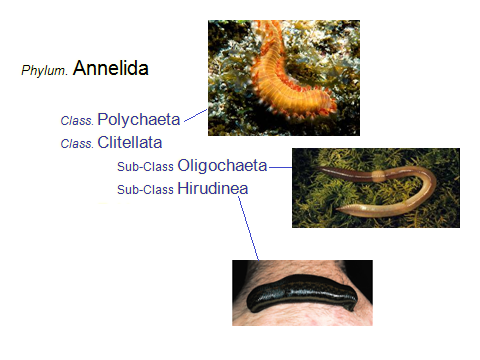 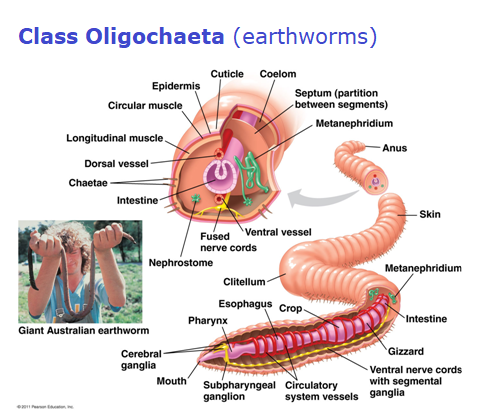 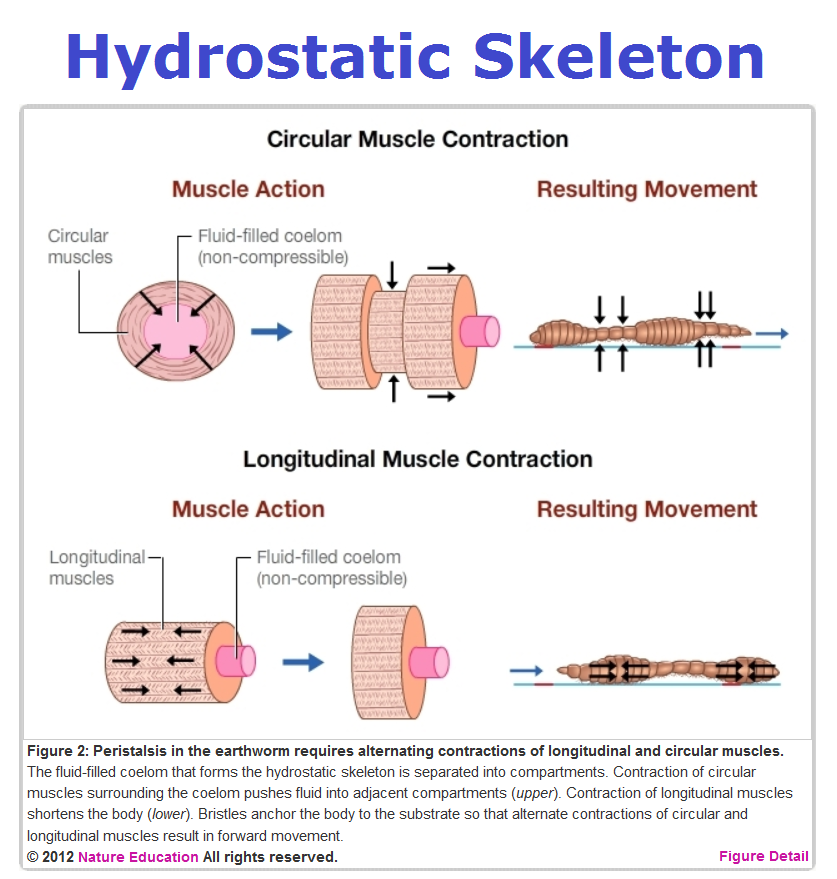 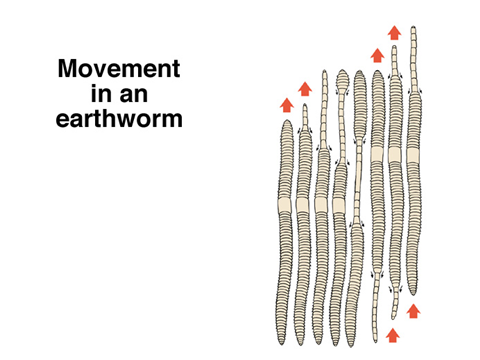  
   ECDYSOZOA (Animals that molt)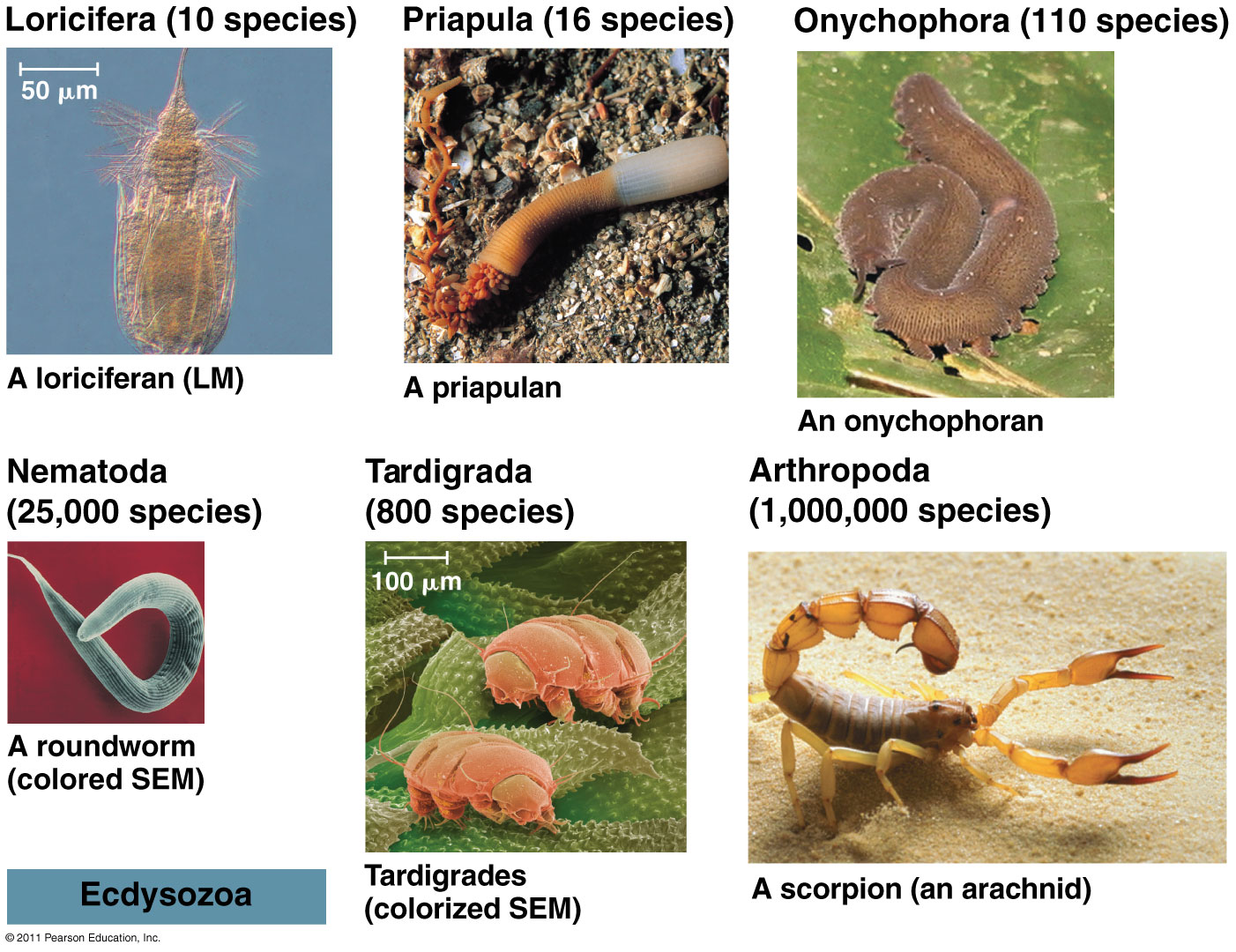 
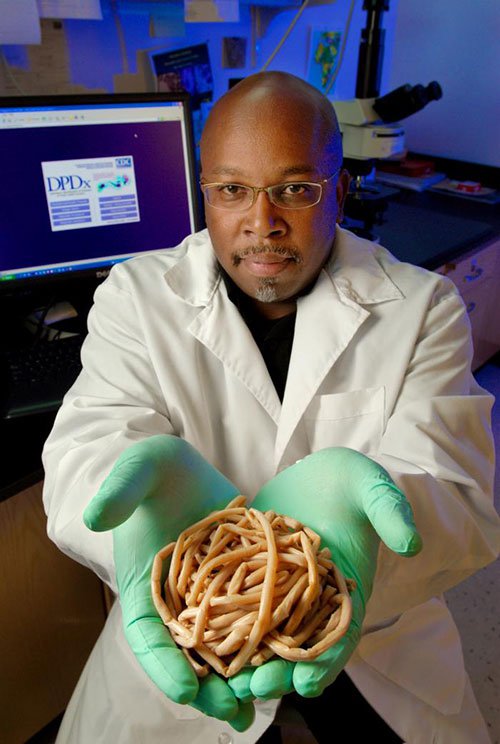
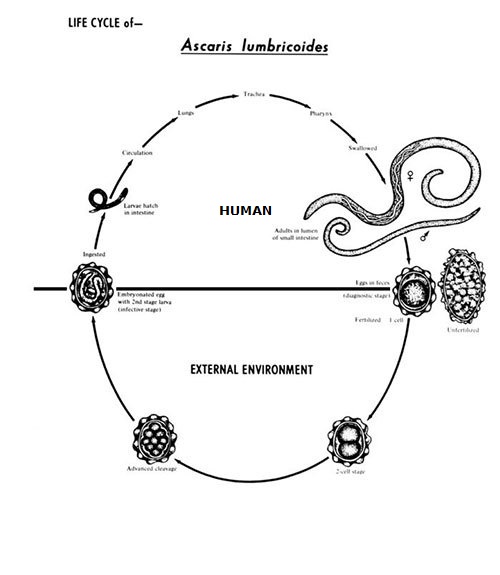
Phylum NEMATODA (roundworms): 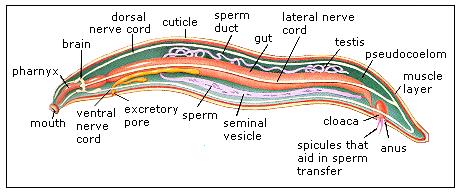

Phylum NEMATOMORPHA (horsehair worms):
Phylum TARDIGRADA ("water bears" or tardigrades):   
 CLICK FOR TARDIGRADE VIDEO Phylum ONYCHOPHORA ("velvet worms"):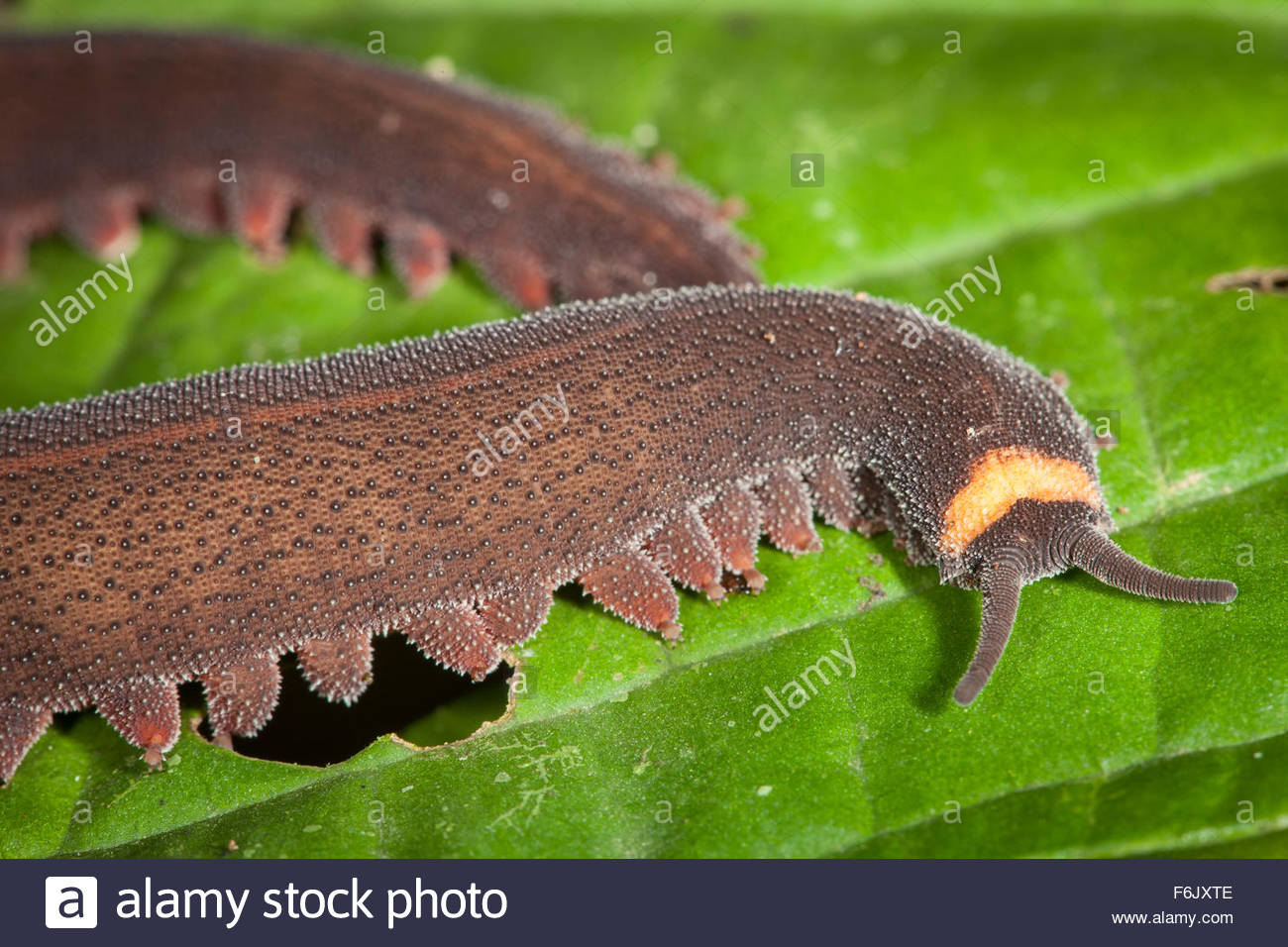   
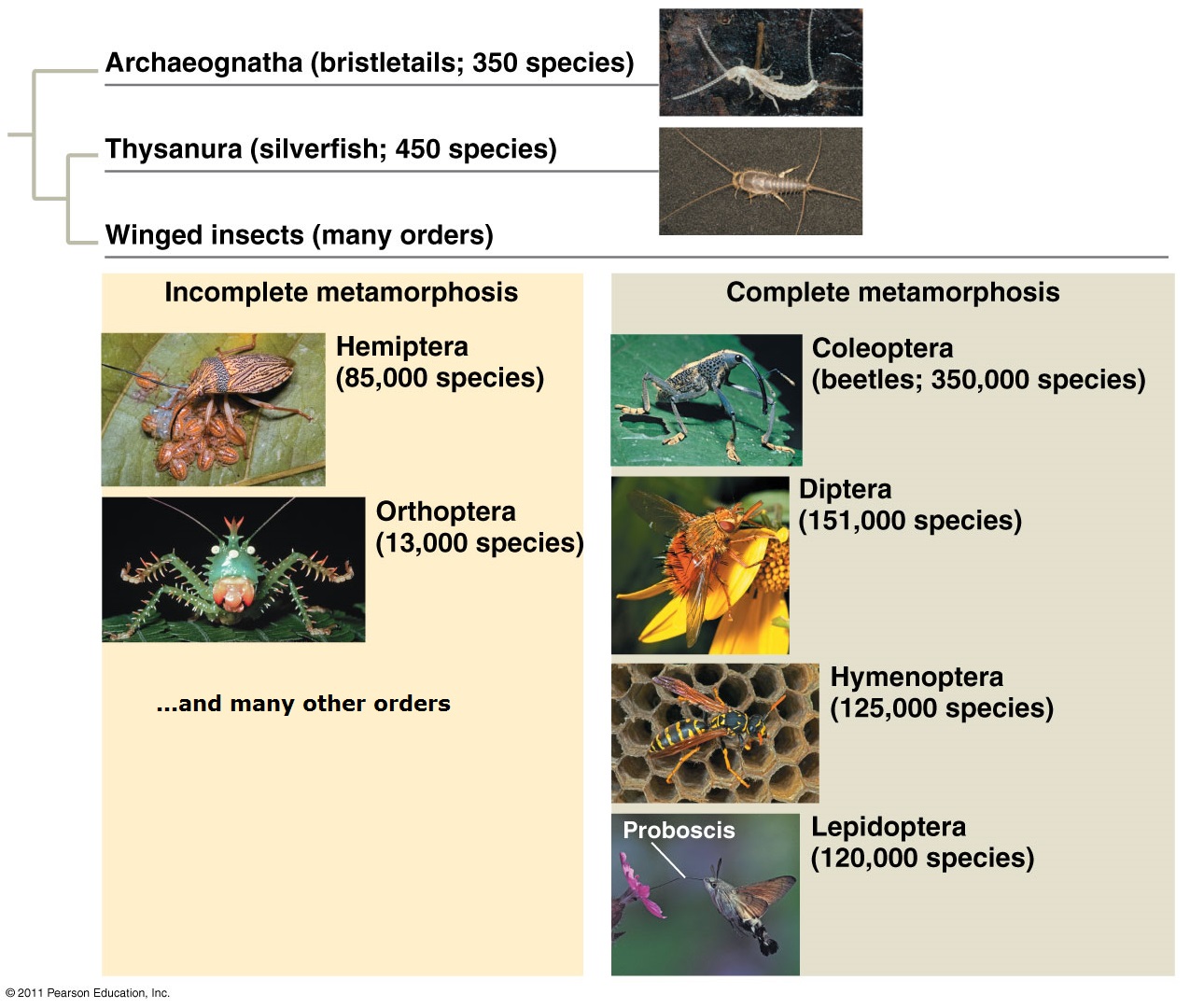
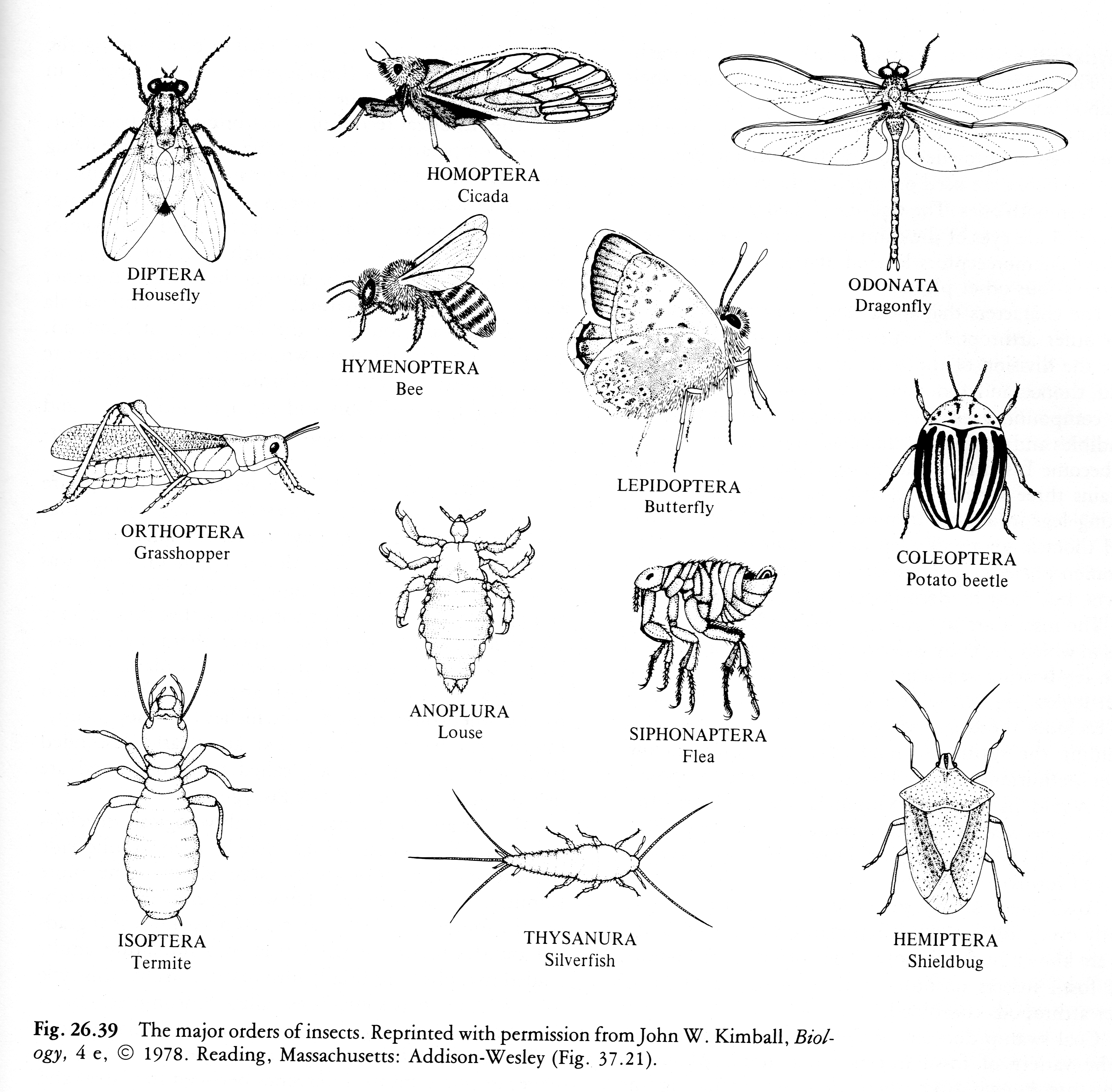
 CLICK FOR ONYCHOPHORA: VELVET WORM VIDEO Phylum ARTHROPODA (animals with jointed legs): Subphylum or Class Trilobita: (extinct trilobites) 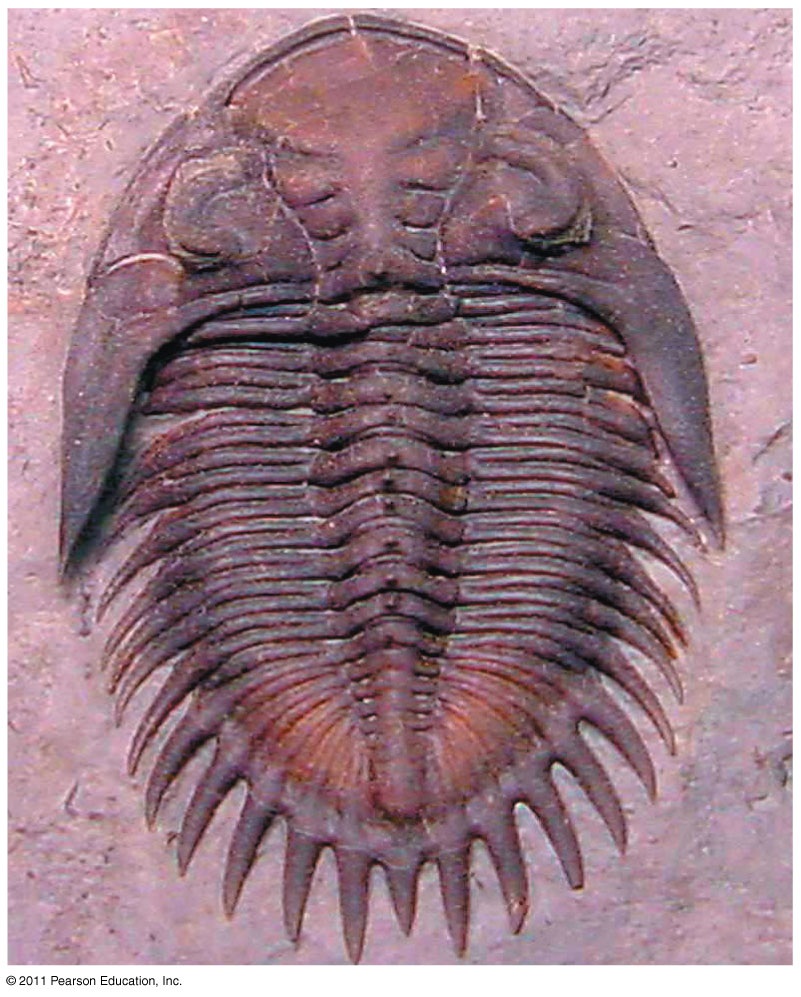 Subphylum or Class Crustacea: 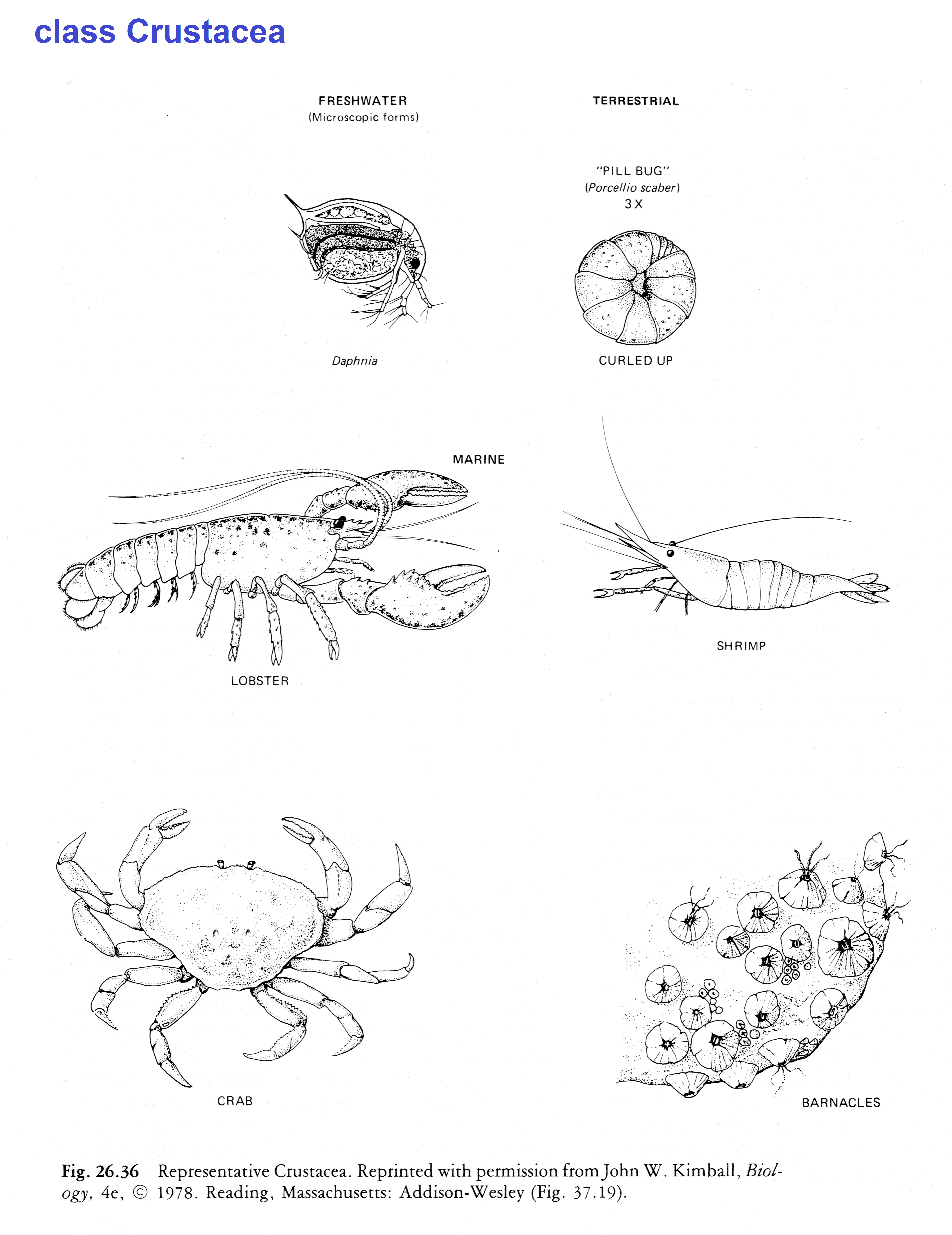 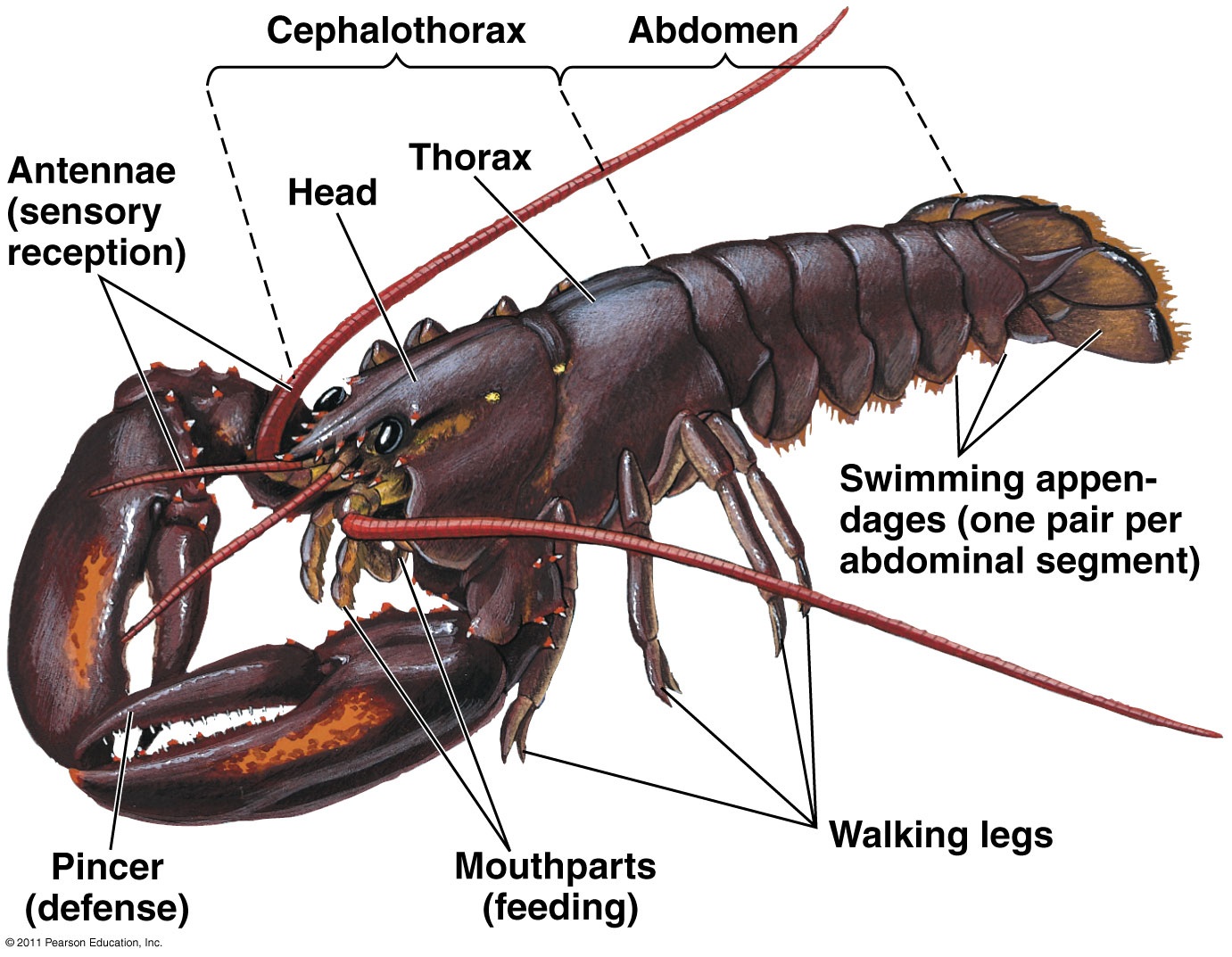 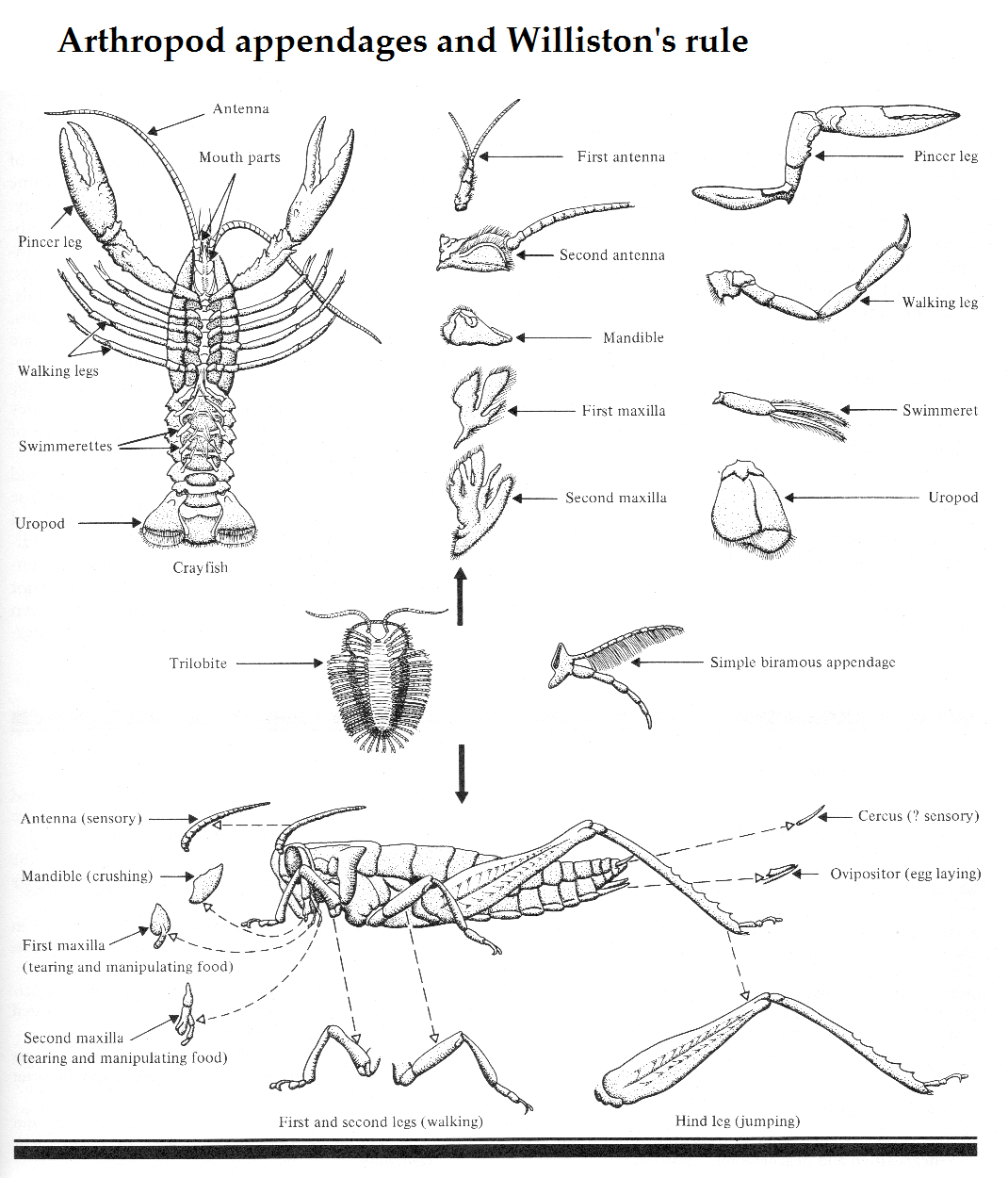 Subphylum Chelicerata: 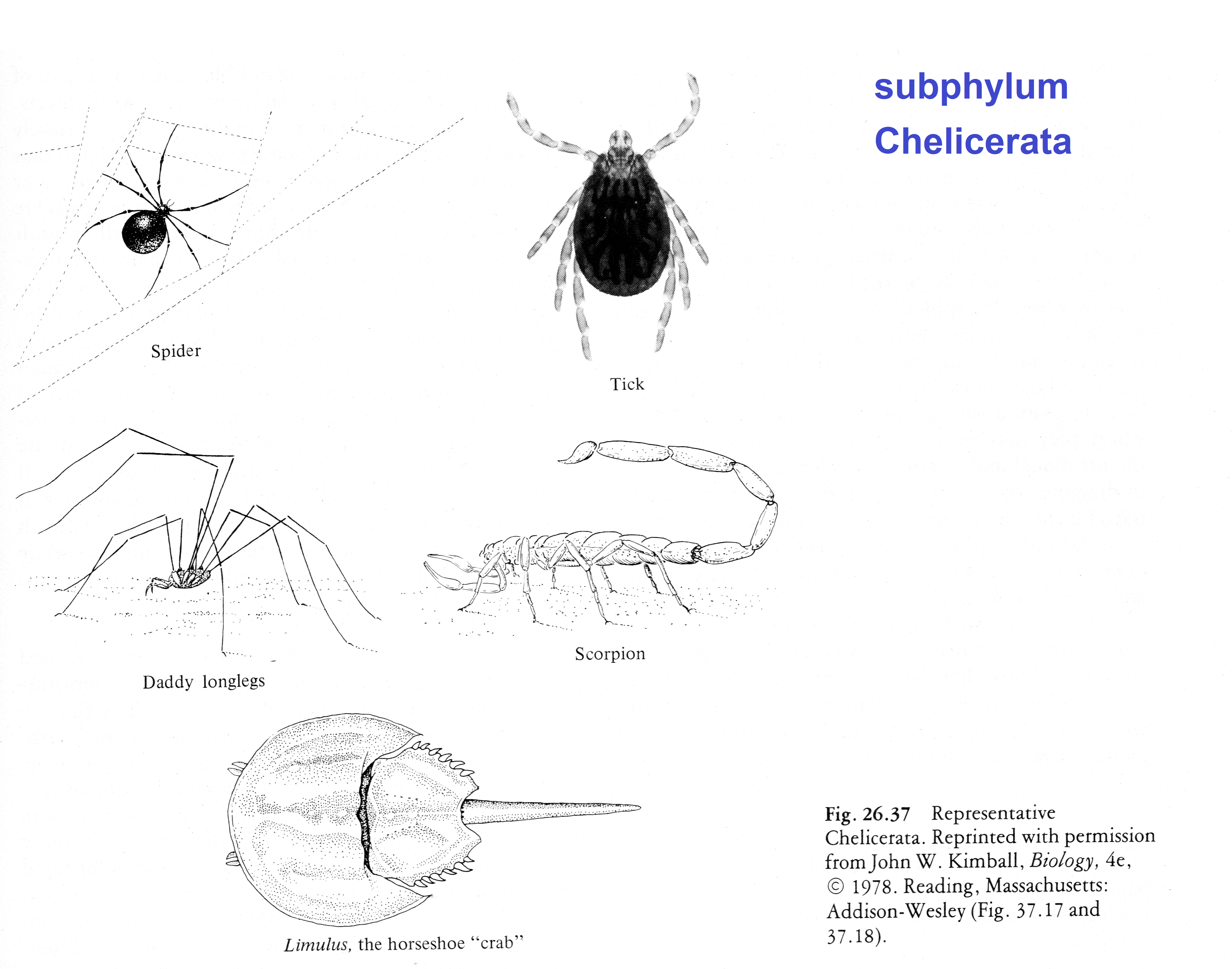 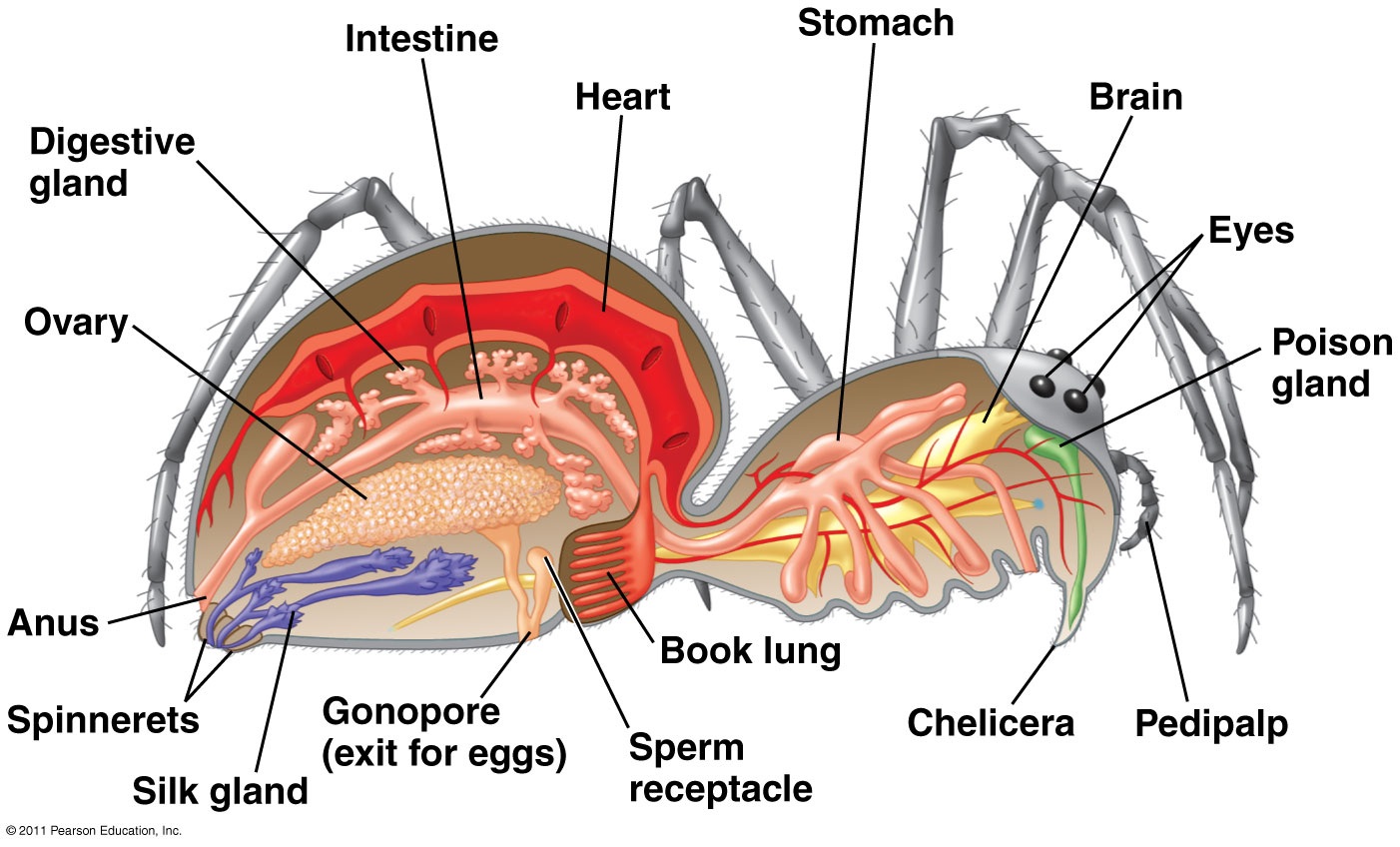 Anatomy of a spider Subphylum Uniramia — myriapods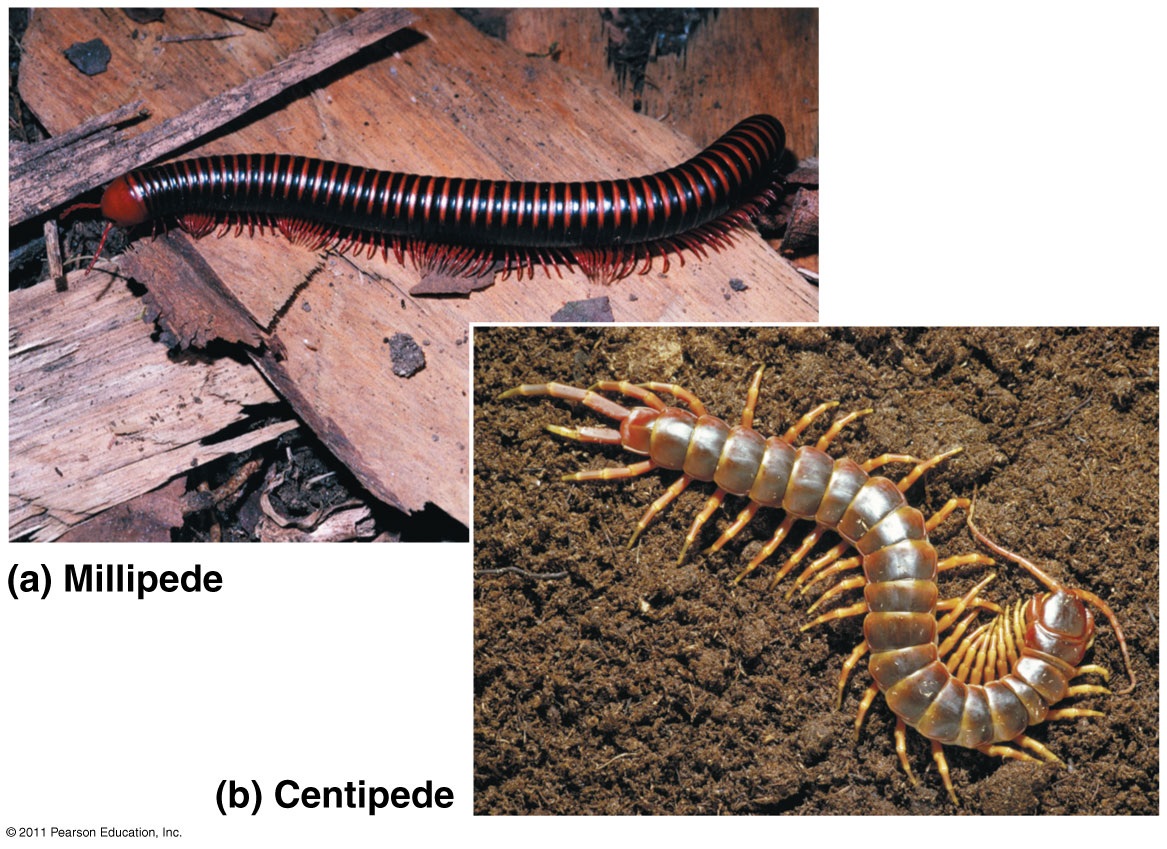 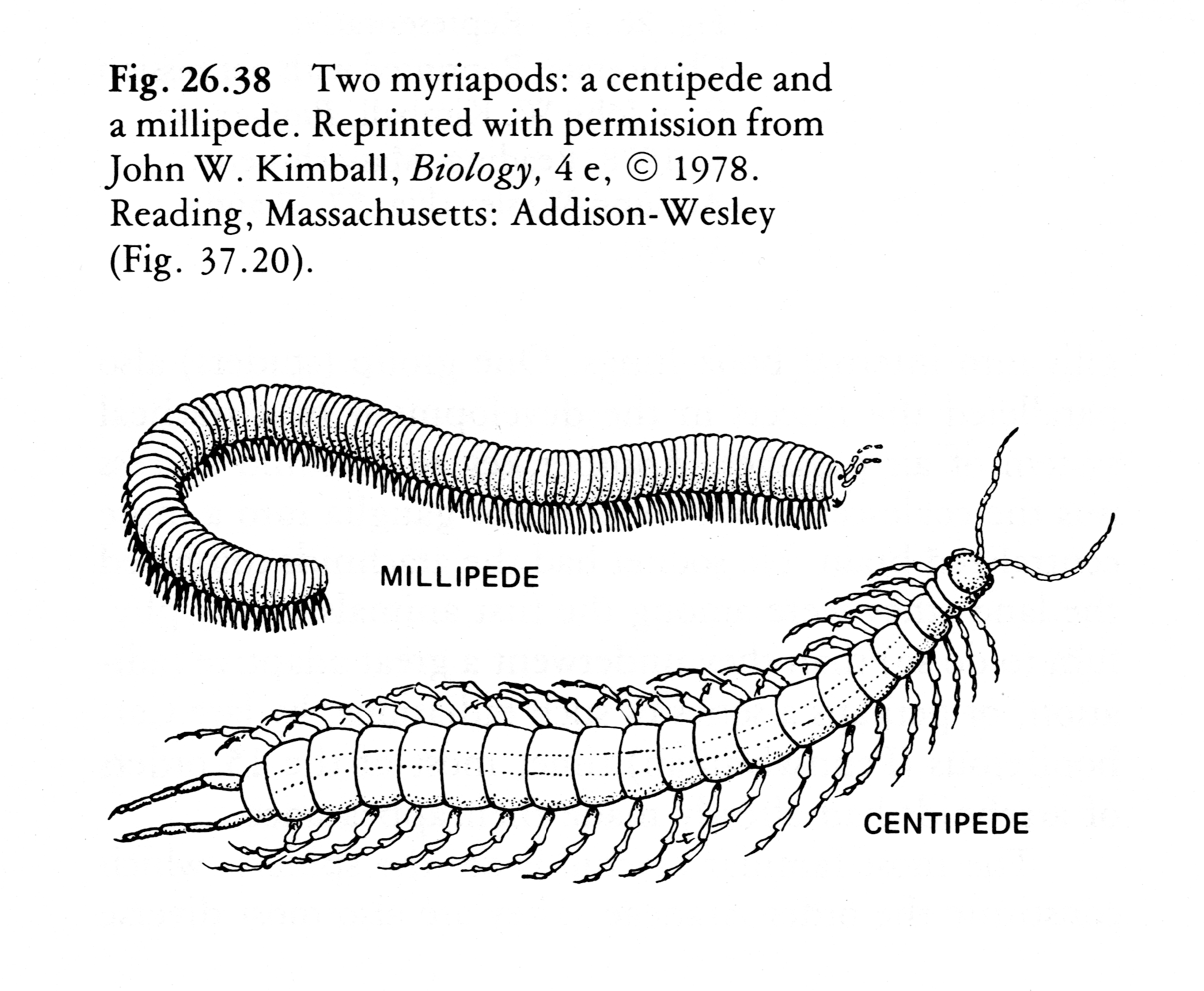  Subphylum Uniramia — Class Insecta:
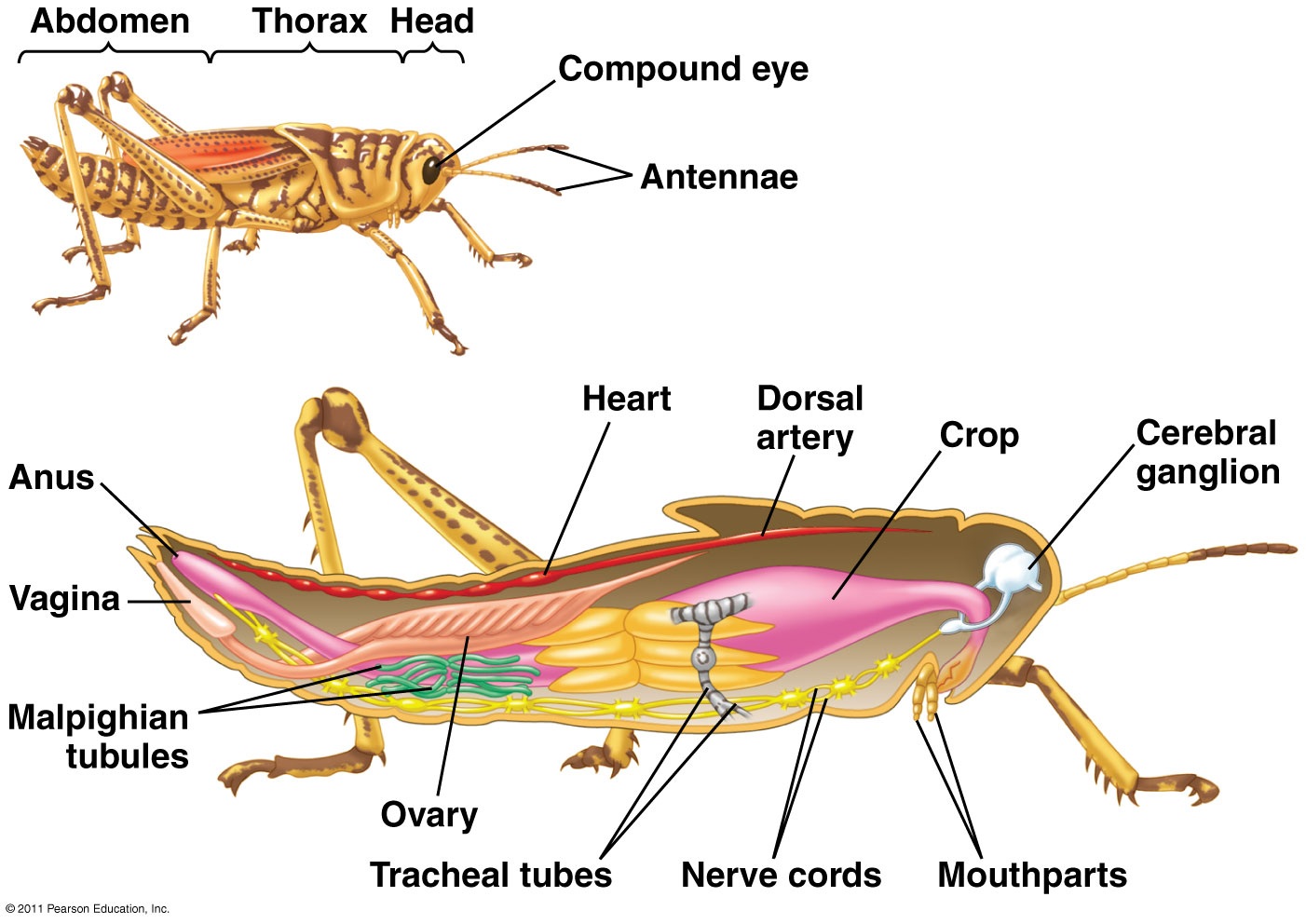 Anatomy of a Grasshopper (order Orthoptera)
| |||||||||||||

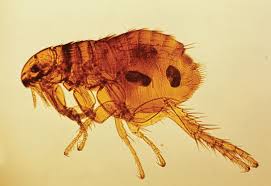 Fleas (order Siphonaptera) | |||||||||||||


 Termites (order Isoptera) |

| 
| 
|

| True bugs (order Hemiptera) Notice the piercing mouthparts and the wings whose transparent rear tips overlap when the wings are folded back |
| Cicada (order Homoptera) | 
|
| Butterflies (order Lepidoptera) | 
| 
|
| Flies (order Diptera) | 
| 
| 
|
| Beetles (order Coleoptera) The leathery outer wings (forewings) are protective; the hind wings, used for flying, are hidden underneath. | 
| 
| 
|
| Order Hymenoptera: social insects (bees, wasps, and ants) | 
| 
| 
|

| 
|  
| 
|
Lophophore-feeding phyla:
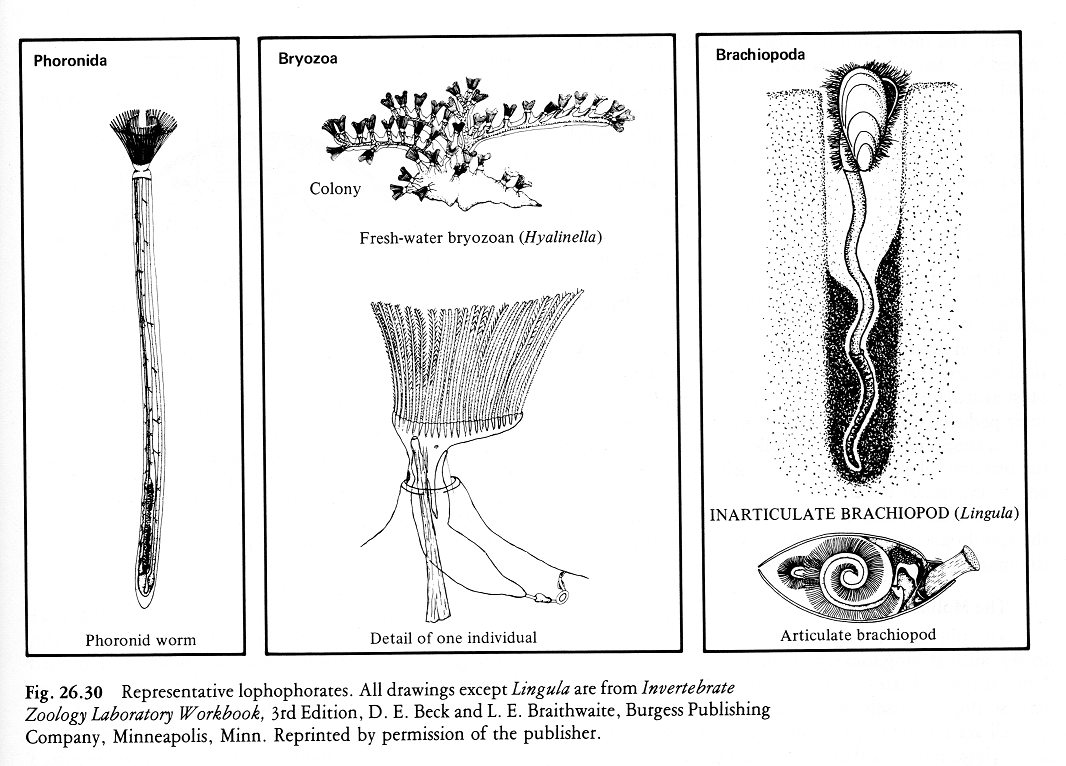


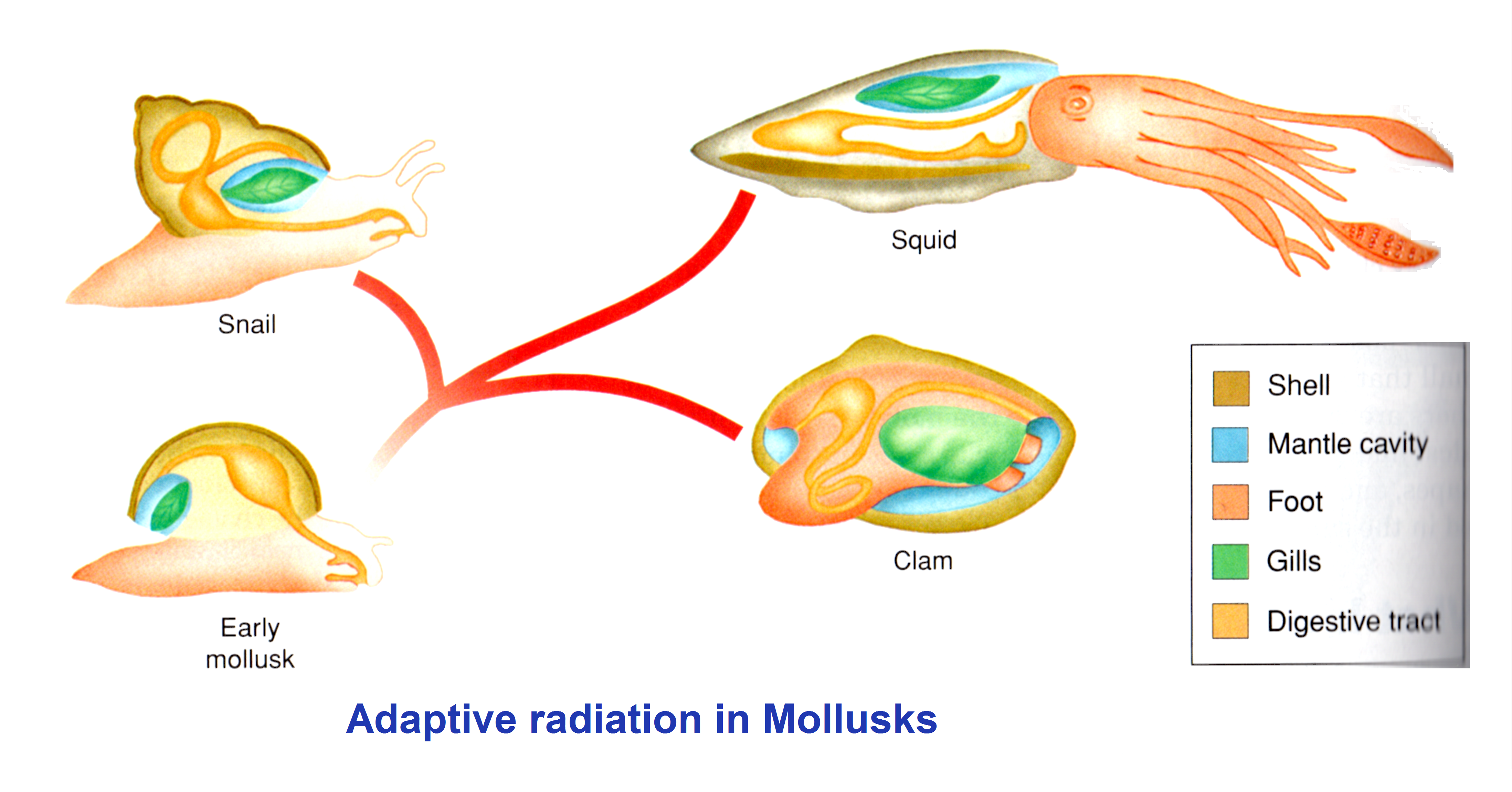
Phylum Mollusca
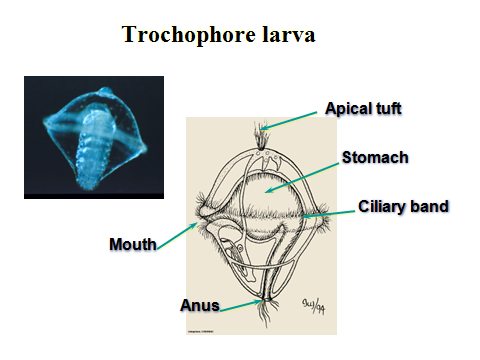
This type of larva occurs in various mollusks and in polychaete annelids.
Scientists think that the common ancestor of all Lophotrochozoa had this type of larva.

This drawing is based on an anatomist's theoretical drawing from the 1930s, envisioning what an ancestral
or generalized mollusk would look like, based on comparative anatomy and based on the fossil genus
Pilina, which had a low-domed conical shell. In the 1960s, a new species was dredged up
from the depths of the Pacific Ocean that matched this diagram almost exactly, and it
was given the name Neopilina and placed in its own class, the Monoplacophora.
Class Polyplacophora (chitons)

| 
| 
|
| Chitons are flat mollusks with 8 segments to their shell.
They cling to rocks and use their radulas to scrape algae off the surface. | ||
Class Gastropoda (snails)
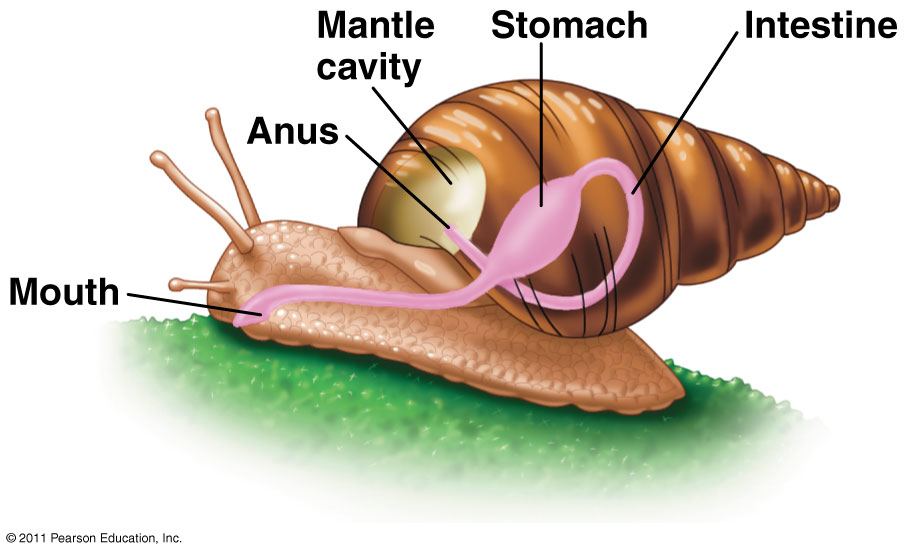
All snails have a well-developed muscular foot and nearly all have a spirally coiled shell.
They all feed using a scraping organ, the radula, that has teeth embedded in a strap that is rhythmically
pulled around a cartilage "tongue"; the radula scrapes surfaces containing encrusted algae and other food.
In most snails, the mantle cavity lies above the head and slightly behind, and it directs the flow of water diagonally.
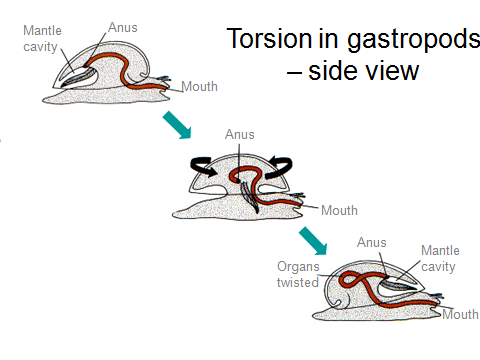
All snails undergo an asymmetrical torsion during their development, bringing the mantle cavity
from the rear to the front. A few, including the land snails and slugs, subsequently undergo
a detorsion, bringing the mantle cavity back to the original rear position.
More snails
|  | 
|

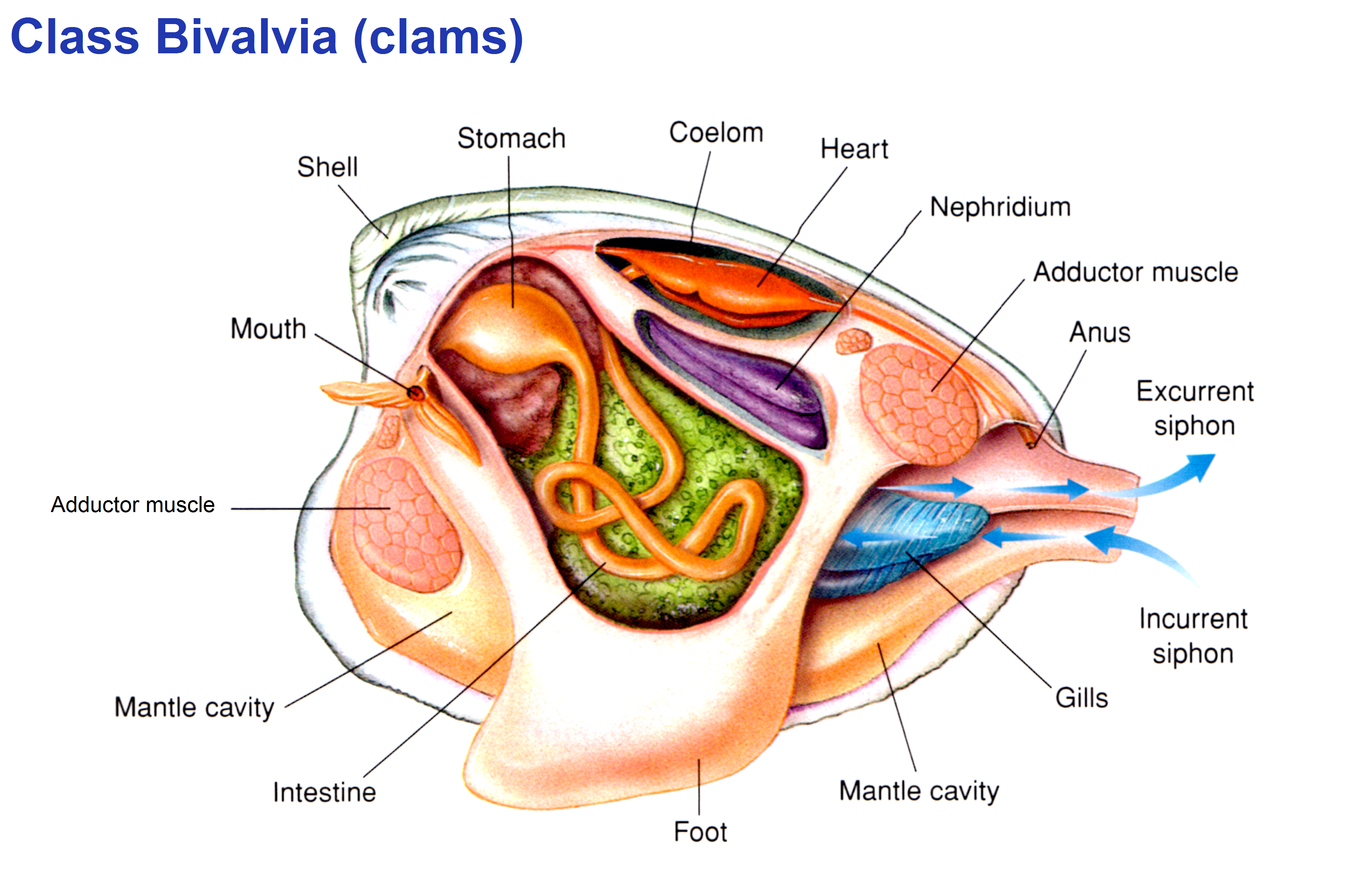

| 
| 
|
Class Cephalopoda
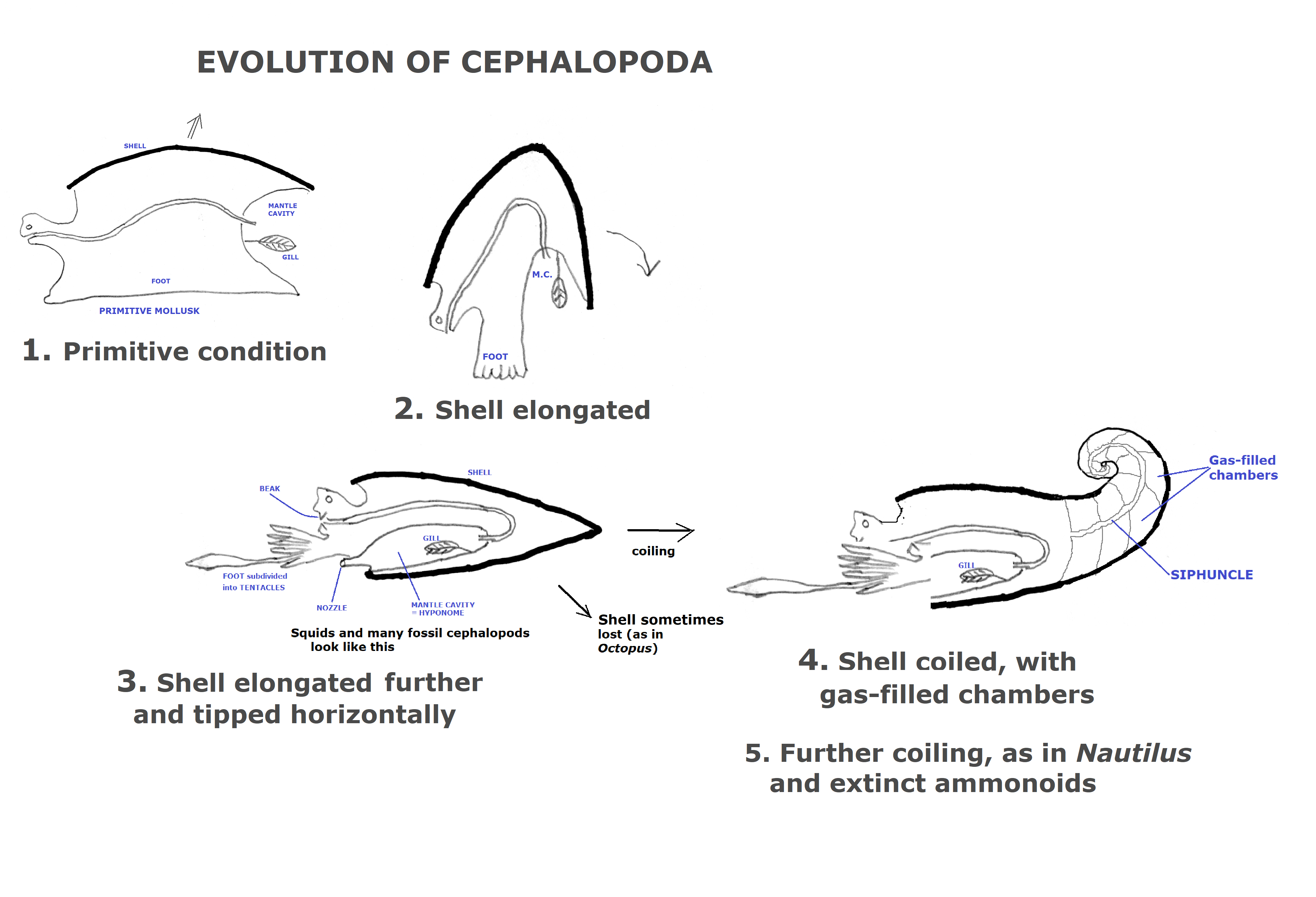

Anatomy of Nautilus, whose coiled shell contains many gas-filled chambers connected by a tube
called the siphuncle. The gas inside the chambers is about 98% N2 and the animal can adjust
the amount of gas to control its buoyancy and thus the depth at which it floats in the water.
Fossils called Ammonites had a similarly coiled shell, varying from 2 inches up to 2 feet across.

Extinct Ammonites (subclass Ammonoidea)

| 
| 
|
Squids and Octopus are cephalopods that have lost their shells
(or, in one case, reduced it to a thin, internal structure just beneath the skin).

| 
|
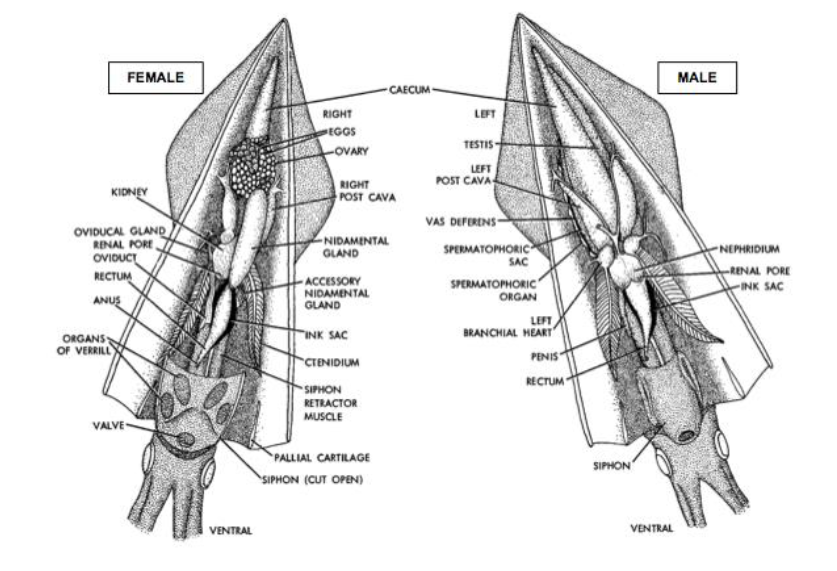
Internal anatomy of a squid
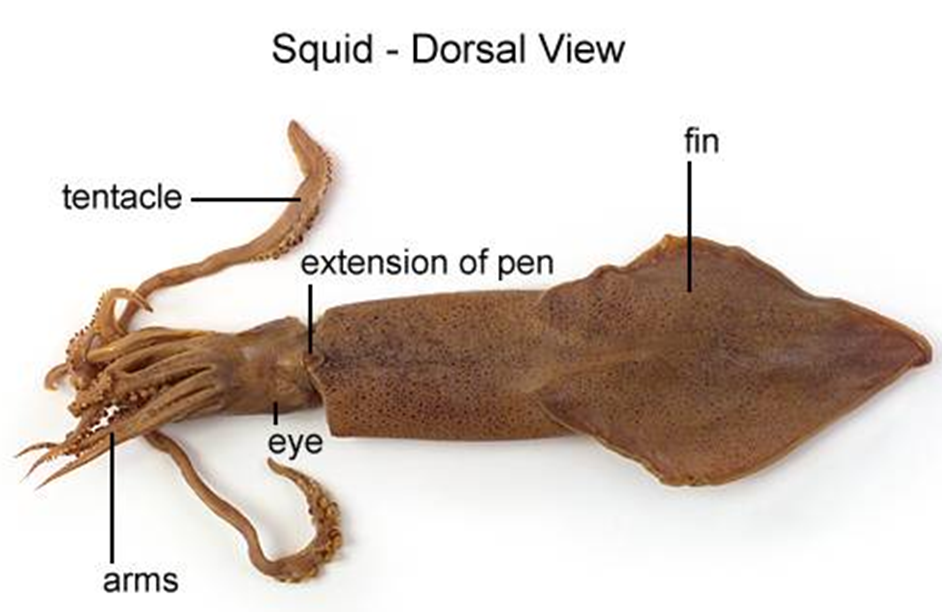
| |

| 
|
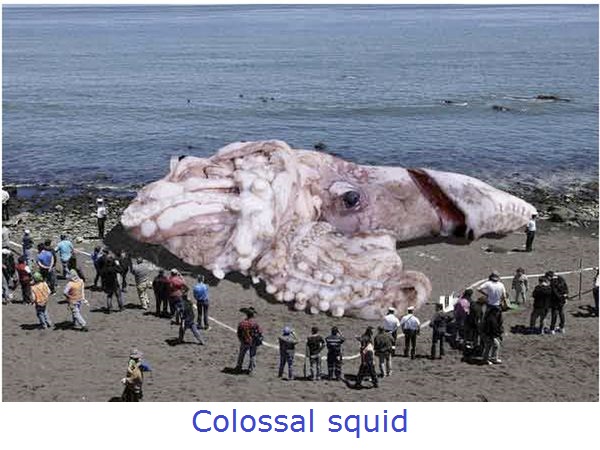
Common squids are just 4-6 inches long, but—
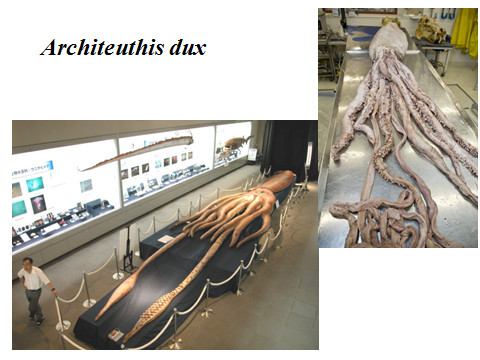
Museum display of a giant squid. For scale, notice the person standing nearby.
Also —

Octopus
| 
|


|
REFERENCE: Animal Classification
· · · • • • • • · · ·
Click here for the
Check-In questions
—— Rev. April 2021 ——